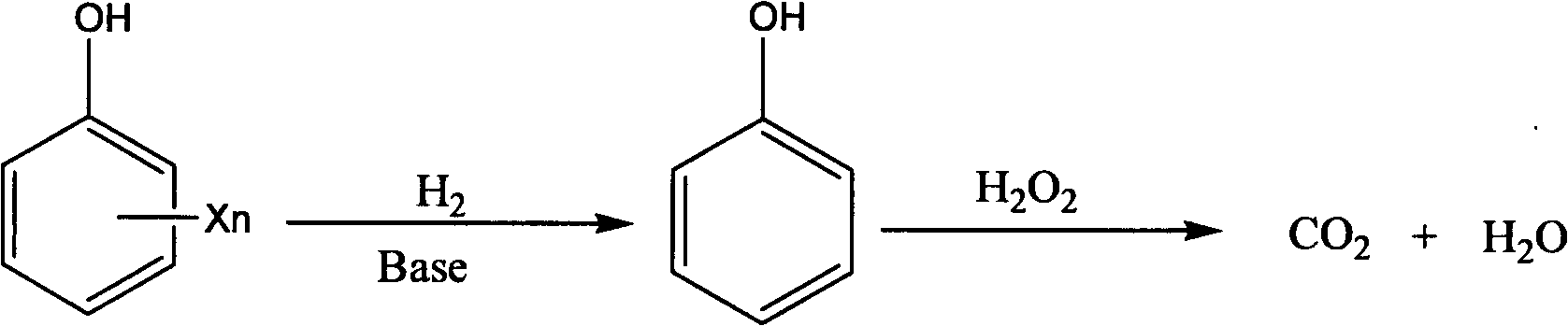
Combined degradation method for processing high concentration halogenated phenol compounds
A technology for halogenated phenols and compounds is applied in the field of joint degradation of high-concentration halogenated phenolic compounds to achieve the effects of reducing environmental pollution, improving stability and reducing grain size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] The preparation of embodiment 1 hydrodehalogenation catalyst
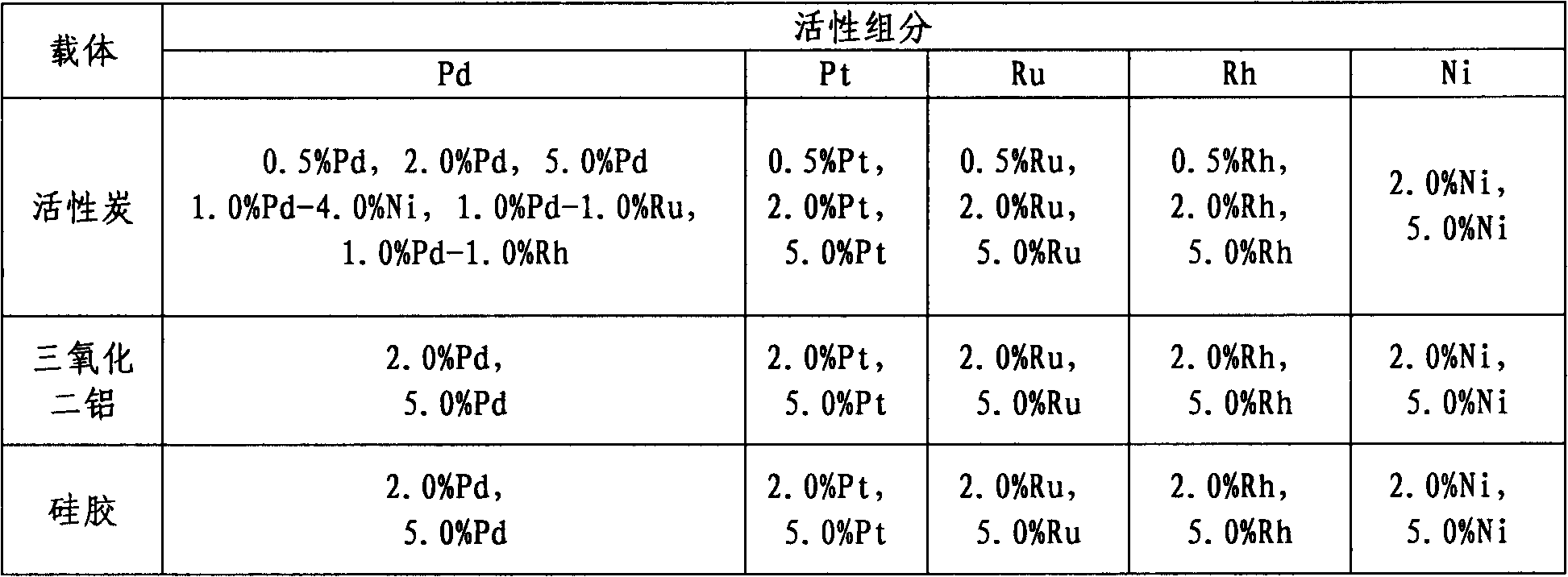
[0023] Dissolve a certain amount of palladium chloride in concentrated hydrochloric acid, dilute it with water and impregnate it into activated carbon, then evaporate to dryness under constant stirring. The obtained solid is ground into powder, then reduced by hydrogen gas, and finally sealed and stored to obtain palladium / carbon catalysts with different contents. The palladium / carbon catalysts with different contents are listed in Table 1. Then, supported catalysts with different carriers and different active components can be prepared, and the prepared catalysts are listed in Table 1.
[0024] Table 1 Catalysts with different supports and different active components
[0025]
Embodiment 2
[0026] The preparation of embodiment 2Raney Ni catalyst
[0027] In a 4L beaker, dissolve 380g of sodium hydroxide in 1.5l of distilled water, stir, and cool to 10°C on an ice bath. Under stirring, add 300g of nickel-aluminum alloy to the lye in small quantities in batches, and the speed of adding should be controlled so that the temperature of the solution does not exceed 25°C (on an ice bath). When all the addition was complete (about 2 hours), the stirring was stopped, the beaker was taken off from the ice bath, and the reaction solution was allowed to rise to room temperature. When the hydrogen generation is slow, it can be heated slowly on a boiling water bath (avoid heating up too fast, in case there are too many bubbles, and the reaction solution overflows), until the generation of the bubbles slows down again (about 8-12 hours, the volume of the solution at this time It should be kept basically constant by adding distilled water). Then stand still, allow the nickel p...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Embodiment 3 Hydrodehalogenation of different halogenated phenolic compounds
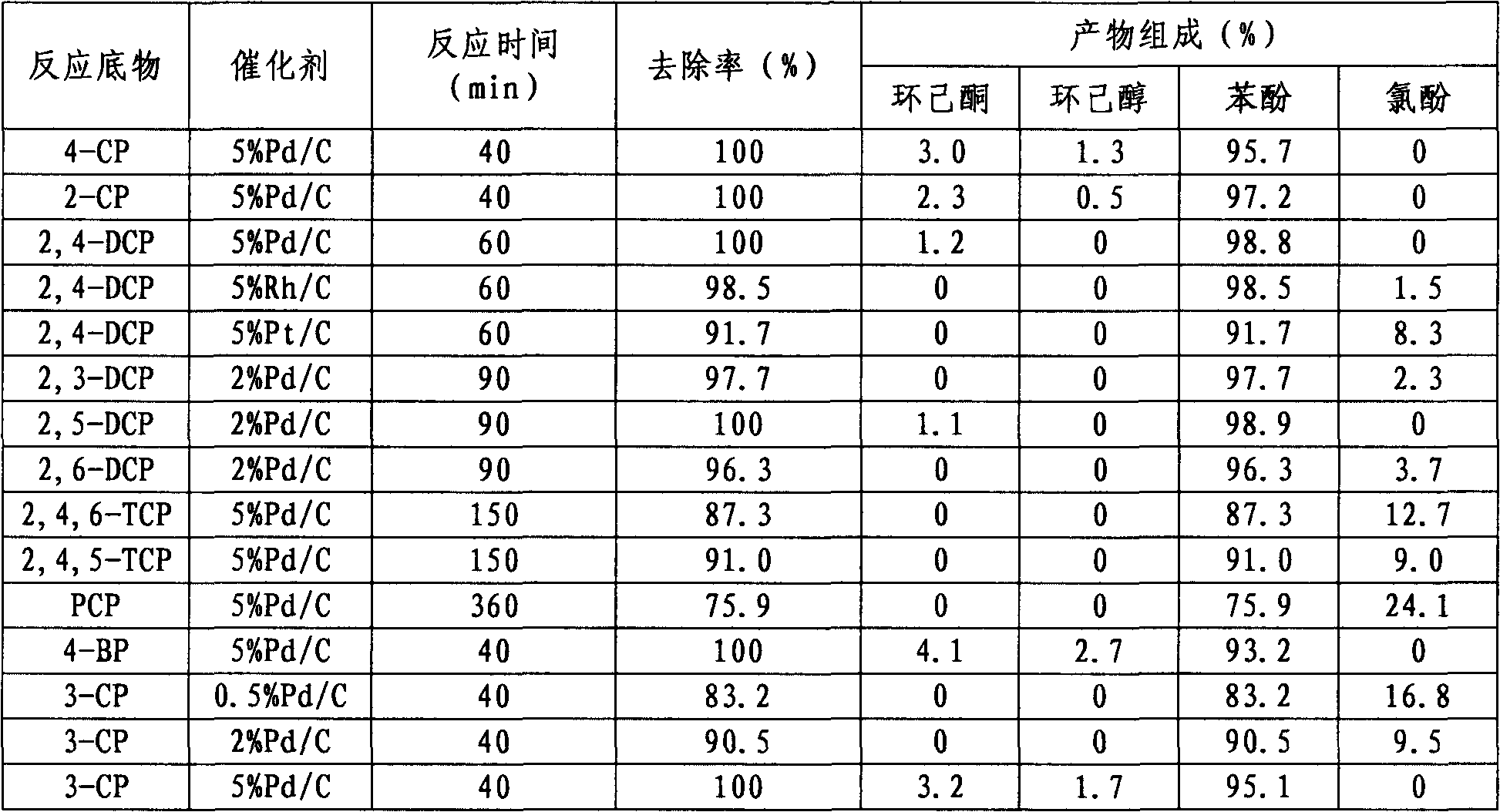
[0029] Weigh 25 mg of the Pd / C catalyst prepared in Example 1, add it to a 100 ml three-necked flask, add 80 ml of 4-CP aqueous solution with a concentration of 5000 ppm, and stir the reactant with a magnetic stirrer for 15 min; then pass N 2 , do this three times, and then pass H 2 , H 2 The flow rate is controlled within the range of 10-30ml / min, and the alkali used is sodium hydroxide. In order to ensure that the second-step oxidation reaction can be carried out relatively quickly, the molar ratio of the amount of alkali to the amount of the reaction substrate is 1.1:1. The reaction temperature was controlled at 30°C, and the reaction pressure was normal pressure. The specific dechlorination results are shown in Table 2.
[0030] Table 2 Hydrodehalogenation of different halogenated phenolic compounds
[0031]
[0032] Remarks: CP refers to monochlorophenol, BP refers to monobromophen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com