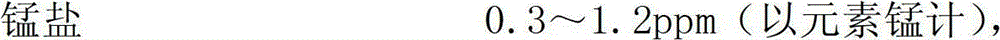Active lactobacillus plantarum drink and preparation method thereof
A technology for Lactobacillus plantarum and beverages, which is applied to dairy products, milk preparations, applications, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in meeting the industrial application requirements of Lactobacillus plantarum, and achieve the effects of obvious probiotic functions, unique flavor and refreshing taste.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-4
[0058] (1) Preparation and sterilization of fermented milk base material: Add 97 grams of fructose syrup, 3 grams of yeast powder FM802 and manganese salt with a final concentration of 10 ppm (calculated as elemental manganese, gluconic acid Manganese), stir well, mix evenly, sterilize at 95°C for 90 minutes, and cool to 37°C;
[0059] (2) Base material fermentation: As shown in Table 1, add different starters to the fermented milk base material, ferment at 37°C, measure the titrated acidity and plantaractobacillus content after 24 hours and 48 hours, see Table 2;
[0060] Table 1 Different starter inoculation methods
[0061]
[0062] CFU: colony-forming unit, colony forming unit.
[0063] A certain amount of diluted bacterial solution is poured or coated, and the microbial single cells in it are dispersed on the agar plate one by one. After culturing, each living cell forms a colony. Unlike the conventional measurement of the number of microorganisms using a microscope, i...
Embodiment 5
[0078] (1) Preparation of fermented milk base material: Add 96 grams of fructose syrup, 3 grams of yeast powder FM802 and manganese salt with a final concentration of 5 ppm (calculated as elemental manganese, manganese gluconate) to 501 grams of fresh skim milk, stir well, and mix Evenly, sterilize at 95°C for 90 minutes, then cool to 37°C;
[0079] (2) Base material fermentation: add Lactobacillus plantarum ST-Ⅲ (5×10 6 CFU / g), fermented at 39°C to a titrated acidity of 120°T;
[0080] (3) Sugar solution preparation and sterilization: Dissolve 60 grams of white sugar and 5 grams of WHGM-1 stabilizer in 334.5 grams of purified water, sterilize at 95°C for 5 minutes, and cool to below 10°C for later use;
[0081] (4) Beverage preparation: Mix 600 grams of fermented milk base material with 399.5 grams of sterilized and cooled sugar liquid, 0.5 grams of yogurt flavor HBS659, homogenize at 25°C and 20MPa, cool down to 5°C by cooling, and fill , refrigerated, to get 1000 grams of...
Embodiment 6
[0084] (1) Preparation of fermented milk base material: Add 48 grams of fructose syrup, 2 grams of yeast powder FM802 and manganese salt with a final concentration of 10 ppm (calculated as elemental manganese, manganese gluconate) to 350 grams of fresh skim milk, stir well, and mix Evenly, sterilize at 95°C for 90 minutes, then cool to 37°C;
[0085] (2) Base material fermentation: add Lactobacillus plantarum ST-Ⅲ (5×10 6 CFU / g), Streptococcus thermophilus TA45 (1×10 6 CFU / g), fermented at 42°C to a titrated acidity of 160°T;
[0086] (3) Sugar solution preparation and sterilization: Dissolve 100 grams of white sugar and 4 grams of AMD-8 stabilizer in 495 grams of purified water, sterilize at 95°C for 5 minutes, and cool to below 10°C for later use;
[0087] (4) Beverage preparation: Mix 400 grams of fermented milk base material with 599 grams of sterilized and cooled sugar solution and 1 gram of yogurt flavor HBS659, homogenize at 25°C and 20MPa, cool down to 5°C by cooling...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com