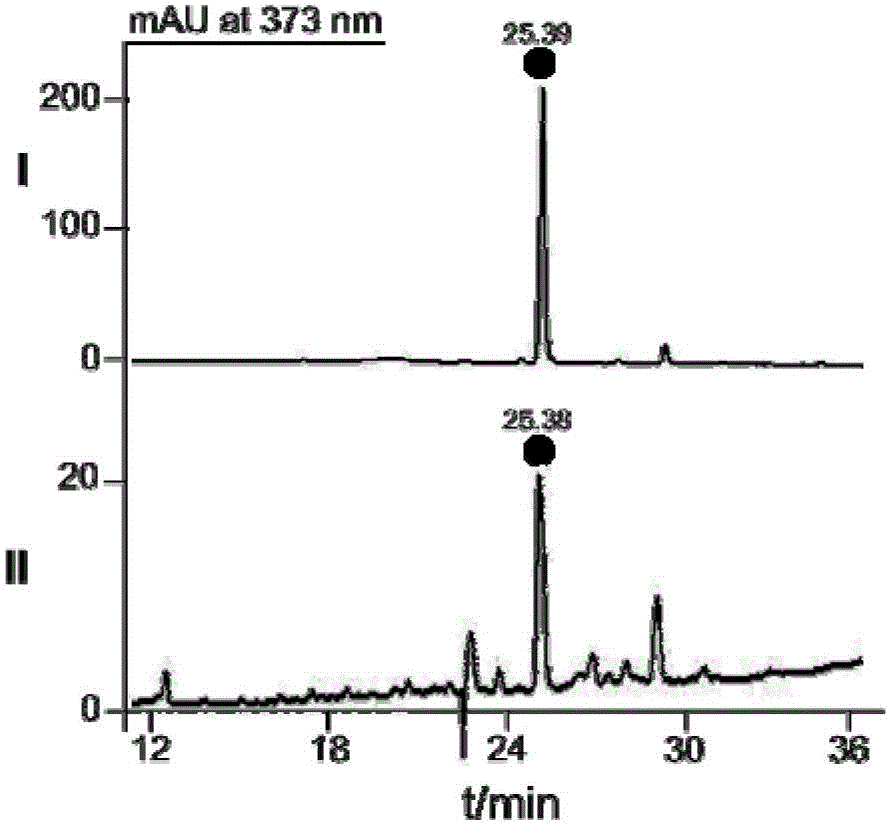
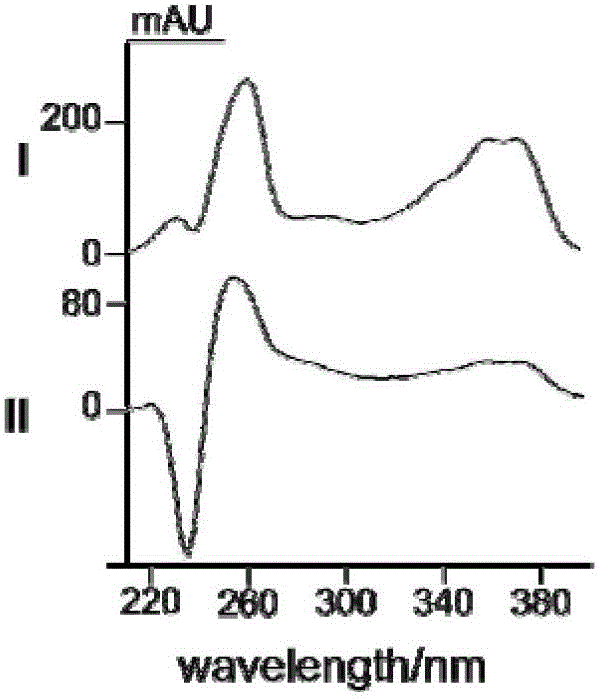
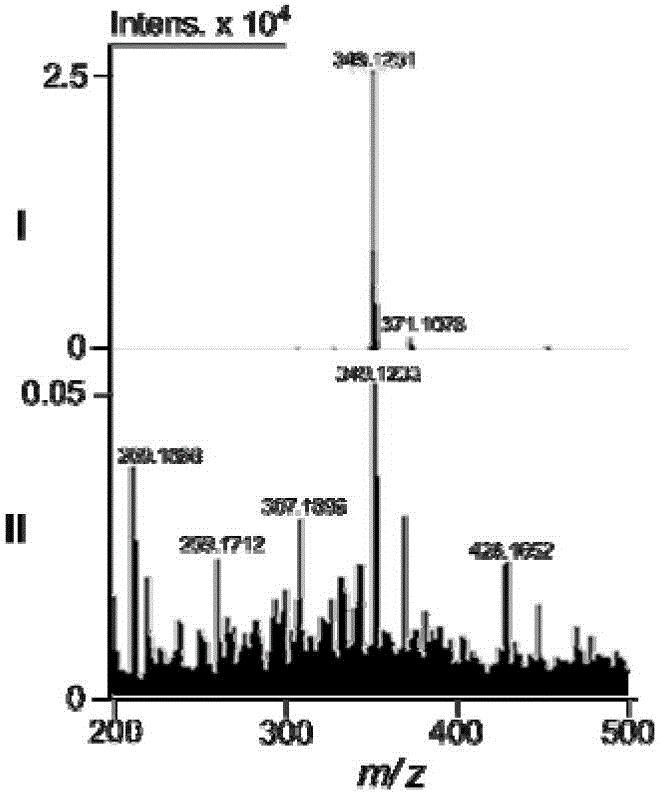
Camptotheca endophytic bacterium LY214 for producing camptothecin and application thereof
A technology of endophytic bacteria and camptothecin, applied in the field of medical biology, can solve the problems of difficult industrial production of production costs, large environmental pollution, cumbersome steps, etc., and achieve simple and easy-to-control separation methods, simple and easy-to-control methods, and rapid growth and reproduction Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1: Isolation and screening of camptothecin-producing endophytes from camptothecin
[0032] The endophytic bacterial strain Paenibacillus polymyxa LY214 was isolated from camptophyllum.
[0033] 1. Test material
[0034] 1.1 Plant material:
[0035] Select the organs or tissues of philodendron that grow normally and healthy as plant materials, such as tree roots, bark, fruits, leaves, branches and other parts.
[0036] The collected plant materials were cut into sections, cleaned and disinfected according to routine operations. In this embodiment, tap water is used to thoroughly rinse to remove dust and other sundries, and the plant material is cut into small pieces of 10mm×10mm with a sterile scalpel, and soaked in 75% ethanol for 5 minutes, 10% sodium hypochlorite solution for 5 minutes, and 1% Triton. 5min, rinse with sterile water 5 times, 1min each time, and finally use sterile filter paper to absorb the surface moisture of each tissue part of Campylocarp...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Camptothecin was obtained from the camptothecin endophytic bacteria strain Paenibacillus polymyxa LY214.
[0046] 1. Culture medium and extraction solvent
[0047] Culture medium: Sabouraud liquid medium (SBA liquid medium), the components are the same as the SBA solid medium in Example 1, but no agar is added.
[0048] Extraction solvent: chloroform-methanol mixed solvent (V / V=4:1)
[0049] 2. Extraction method of camptothecin
[0050] 2.1 Fermentation culture
[0051] The strain Paenibacillus polymyxa LY214 preserved in Example 1 was prepared according to conventional methods to obtain seed liquid. Inoculate 50ml of seed liquid into 500ml of SBA liquid medium, culture at 28±2°C, shaker 160±20rpm, for 8-15 days, and obtain a fermentation mixture.
[0052] 2.2 Preparation of fermented extract
[0053] The fermentation mixture was centrifuged at 4000rpm for 15min, filtered, and the filtrate and mycelia were collected respectively.
[0054] The obtained filtrate was...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Camptothecin was obtained by using the camptothecin endophytic bacterial strain Paenibacillus polymyxa LY214, which is the same as Example 2 and will not be repeated. The difference is that a seed liquid preparation step is added before the fermentation culture, including strain activation and seed culture.
[0058] Activation of strains: the strain Paenibacillus polymyxa LY214 preserved in Example 1 was inoculated on SBA solid medium for activation, and cultured for 5-7 days to obtain activated strains;
[0059] Seed culture: Inoculate the activated strains into 50ml SBA liquid medium, culture at 28±2°C, shaker 160±20rpm, for 2-3 days to obtain seed liquid.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com