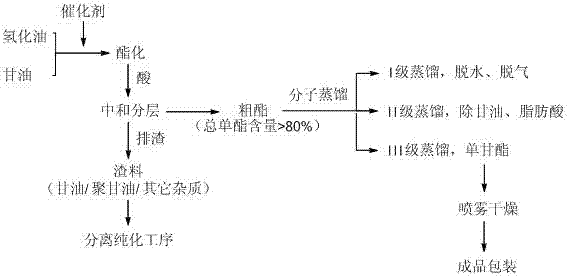
Process for preparing high-purity molecular distillation monoacylglycerol
A molecular distillation and monoglyceride technology, which is applied in the direction of fat oil/fat refining, fat production, fatty acid esterification, etc., can solve the problems of equipment loss, poor economic benefits, high energy consumption, etc., to reduce emissions and reduce environmental protection costs , the effect of improving economic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] (1) Synthesis of fatty acyl monoglycerides: Take 1kg of glycerin and 10g of NaOH into the reaction kettle, mix well, reduce the pressure to 3000Pa, heat to 200°C for 30min. Add 1.5kg of hydrogenated oil and 30g of benzyltriethylammonium chloride into the mixing kettle, mix evenly, and heat to 200°C, then add them into the reaction kettle in three times with an interval of 30 minutes each time. After all the reaction materials were added into the reactor, the reaction was continued for 30 minutes. After the esterification reaction was completed, phosphoric acid was added for neutralization, and left to stand for 30 minutes, and the reactants were separated into layers. The upper layer is the glyceride layer, and the lower layer is unreacted materials and impurities generated during the reaction. Release the glyceride layer and the slag layer successively. The glyceride layer uses the method described in the national standard GB15612-1995 to measure the monoglyceride co...
Embodiment 2
[0026] (1) Synthesis of fatty acyl monoglycerides: Take 1kg of glycerin and 10g of NaOH into the reaction kettle, mix well, reduce the pressure to 3000Pa, heat to 200°C for 30min. Add 1.5kg of hydrogenated oil, 20g of benzyltriethylammonium chloride and 18g of polyethylene glycol dialkyl ether into the mixing tank, mix evenly, and heat to 200°C, then add it into the reaction tank in three times, each interval 30min. After all the reaction materials were added into the reactor, the reaction was continued for 30 minutes. After the esterification reaction was completed, phosphoric acid was added for neutralization, and left to stand for 30 minutes, and the reactants were separated into layers. The upper layer is the glyceride layer, and the lower layer is unreacted materials and impurities generated during the reaction. Release the glyceride layer and the slag layer successively. The glyceride layer uses the method described in the national standard GB15612-1995 to measure the...
Embodiment 3
[0031] (1) Synthesis of fatty acyl monoglycerides: Take 1kg of glycerin and 10g of NaOH into the reaction kettle, mix well, reduce the pressure to 3000Pa, heat to 200°C for 30min. Add 1.5kg of hydrogenated oil and 28g of hexadecyltributylphosphonium chloride into the mixing kettle, mix evenly, heat to 200°C, and add to the reaction kettle in three times with an interval of 30 minutes each time. After all the reaction materials were added into the reactor, the reaction was continued for 30 minutes. After the esterification reaction was completed, phosphoric acid was added for neutralization, and left to stand for 30 minutes, and the reactants were separated into layers. The upper layer is the glyceride layer, and the lower layer is unreacted materials and impurities generated during the reaction. Release the glyceride layer and the slag layer successively. The glyceride layer uses the method described in the national standard GB15612-1995 to measure the monoglyceride content ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com