Preparation of solid dispersion of paclitaxel and its homologues and oral preparations thereof
A technology of solid dispersions and homologues, applied in the field of medicine, can solve problems such as limitations in clinical application, achieve tumor suppression effects, significant effects, and improve bioavailability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
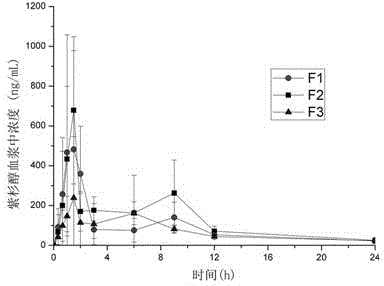
[0034] Example 1: Preparation of paclitaxel-HPMCAS-LG solid dispersion microspheres (without micronized silica gel)
[0035]Weigh paclitaxel (0.1, 0.3, 0.8g) and hypromellose acetate succinate (HPMCAS-LG) (1.9g, 1.7g, 1.2g) (Shin-Etsu Chemical Co. 2g) into a 50mL Erlenmeyer flask with a ground mouth, add 3~8mL acetone and 3~6mL dichloromethane, and stir until completely dissolved. A drug-polymer solution is formed under magnetic stirring. Use distilled water containing 0.05%~0.15% surfactant sodium dodecylsulfonate as a poor solvent, take 250mL and place it in a columnar preparation container. Slowly add the above suspension into the poor solvent under the stirring (500~700rpm) of the push-type stirring paddle. Once the suspension is poured into a poor solvent, translucent emulsion droplets are formed, and as dichloromethane and acetone continue to diffuse into the poor solvent, the emulsion droplets gradually solidify into microspheres. After stirring for 20-40min, filter ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Paclitaxel-hypromellose phthalate (HP55) solid dispersion microspheres (without micronized silica gel)
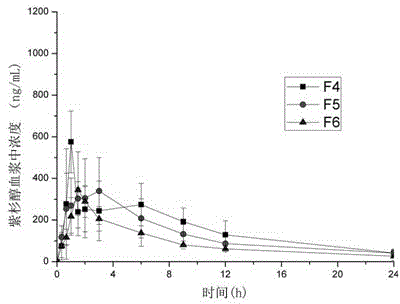
[0040] Weigh paclitaxel (0.1, 0.3, 0.7g) and HP55 (1.9g, 1.7g, 1.3g) (Japan Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.) (the total amount of drug and polymer is 2g) in a 50mL conical flask with a ground mouth, Add 3~5mL of acetone and 6~8mL of dichloromethane, stir until completely dissolved, and form a drug-polymer solution under magnetic stirring. Other preparation methods are the same as in Example 1. The overall recovery rate is 60-85%. The obtained preparations are named as F4, F5, and F6, and the drug content in the prescription is about 5%, 15%, and 35%.
[0041] It can be seen from Table 2 that better oral bioavailability can also be obtained by using hypromellose phthalate (HP55) as the solid dispersion carrier. As the proportion of drug content in solid dispersion increases, Tmax decreases, but there is no significant difference between F5 and F6. Depend o...
Embodiment 3
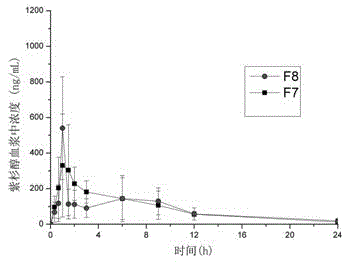
[0044] Embodiment 3: Paclitaxel - Preparation of HPMCAS-LG (or HP55) solid dispersion (without micropowdered silica gel, solvent evaporation method)
[0045] Weigh 2 parts of paclitaxel 100mg, mix them with polymer materials HPMCAS-LG (300mg) and HP55 (300mg) respectively (the total amount of drug and polymer in each prescription is 400mg), and add them to a mixed solvent of 2mL acetone and 2mL dichloromethane After dissolving, evenly spread on the glass plate. Place in an oven at 45°C for 12 hours to evaporate the organic solvent to dryness. The solid dispersion mixture was taken off with a razor blade, and the resulting preparations were respectively F7 and F8, and the drug content in the prescription was 25%. It can be seen from Table 3 that better oral bioavailability can also be obtained by using a simple solvent evaporation method. This shows that the combination of drugs and suitable polymers is one of the key factors to improve the oral bioavailability of drugs.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com