Method for increasing the advantages of starch in pulped cellulosic material in the production of paper and paperboard
一种纤维素物质、纸板的技术,应用在造纸、增强剂添加、非纤维浆添加等方向,能够解决协议目标问题、助长化学需氧量、降低机生产率等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0480] The following experiments were carried out at various commercial papermaking installations throughout Europe. Examples 1 and 4 were carried out in a closed system, and the remaining examples were carried out in an open system. The starting material for each example was 100% recycled paper.
[0481] The following table 4 summarizes the dosage and feeding point of the following biocides and polymers:
[0482] Table 4:
[0483]
[0484] CEPI-Confederation of European Paper Industries
[0485] For comparison purposes, it must be noted that the usual dosage of ammonium bromide biocide is 0.005 to 0.008% Cl 2 Active matter per ton of paper produced, ie the dose used in the experiments according to the invention was 2 to 10 times higher than the conventional dose.
example 1
[0486] Example 1 - Using Setup A (Experiments show the use of (a) Polymer Aid, but no Biocide or Polymer A; (b) Polymer Aid A and Biocide, but no Polymer A; and (c) polymer additive A, biocide, and the effect of polymer A on microbial degradation and starch fixation on cellulose):
[0487] The following experiments investigate the positive effect of using the biocides according to the invention in combination with cationic polymers.
[0488] The biocide used is (a) 35% NH prepared in situ according to European patent EP-A517102, European patent EP785908, European patent EP1293482 and European patent EP1734009 4 Br and 13% NaOCl, as an inorganic biocide; and (b) bronopol / 5-chloro-2-methyl-2H-isothiazolin-3-one / 2-methyl.2H-isothiazoline -3-ketone (BNPD / Iso) is a two-component oxidizing biocide composed of organic biocides.
[0489] The cationic polymer used is a copolymer consisting of acrylamide (about 69 mole-%) and quaternized N.N-dimethylaminopropyl acrylamide (DIMAPA-Quat...
Embodiment 2
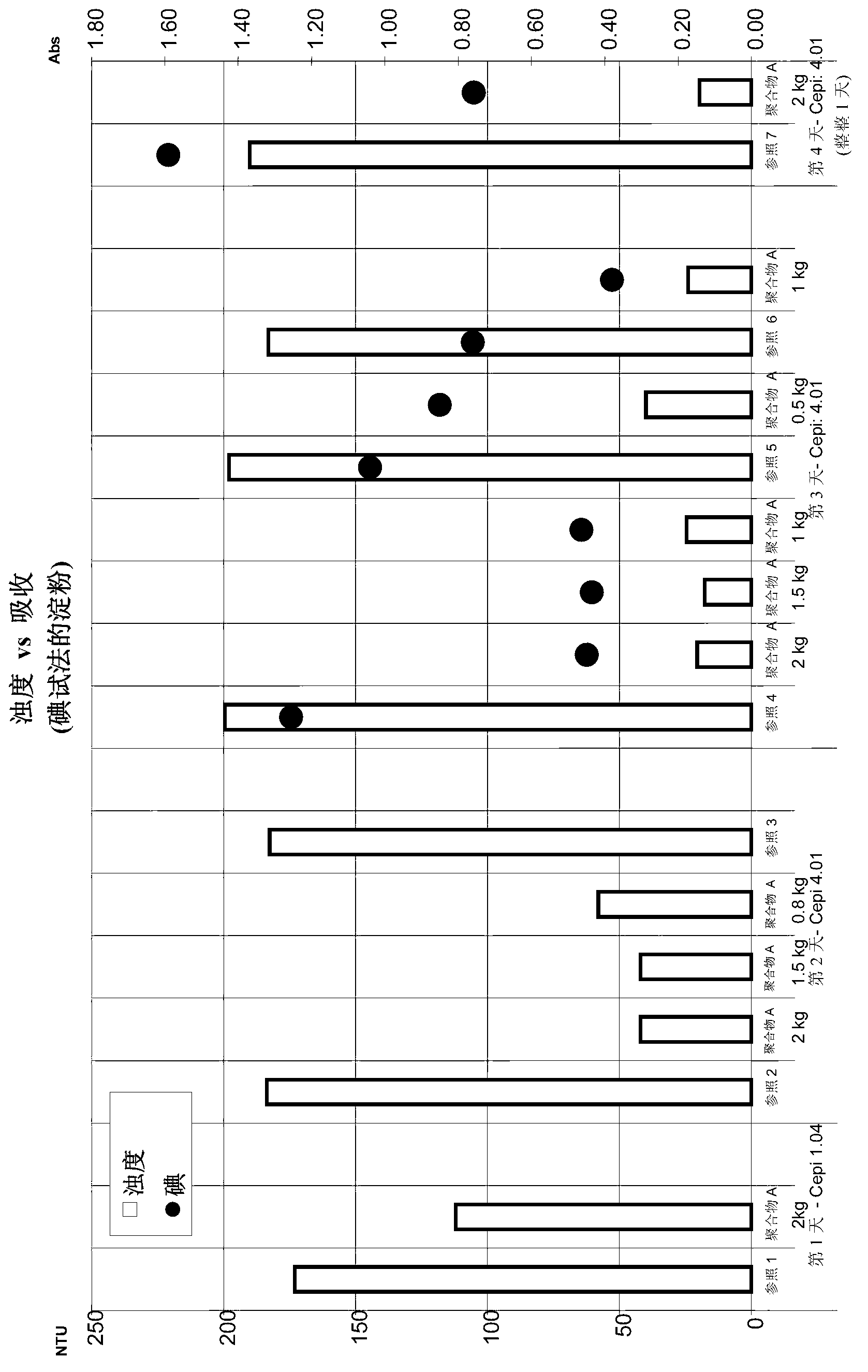
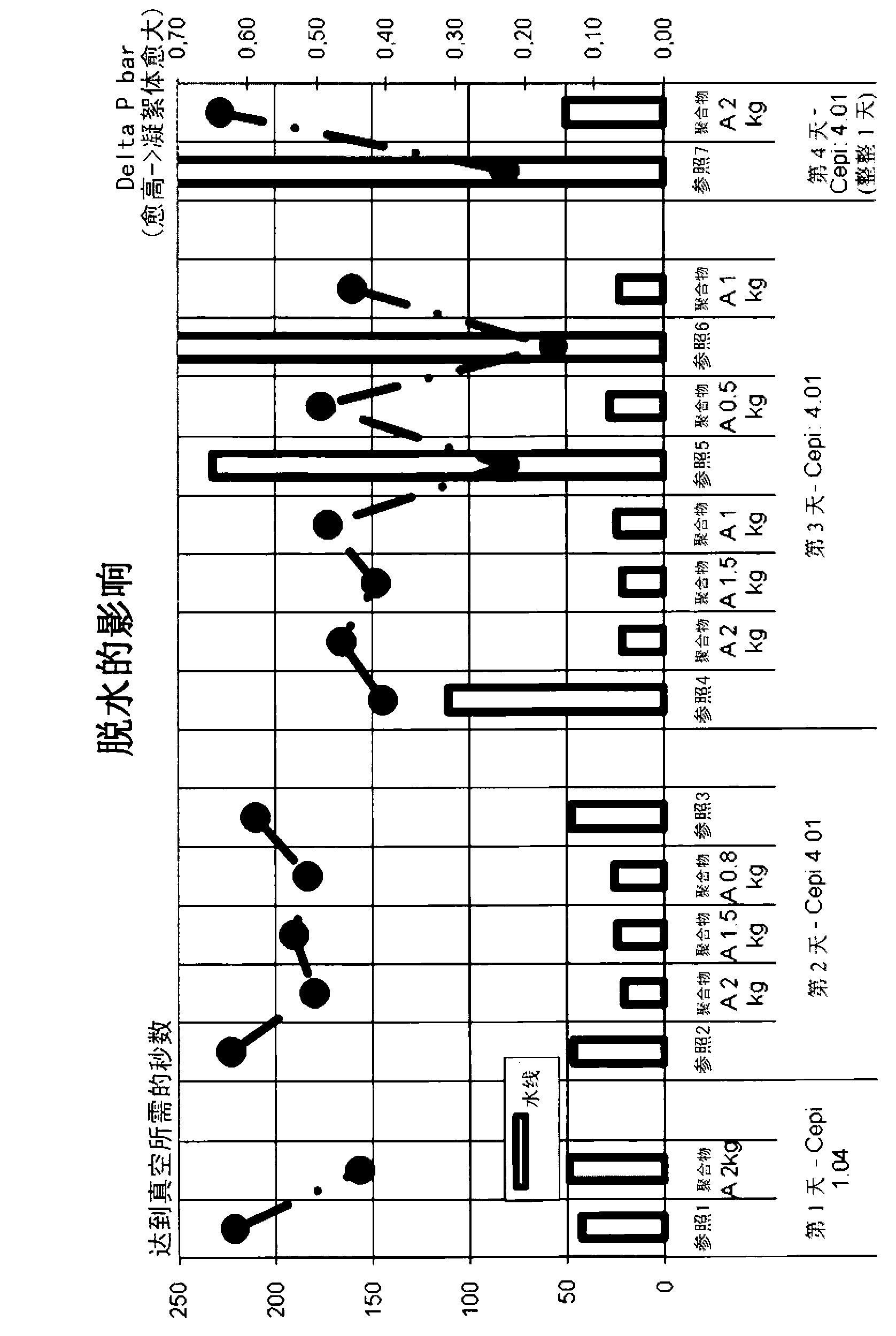
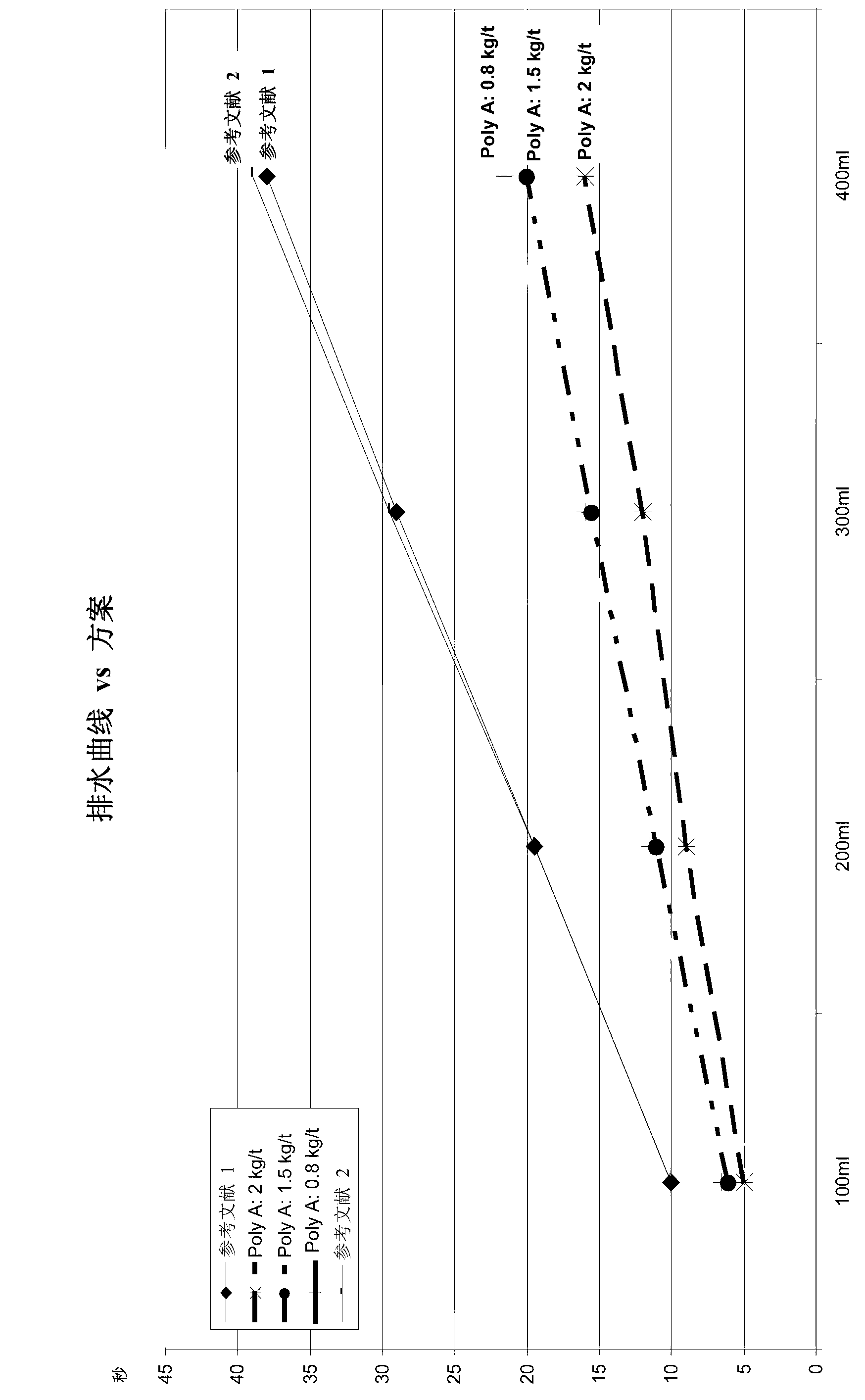
[0498] Example 2 - using setting A (experiments show the use of various doses of polymer A, and fixed doses of polymer additive A and biocide, on the impact of fixed starch, turbidity, and drainage):
[0499] The following experiments used the biocide and the cationic polymer according to Example 1 in the paper production process as follows:
[0500] In the beating step, a thick stock of recycled pulp consisting of European Paper Union Standard 1.04 or 4.01 with a consistency of 35 to 45 g / l was used, treated with a biocide to prevent starch degradation.
[0501] Then add the polymer A and the polymer auxiliary agent A to the thick slurry of the recycled pulp, and then mix with the pulp to simulate the addition of the pulp chest. Dilute the sample with tap water or white water to form a thin slurry with a consistency of 7 to 9 g / l. Then add the standard retention aid program, and then put the sample into the vacuum drainage test (VDT) device or DFR device (DFR=Drainage Freene...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com