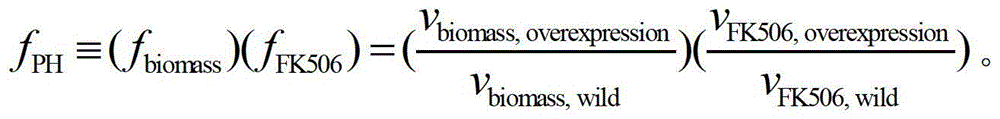Genome-scale metabolic network model of fk506-producing strain Streptomyces tsukuba to guide next-level pathway transformation
A Streptomyces tsukuba, genome-scale technology, applied in the field of metabolic engineering molecular transformation of microbial strains, can solve problems such as unknown and complex topology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
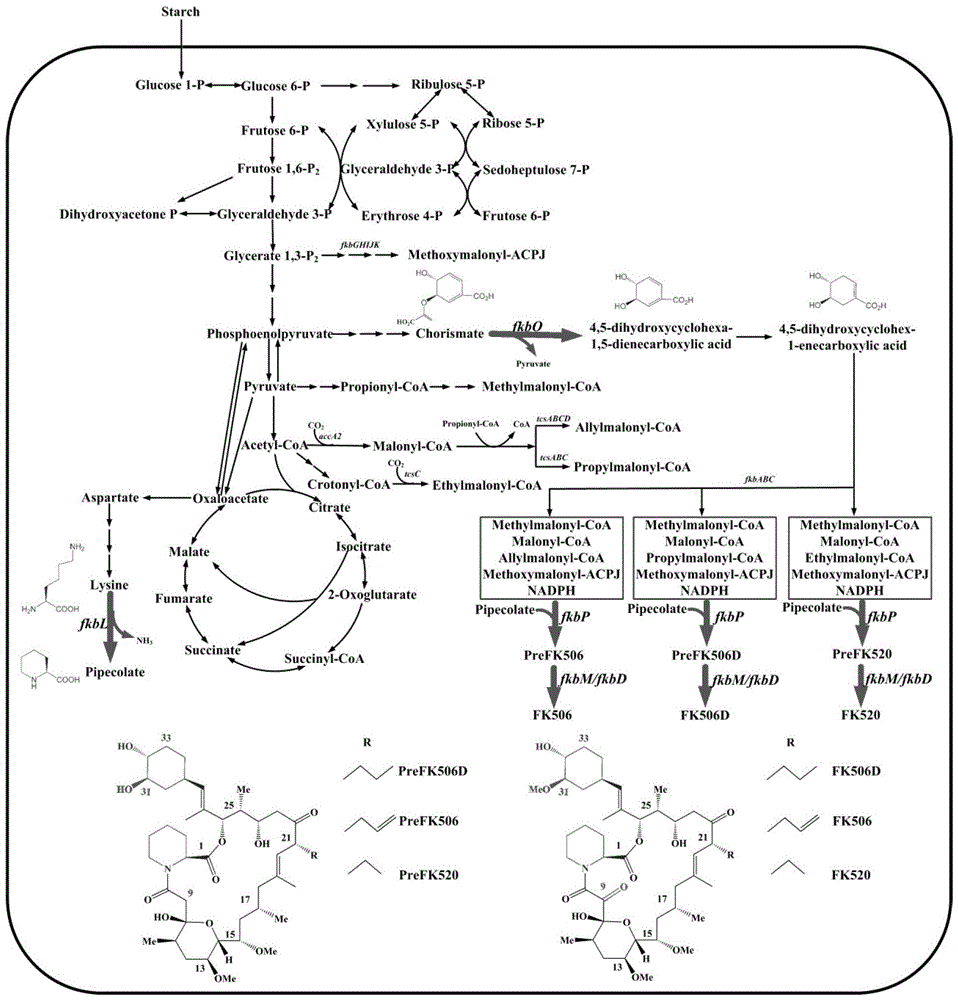
[0046] The model is based on annotated genes and physiological and biochemical information, including 865 biochemical reactions and 621 metabolites. 735 reactions of this network are unique, and the rest are identical reactions encoded by isozymes. Through comparative analysis with the genome of Streptomycescoelicolor, it was found that the metabolic genes were highly conserved. The model mainly includes glycolysis pathway, pentose phosphate pathway, tricarboxylic acid cycle, pyruvate metabolism, glyoxylate cycle metabolism, biomass precursor synthesis, coenzyme synthesis, nitrogen-sulfur metabolism and porphyrin and other related reactions. Including the synthesis pathway reaction of FK506 and its by-products FK520 and FK506D, the bacterial synthesis reaction ( figure 1 ).
Embodiment 2
[0048] According to the prediction of the secondary pathway gene cluster special pathway gene in Example 1, the initial intracellular flux distribution of Streptomyces tsukuba obtained by the flux balance analysis calculation, each non-zero flux reaction was doubled, and the MOMA algorithm was used to obtain the expansion Intracellular flux distribution of each mock strain after multiplication, according to f PH The calculation formula for screening secondary pathway amplified target genes of FK506 biosynthesis ( figure 1 ).
[0049] f PH ≡ ( f biomass ) ( f FK 506 ) = ( v biomass , overexpression ...
Embodiment 3
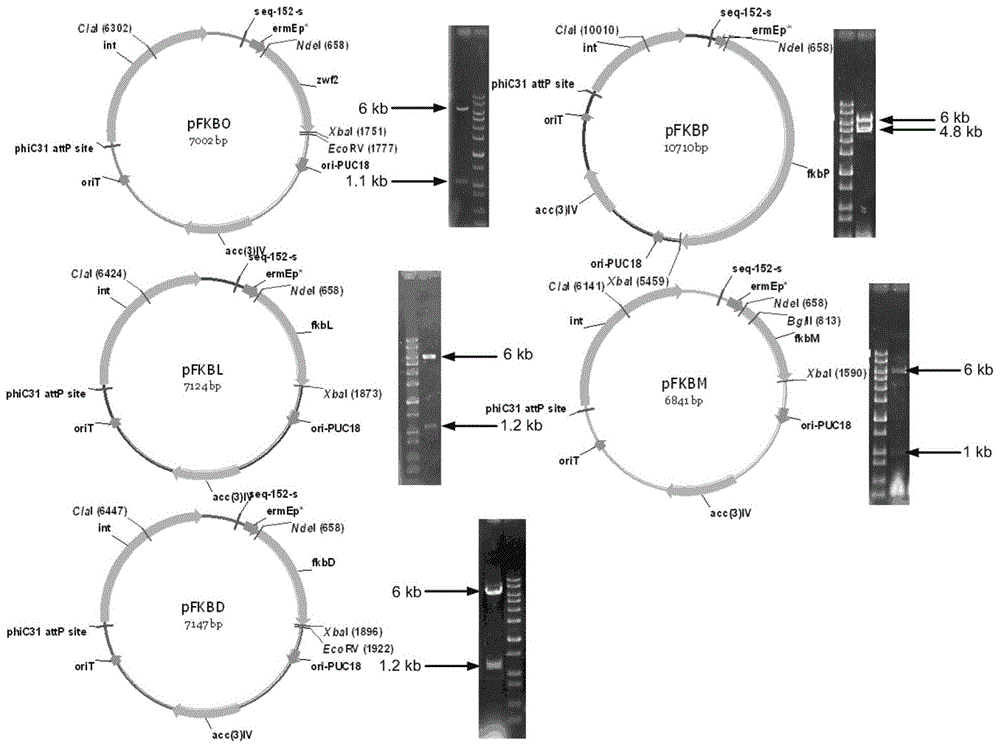
[0051] According to Example 2, predict secondary pathway gene cluster special pathway genes—cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid synthesis pathway gene fkbO, percolic acid synthesis pathway gene fkbL and fkbP, FK506 rear modification pathway structural gene fkbM and fkbD, to Streptomyces tsukuba carry out molecular modification. Using the S.tsukubaensis genome as a template, fkbO-F / fkbO-R, fkbL-F / fkbL-R, fkbP-F / fkbP-R, fkbM-F / fkbM-R, fkbD-F / fkbD-R were used as Primers (Table 1) amplify the fkbO gene, fkbL gene, fkbP gene, fkbM gene and fkbD gene, and the PCR products include the ribosome binding sites of each gene itself. Respectively, the fkbO gene, fkbL gene, fkbP gene, fkbM gene and fkbD gene PCR products were digested with NdeI-XbaI and then ligated into the same digested pIB139, and the ligated products were transferred into the prepared Escherichia coli competent cells JM109 or DH5α , after transformation, spread onto a screening plate containing 50 μg / mL apramycin and culture ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com