Preparation method of surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate
A surface-enhanced Raman and substrate technology, applied in the field of surface spectroscopy, can solve the problems of complex process, harsh substrate requirements, unsuitable substrates, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing costs, mild imprinting conditions, and saving raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
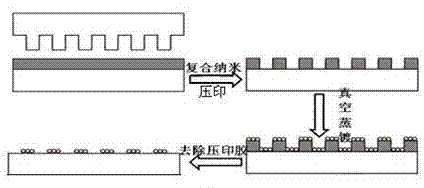
[0021] A method for preparing a surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate, comprising the steps of:
[0022] 1. Prepare a flexible nanoimprint template with a double-layer composite structure with a pattern: the upper layer of the double-layer composite template is a flexible polymer elastomer substrate, and the Young's modulus ranges from 1 to 5 N / mm 2 , the lower layer is a rigid light-cured polymer imprint layer with a Young's modulus in the range of 20 N / mm 2 Above, its thickness is 20-500 nm, and the upper and lower layers are tightly bonded by bonding or chemical bonds; the lower layer is a rigid photocurable polymer imprint layer, and its surface is bonded with a layer of low surface energy fluorinated organic small molecules or polymer anti-corrosion sticky layer.
[0023] 2. Embossing ordered nanostructure patterns: using a composite nanoimprinting method to imprint ordered nanostructure patterns on the cleaned substrate surface with a flexible nanoimprint template...
Embodiment 1
[0029] A silicon wafer was selected as the substrate, and a layer of 500 nm multifunctional acrylate prepolymer was spin-coated on the surface of the cleaned 1 cm×1 cm substrate as a UV-curable nanoimprint adhesive, and the flexible nanoimprint template (as dots Array structure, the size of each groove is 800 nm×800 nm, and the pitch is 1 μm) to press the imprinting glue, so that the raised part of the imprinting template is in direct contact with the bottom of the substrate, and the template is removed after the imprinting glue is finalized , that is, an ordered lattice structure was built on a silicon wafer substrate by using a composite nanoimprint method, a layer of gold particles with a thickness of 50 nm was evaporated on the substrate, and finally O 2 The reactive ion etching process removed the barrier layer of the nanoimprint adhesive, thereby obtaining a uniformly distributed gold particle lattice with a pitch of 800 nm and a size of 1 μm×1 μm as the SERS substrate.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Young's modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Young's modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com