Process for preparing sodium copper chlorophyllin from ginkgo leaf leftovers
A technology of sodium copper chlorophyllin and leftovers, applied in organic chemistry and other fields, can solve problems such as waste, unsatisfactory product purity, and high production costs, and achieve the effects of reducing production costs, improving competitiveness, and stabilizing quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] (1) Extraction and concentration: 100g ginkgo leaf leftovers were heated and refluxed for 6 hours with ethanol with a mass concentration of 90% at 80°C for 6 hours, extracted twice, and the residue was removed by filtration, and the obtained filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to 70% of the original volume (for evaporate part of the solvent);
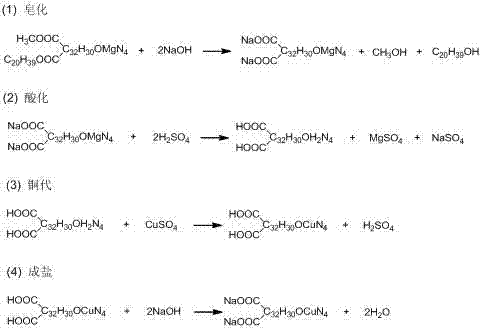
[0053] (2) Saponification: Adjust the pH of the filtrate treated in step (1) to about 11 with 20% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, heat to 40°C, saponify for 20 minutes, cool to room temperature, and filter to remove the unsaponifiable viscous Obtain filtrate with impurities;
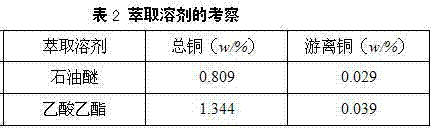
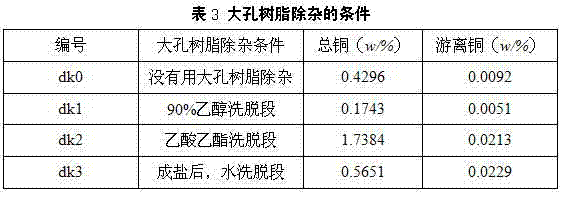
[0054] (3) Ethyl acetate extraction and impurity removal: Ethanol is evaporated from the filtrate obtained in step (2) under reduced pressure, water equal to the volume of the filtrate from which ethanol has been evaporated is added, and the mixed solution is obtained by stirring evenly, and an equal volume of the mixed solution is added to ...
Embodiment 2
[0059] (1) Extraction and concentration: 100g of ginkgo leaf leftovers were extracted with ethanol with a mass concentration of 95% under reflux at 70°C for 4 hours, extracted once, and the residue was removed by filtration, and the obtained filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to 80% of the original volume;
[0060] (2) Saponification: Adjust the pH of the filtrate treated in step (1) to about 12 with 40% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, heat to 30°C, saponify for 60 minutes, cool to room temperature, and filter to remove the unsaponifiable viscous Obtain filtrate with impurities;
[0061] (3) Ethyl acetate extraction and impurity removal: Ethanol is evaporated from the filtrate obtained in step (2) under reduced pressure, and water equal to the volume of the filtrate from which ethanol has been evaporated is added, and the mixture is obtained by stirring evenly, and the volume of the mixture is added to the mixture. twice as much ethyl acetate, extracted 4 time...
Embodiment 3
[0066] (1) Extraction and concentration: 100g of ginkgo biloba leftovers were heated and refluxed with ethanol with a mass concentration of 95% at 75°C for 5 hours, extracted once, and the residue was removed by filtration, and the obtained filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to 75% of the original volume;
[0067] (2) Saponification: Adjust the pH of the filtrate treated in step (1) to about 11 with 20% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, heat to 30°C, saponify for 30 minutes, cool to room temperature, and filter to remove the unsaponifiable viscous Obtain filtrate with impurities;
[0068] (3) Ethyl acetate extraction and impurity removal: Ethanol is evaporated from the filtrate obtained in step (2) under reduced pressure, water equal to the volume of the filtrate from which ethanol has been evaporated is added, and the mixed solution is obtained by stirring evenly, and an equal volume of the mixed solution is added to the mixed solution ethyl acetate, extracted ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com