Method for preparing iron tailing into ceramic frit glaze
A technology of iron tailings and frit glaze, which is applied in the field of comprehensive utilization of iron tailings resources and building ceramic materials, can solve the problems of large fluctuations in the composition of iron tailings, unfavorable mica dispersion of mud, and restrictions on the application of iron tailings. The effect of firing temperature range, overcoming adverse effects, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
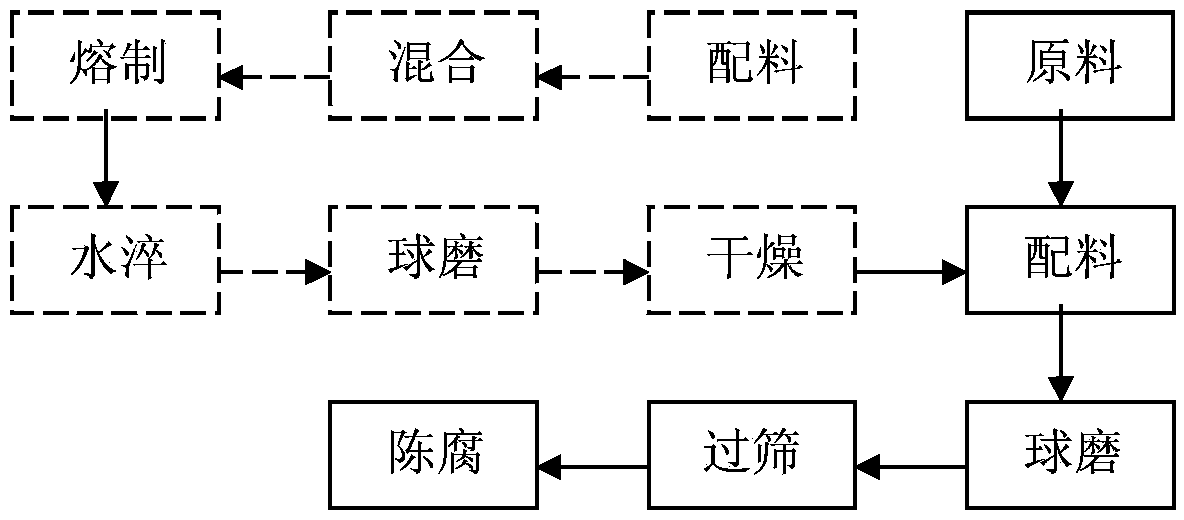
[0020] 1. The mass fraction used is: 45% iron tailings_18% potassium feldspar_10% albite feldspar_3% wollastonite_20% quartz_4% industrial iron oxide_0% zirconium silicate_0% calcite After batching, it is mixed by a mixer for 1 hour, then melted in an oxidizing atmosphere for 15 minutes without constant stirring, and the melting temperature is 1280°C. Then after water quenching and ball milling for 8-10 hours (subject to 80-mesh sieve), the frit is obtained after drying.
[0021] 2. Use the frit obtained above, according to the mass fraction of the components: 85% frit, 7% calcite, 4% kaolin, 0% industrial iron oxide, 4% quartz, 0% strontium carbonate, and 0% albite feldspar . Ordinary ball milling is used for 20~22 hours (ball: material: water = 1:2:0.8), and the glaze slurry is obtained through aging. The glaze slurry is passed through a 250-mesh sieve, and the remaining 0.05% is sieved, and the concentration of the glaze slurry is 1.80g / cm3.
[0022] 3. Take the dry bod...
Embodiment 2
[0027] 1. The mass fraction used is: 52% iron tailings_23% potassium feldspar_14% albite feldspar_5% wollastonite_0% quartz_6% industrial iron oxide_0% zirconium silicate_0% calcite After batching, it is mixed by a mixer for 1 hour, then melted in an oxidizing atmosphere for 15 minutes without constant stirring, and the melting temperature is 1280°C. Then after water quenching and ball milling for 8-10 hours (subject to 80-mesh sieve), the frit is obtained after drying.
[0028] 2. Use the frit obtained above, according to the mass fraction of the components: 73% frit, 7% calcite, 4% kaolin, 4% industrial iron oxide, 12% quartz, 0% strontium carbonate, and 0% albite feldspar . Ordinary ball milling is used for 20~22 hours (ball: material: water = 1:2:0.8), and the glaze slurry is obtained through aging. The glaze slurry is passed through a 250-mesh sieve, and the remaining 0.05% is sieved, and the concentration of the glaze slurry is 1.75g / cm3.
[0029] 3. Take the dry bod...
Embodiment 3
[0034] 1. The mass fraction used is: 45% iron tailings_18% potassium feldspar_10% albite feldspar_3% wollastonite_20% quartz_4% industrial iron oxide_0% zirconium silicate_0% calcite After batching, it is mixed by a mixer for 1 hour, then melted in an oxidizing atmosphere for 15 minutes without constant stirring, and the melting temperature is 1280°C. Then after water quenching and ball milling for 8-10 hours (subject to 80-mesh sieve), the frit is obtained after drying.
[0035] 2. Use the frit obtained above, according to the mass fraction of the components: 92% frit, 0% calcite, 0% kaolin, 0% industrial iron oxide, 0% quartz, 8% strontium carbonate, and 0% albite feldspar . Ordinary ball milling is used for 20~22 hours (ball: material: water = 1:2:0.8), and the glaze slurry is obtained through aging. The glaze slurry is passed through a 250-mesh sieve, and the remaining 0.05% is sieved, and the concentration of the glaze slurry is 1.90g / cm3.
[0036] 3. Take the dry bod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com