Active organic bacterial fertilizer and preparation method thereof
An organic bacteria and active technology, applied in the field of microbial fertilizers, can solve the problems of few beneficial bacteria and single fertilizer in fertilizers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
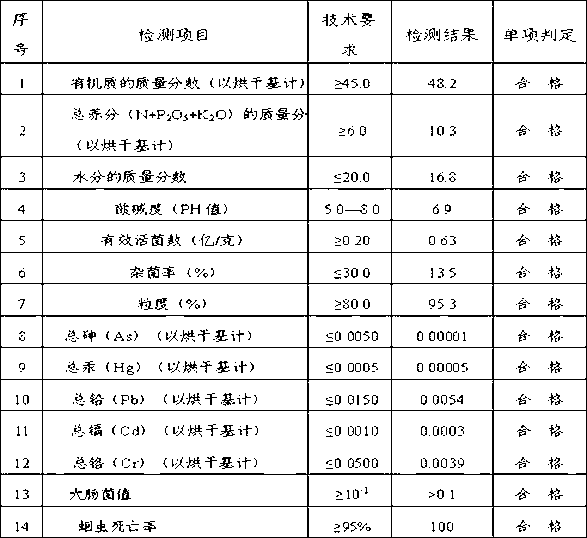
[0054] Collect 100 samples of organic substances containing specific microorganisms from furfural slag and plant ash to be produced as fertilizers, and isolate 56 strains of bacillus, 132 strains of yeast, 27 strains of photosynthetic bacteria, 18 strains of actinomycetes, 23 strains of lactic acid bacteria, and filamentous fungi 18 plants. Through statistical analysis, 16 excellent strains were determined from various strains. Classify the 16 candidate strains according to Bacillus, Saccharomyces, Actinomycetes and Filamentous Fungi, Photosynthetic Bacteria and Lactic Acid Bacteria, and first select the strain with the highest efficiency in each category as the core strain. Under indoor culture conditions, two different strains were cultured in the same petri dish to observe whether there was any antagonism between them. If antagonism was found, another strain from the same species was selected for cultivation. Through comparative observation experiments, it was determined t...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Collected 100 samples of organic matter containing specific microorganisms from activated sludge, livestock and poultry manure, plant ash, and crop straw, and isolated 52 strains of bacillus, 112 strains of yeast, 26 strains of photosynthetic bacteria, and 20 strains of actinomycetes , 25 strains of lactic acid bacteria, 20 strains of filamentous fungi. Through statistical analysis, 24 excellent strains were determined from various strains. Classify the 24 candidate strains according to Bacillus, Yeast, Actinomycetes and Filamentous Fungi, Photosynthetic Bacteria and Lactic Acid Bacteria, and first select the strain with the highest efficiency in each category as the core strain. Under indoor culture conditions, two different strains were cultured in the same petri dish to observe whether there was any antagonism between them. If antagonism was found, another strain from the same species was selected for culture. Through comparative observation experiments, it was dete...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Example 3. Fermentation process is identical with embodiment 2. After the decomposing process is completed, the mixture is dried, and the drying is multiple dryings, and the temperature of the drying is controlled at 40-60°C; preferably twice, the temperature of the first drying is controlled at 55-60°C ℃, the second drying temperature is controlled at 45-55 ℃. After drying, pass through a 60-mesh sieve. Finally, a powdered active organic bacterial fertilizer is obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com