Method for specifically separating sphingomonas yanoikuyae by combining streptomycin resistance surface plate based on special primer polymerase chain reaction (PRC)
A sphingomonas, resistant plate technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problem of small detection spectrum, inability to amplify, amplify sphingosine Alcoholmonas and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
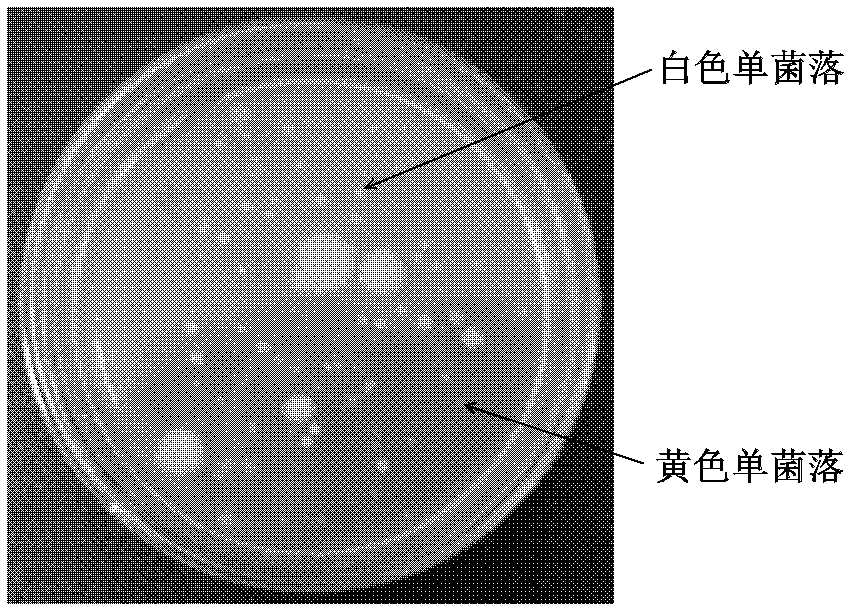
[0054] The petroleum-contaminated soil in the Shenfu irrigation area was collected, passed through a 1mm sieve, and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C. Weigh 5g of the soil sample and place it in a sterilized Erlenmeyer flask filled with glass beads, add 45mL of physiological saline, and shake at 150rpm for 2h. Then the suspension was left to stand, the supernatant was taken, and the soil suspension was diluted 10 times with physiological saline. Take 0.1ml to dilute to 10 -2 -10 -6 The soil suspension was spread onto the LB solid medium plate added with streptomycin, and the final concentration of streptomycin was 50 μg ml -1 , 30°C inverted culture for 4 days. Pick the yellow colony grown on the LB streptomycin resistance plate, and repeatedly streak on the LB streptomycin resistance plate until a single colony is isolated.
[0055] LB liquid medium formula is: tryptone 10g, yeast extract powder 5g, NaCl10g, distilled water to 1000ml, pH7.2-7.4; LB solid medium formula is: ...
Embodiment 2
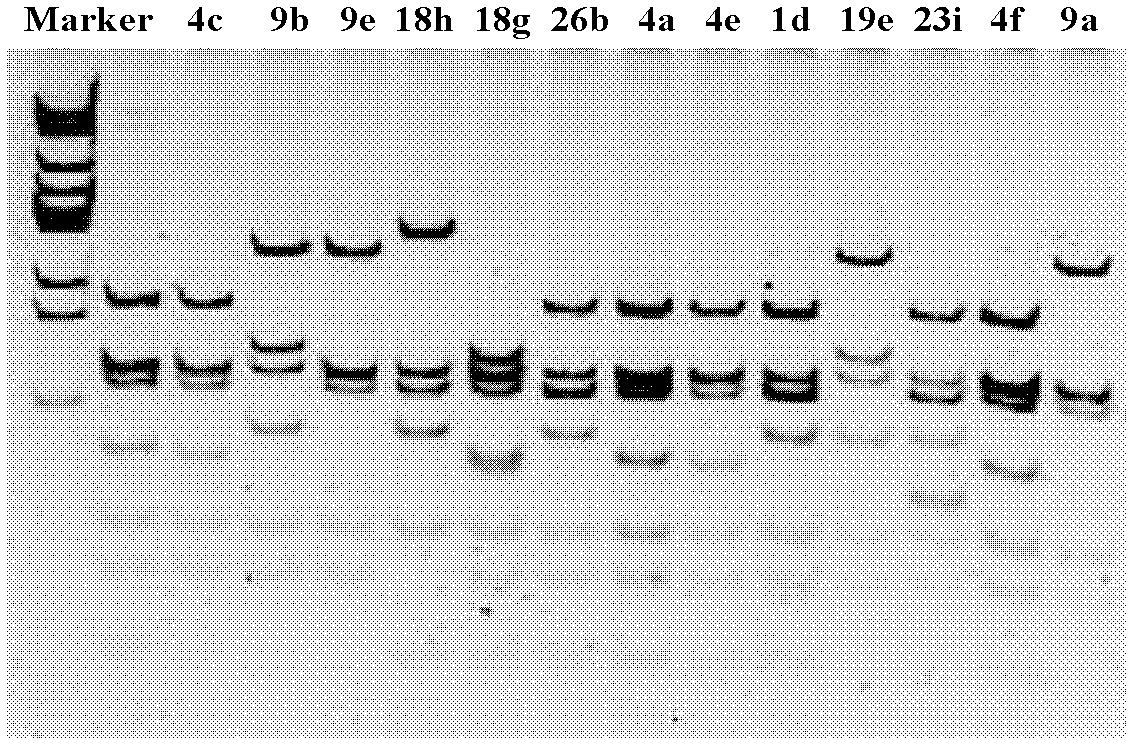
[0058] The PCR product of the correct fragment size amplified in Example 1 was genetically typed by three enzyme digestions, enzyme digestion reaction system (20 μl): 0.5 μl each of the three endonucleases, 2 μl 10× buffer, 0.5 μl bovine serum Albumin (BSA), 2 μl PCR product, 14 μL ultrapure water. The total reaction volume was 20 μl, at 37°C, in a water bath for 2 hours, and 2 μl of 10×loading buffer was added to terminate the digestion reaction. The digested products were separated by 10% polypropylene gel electrophoresis at 90V for 1h. Different restriction enzyme fingerprints can represent different strain genotypes.
[0059] Select a representative strain from each of the above genotypes, and use the bacterial universal primer 27f / 1492r to amplify the full-length sequence of 16SrDNA. The primer sequences are, respectively, 27f: 5'-AGAGTTTGATC[C / A]TGGCTCAG-3'; : 5'-TACGG[A / T / C]TACCTTGTTACGACTT-3'. The PCR reaction system used was the same as in Example 1; the PCR reacti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com