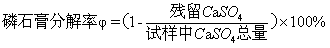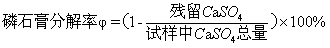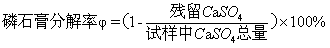Low-temperature phosphogypsum decomposition method
A phosphogypsum and low-temperature technology, applied in the field of low-temperature decomposition of phosphogypsum, and reducing the decomposition temperature of phosphogypsum during the decomposition process of phosphogypsum, can solve the problems of waste of land resources and sulfur-calcium resources, complex components of decomposition products, complex additive components, etc., to achieve Effect of increasing content, low price, and reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Embodiment 1: the method for this low-temperature decomposition of phosphogypsum, the specific content is as follows:
[0022] (1) The main chemical components of the phosphogypsum raw materials used in this example are: calcium oxide 35.36%, sulfur dioxide 47.12%, iron oxide 3.01%, aluminum oxide 2.05%, phosphorus pentoxide 1.20%, fluorine 0.06%, silicon dioxide 11.20% %;
[0023] (2) Crushing and grinding the dried phosphogypsum raw material, and sieving to a particle size between 0.074-0.150mm;
[0024] (3) Mix phosphogypsum with a mass percentage of 86% and calcium chloride with a mass percentage of 14% (particle size less than 0.074mm), stir evenly, then dry the mixture at 100°C for 6 hours and put it in a tube furnace. Heating to 650°C at a heating rate of 10°C / min, while introducing hydrogen sulfide gas (5% concentration by volume) at a gas rate of 300mL / min, the carrier gas is nitrogen, and keeping at 650°C for 45 minutes. The gas analyzer measures the content...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Embodiment 2: the method for this low-temperature decomposition of phosphogypsum, the specific content is as follows:
[0028] (1) The main chemical components of phosphogypsum used in this example are: calcium oxide 35.36%, sulfur dioxide 47.12%, iron oxide 3.01%, aluminum oxide 2.05%, phosphorus pentoxide 1.20%, fluorine 0.06%, silicon dioxide 11.20%;
[0029] (2) Crushing and grinding the dried phosphogypsum raw material, and sieving to a particle size between 0.074-0.150mm;
[0030] (3) Mix phosphogypsum with a mass percentage of 71% and calcium chloride with a mass percentage of 29% (particle size less than 0.074mm), stir evenly, then dry the mixture at 125°C for 3 hours and put it into a tube furnace. Heating to 700°C at a heating rate of 15°C / min, while introducing hydrogen sulfide gas (volume percentage concentration: 10%) at a gas velocity of 150mL / min, the carrier gas is nitrogen, and keeping at 700°C for 30 minutes. The gas analyzer measures the content of ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: the method for this low-temperature decomposition of phosphogypsum, the specific content is as follows:
[0034] (1) The main chemical components of phosphogypsum used in this example are: calcium oxide 35.36%, sulfur dioxide 47.12%, iron oxide 3.01%, aluminum oxide 2.05%, phosphorus pentoxide 1.20%, fluorine 0.06%, silicon dioxide 11.20%;
[0035] (2) Crushing and grinding the dried phosphogypsum raw material, and sieving to a particle size of 0.074-0.150mm;
[0036](3) Mix 80% by mass phosphogypsum and 20% by mass calcium chloride (particle size less than 0.074mm), stir well, then dry the mixture at 110°C for 4 hours and put it into a tube furnace. Heating to 675°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min, while introducing hydrogen sulfide gas (3% volume percent concentration) at a gas rate of 50mL / min, nitrogen as a carrier gas, and keeping at 675°C for 60 minutes. The gas analyzer measures the content of various gases in the tail gas in real time and collects t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com