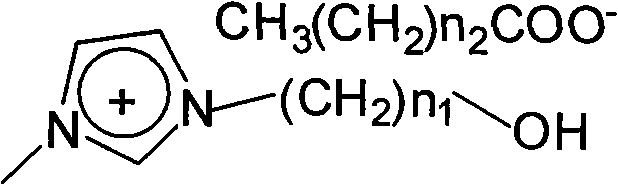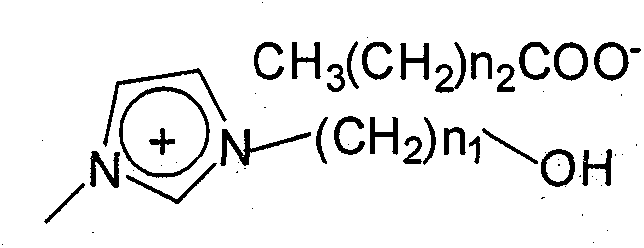Method of in-situ enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose in ionic liquid
A technology of ionic liquid and in-situ enzymatic hydrolysis, which is applied in the direction of fermentation, can solve the problems of cumbersome steps and large amount of organic solvent used for regenerated cellulose, and achieve the effects of simplifying the experimental process, overcoming the volatilization of solvents, and reducing consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] Microcrystalline cellulose raw material: molecular weight 25,000-50,000, degree of polymerization 153-300, ash content <0.6%, particle size 25-190 μm.
[0016] Determination method of reducing sugar content
[0017] DNS reagent: 1.6g DNS and 21g NaOH, dissolved in 200mL water, 185g potassium sodium tartrate dissolved in 500mL water, mixed with the above solution, added 5g crystalline phenol, 5g anhydrous sodium sulfite, stirred and dissolved, cooled to a constant volume in a 1000mL volumetric flask, stored Use after 7-10 days in the brown bottle.
[0018] Glucose standard curve: dry glucose at 105°C for 2 hours to constant weight, accurately weigh 0.1g, dissolve in distilled water, and set the volume to 100mL. The concentration is 1.0mg / mL. Take 10 20mL graduated test tubes with stoppers, add 0mL, 0.2mL, 0.4mL, 0.6mL, 0.8mL, 1.0mL, 1.2mL, 1.4mL, 1.6mL, 1.8mL glucose standard solution in turn, and then add Distilled water, the total volume is 2.0mL, then add 0.5mL DNS ...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Microcrystalline cellulose raw material: molecular weight 25,000-50,000, degree of polymerization 153-300, ash content <0.6%, particle size 25-190 μm.
[0023] The assay method of reducing sugar amount: refer to embodiment 1.
[0024] Add 0.5 mol (41.05 g) of N-methylimidazole and 0.5 mol (54.25 g) of chlorobutanol into a 250 mL three-necked flask equipped with a reflux device, mix well, react at 80°C for 24 hours, add 50 mL of diethyl ether to extract 4 times, and depressurize Ether is removed by distillation to obtain ionic liquid 1-hydroxybutyl, 3-methylimidazolium chloride salt ([C 4 OHmim]Cl); Then add 0.5mol (about 95g) [C 4 OHmim]Cl and 100mL of absolute ethanol were dissolved and mixed evenly, then 0.55mol (about 53.90g) of potassium acetate dissolved in absolute ethanol was added, after mixing, react at 50°C for 5h for ion exchange, and filtered under reduced pressure to form salt and unreacted salt , remove absolute ethanol by distillation under reduced pres...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Microcrystalline cellulose raw material: molecular weight 25,000-50,000, degree of polymerization 153-300, ash content <0.6%, particle size 25-190 μm.
[0028] The assay method of reducing sugar amount: refer to embodiment 1.
[0029] Add 0.5mol (41.05g) N-methylimidazole and 0.5mol (40.25g) chloroethanol into a 250mL three-neck flask equipped with a reflux device, mix well, react at 80°C for 24h, add ether 50mL to extract 4 times, and distill under reduced pressure Remove ether, obtain ionic liquid 1-hydroxyethyl, 3-methylimidazolium chloride salt ([C 2 OHmim]Cl); Then add 0.5mol (about 80g) [C 2OHmim]Cl and 100mL of absolute ethanol were dissolved and mixed evenly, then 0.55mol (about 52.80g) of sodium propionate dissolved in absolute ethanol was added, and after mixing, it was reacted at 50°C for 5h for ion exchange, and filtered under reduced pressure to form salt and unreacted Salt, decompression distillation removes dehydrated alcohol, cools and stands still and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com