Method for preparing rare earth by reducing ammonia nitrogen oxygen demand (COD) and adjusting potential of hydrogen (pH) value from rare earth mine leach liquor
A technology for leaching liquid and rare earth ore, which is applied in the field of rare earth production by reducing the ammonia nitrogen oxygen demand (COD) and adjusting the pH value from the leach liquid of rare earth ore. Application and other issues, to achieve the effect of reducing secondary pollution, improving the environment, and subtracting the acid-dissolving process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
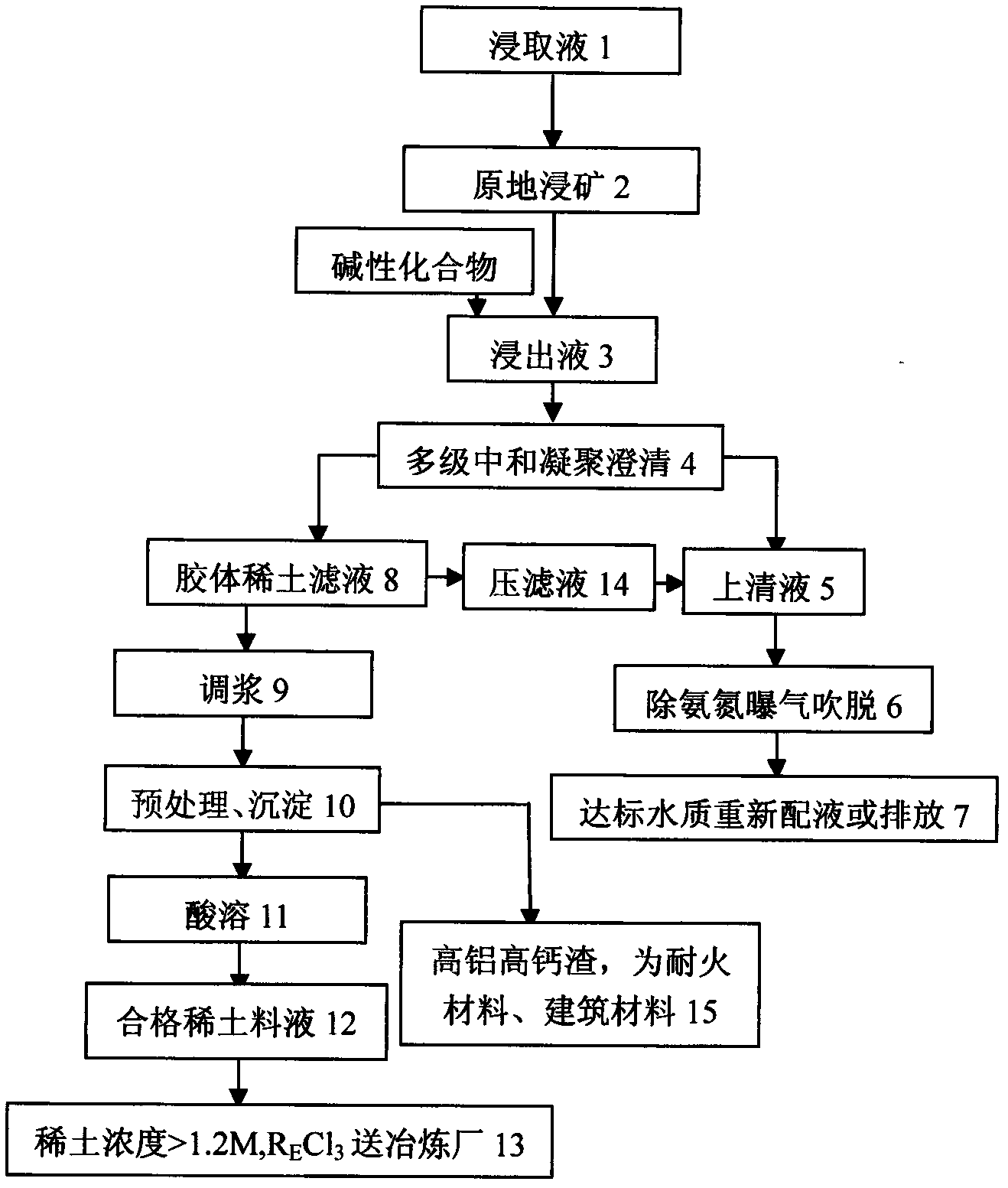
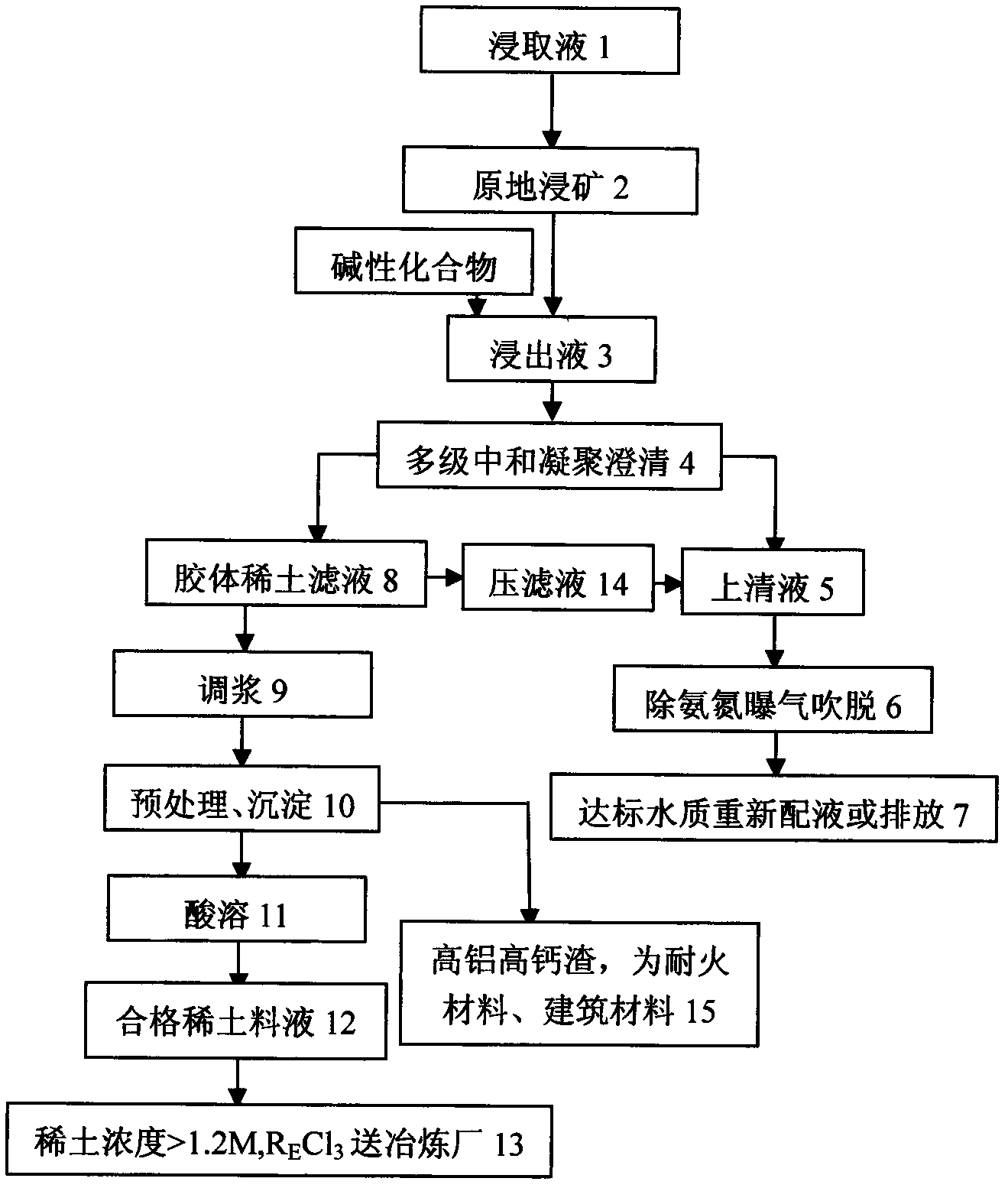
[0019] Use 2.0% ammonium bisulfate solution as leaching agent 1 to carry out raw ore leaching 2 to rare earth mines, and leaching solution 3 is rare earth mother liquor containing rare earth oxide 3.65g / L, aluminum: 0.75%, lead: 0.02g / L, calcium: 0.25g / L, Copper: 0.015g / L, Ammonia Nitrogen: 325mg / L.pH: 4.8, Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD): 120mg / L, after neutralization and precipitation, coagulation, clarification, removal of ammonia nitrogen, reflux, aeration , blowing off and other processes, discharge supernatant to detect rare earth concentration: 0.001g / L, all heavy metals are trace, pH: 8.5 ammonia nitrogen: 30mg / L, chemical oxygen demand (COD): 25mg / L The recovery rate of rare earth in the whole process More than 96%, the water quality treatment reaches the national second and third level discharge standards. At the same time, using rare earth hydroxides to prepare rare earth chloride feed liquid C RE : 154.54~176.46g / L, specific gravity: 1.28g / mL Al 2 o 3 : 1.5g / L, can...
example 2
[0021] The weathering crust leaching type (ion adsorption) rare earth ore is subjected to an in-situ leaching process, using 5.0% ammonium chloride solution as the leaching agent 1, and the leaching solution 3 contains a rare earth concentration of 6.8g / L, aluminum: 0.85g / L, and lead: 0.02g / L, copper: 0.02g / L, pH: about 5, ammonia nitrogen: 252g / L, chemical oxygen demand (COD): 115g / L, after neutralization precipitation hydrolysis, multi-stage coagulation, ammonia nitrogen removal, reflux, Aeration, stripping and other processes, supernatant discharge and dosing, detection of rare earth concentration 0.001g / L. Each heavy metal is trace, pH: 9.1, ammonia nitrogen: 25g / L, chemical oxygen demand (COD): 30mg / L. The rare earth recovery rate of the whole process is over 96%, and the water quality has been improved to meet the national second and third level discharge standards. At the same time, using rare earth hydroxides to prepare rare earth chloride feed liquid C RE : 154.54~17...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com