Method for clearing non-human animal skin heterologous antigen, and low immunogenicity non-human animal skin preparation method
An animal skin, immunogenic technology, applied in medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problem of no clear indication of α-Gal antigen, and achieve the effect of low price, wide material source and high enzymatic activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
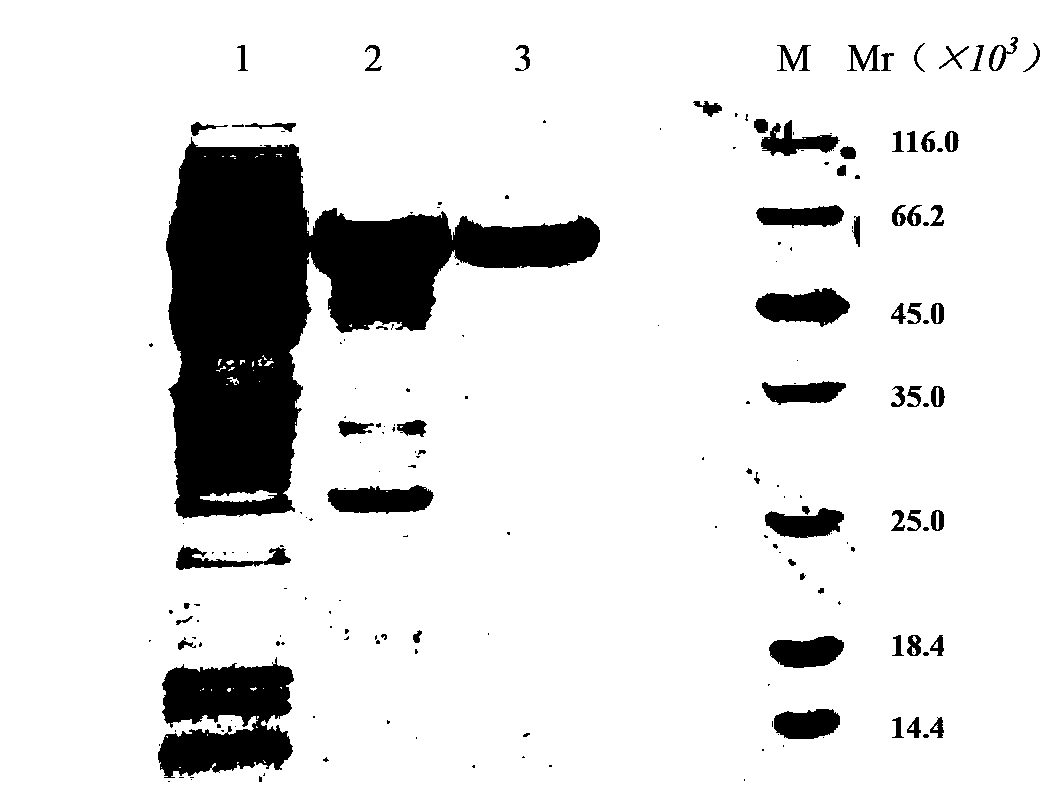
[0057] Embodiment 1, preparation recombinant α-galactosidase
[0058] Take the recombinant α-galactosidase strain pET22b-Gal / BL21(DE3) frozen at -70°C (see the Chinese patent document with publication number CN101845425A for the construction method), and put it on the LB plate (Amp + ) on the line to activate the strain, pick a single clone and culture overnight (10-12 hours) on the second day, and transfer to expand the culture to D on the third day 600 Add IPTG (final concentration: 0.1mM) to induce the expression of the target protein at 0.8, the induction time is 4 hours, collect the bacteria by centrifugation, and use Buffer A (20mM citric acid-disodium hydrogen phosphate buffer, 25mM NaCl, pH5.0) Suspend the cells, sonicate and lyse the cells, collect the supernatant by centrifugation (4°C, 9000r / min for 20min), and load the supernatant onto a cation chromatography column (Hitrap TM SP-HP), wash the column with 10 times the column volume of Buffer A, and use Buffer B (...
Embodiment 2
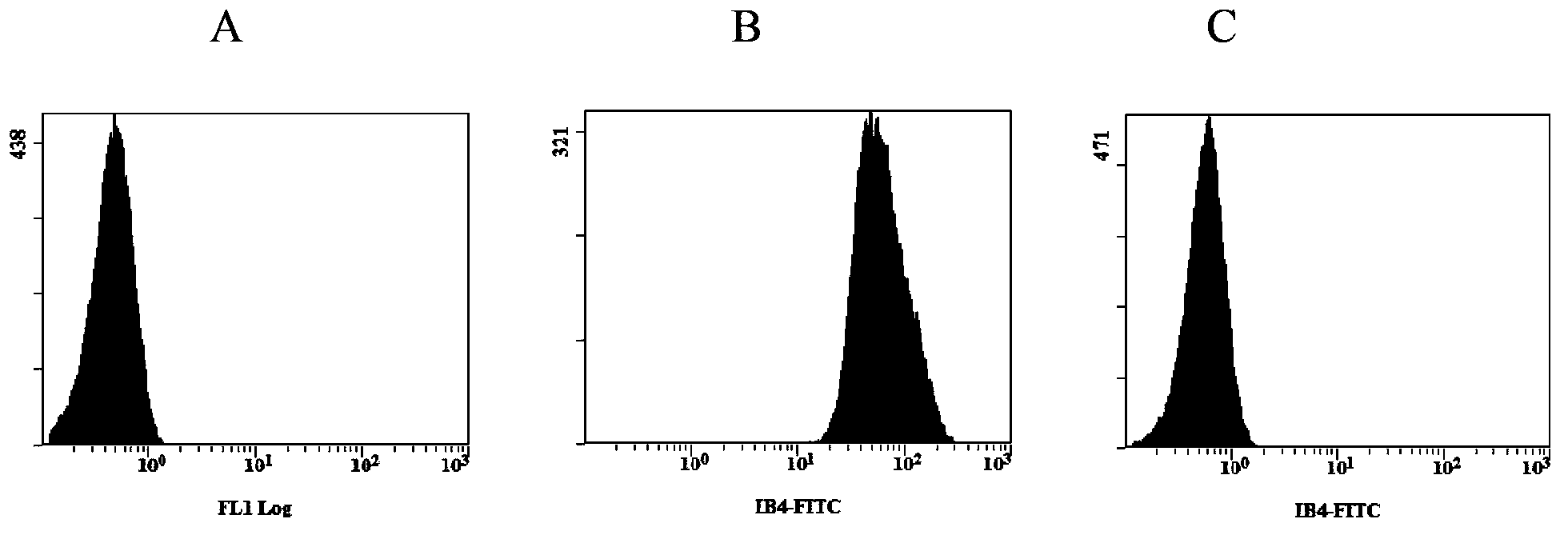
[0059]Embodiment 2, the detection of enzymatic hydrolysis experiment of porcine erythrocyte and α-Gal antigen clearance rate
[0060] In the experiment, the recombinant α-galactosidase can be prepared according to the method of Example 1; the enzymatic hydrolysis buffer is a glucose solution with a mass concentration of 5%.
[0061] Pig erythrocytes were washed twice with enzymatic hydrolysis buffer at a volume ratio of 1:1 and 1:4, so that the hematocrit was 40%; a recombinant α-galactosidase ( Prepared as in Example 1), slowly shake and incubate for 1 hour in an enzymatic hydrolysis reaction box at 26°C; then use PBS solution (recipe: each L contains 8g of NaCl, Na 2 HPO 4 1.44g, KCl0.2g, KH 2 PO 4 0.24g) wash red blood cells 4 times at a volume ratio of 1:4, add 1 / 2 volume of MAP solution (recipe: every L contains C 6 h 5 Na 3 o 7 .2H 2 O1.5g, C 6 h 8 o 7 .H 2 O0.2g, C 6 h 12 o 6 .H 2 O7.93g, NaH 2 PO 4 .2H 2 O0.94g, C 5 h 5 N 5 0.14g, NaCl4.97g, C 6 ...
Embodiment 3
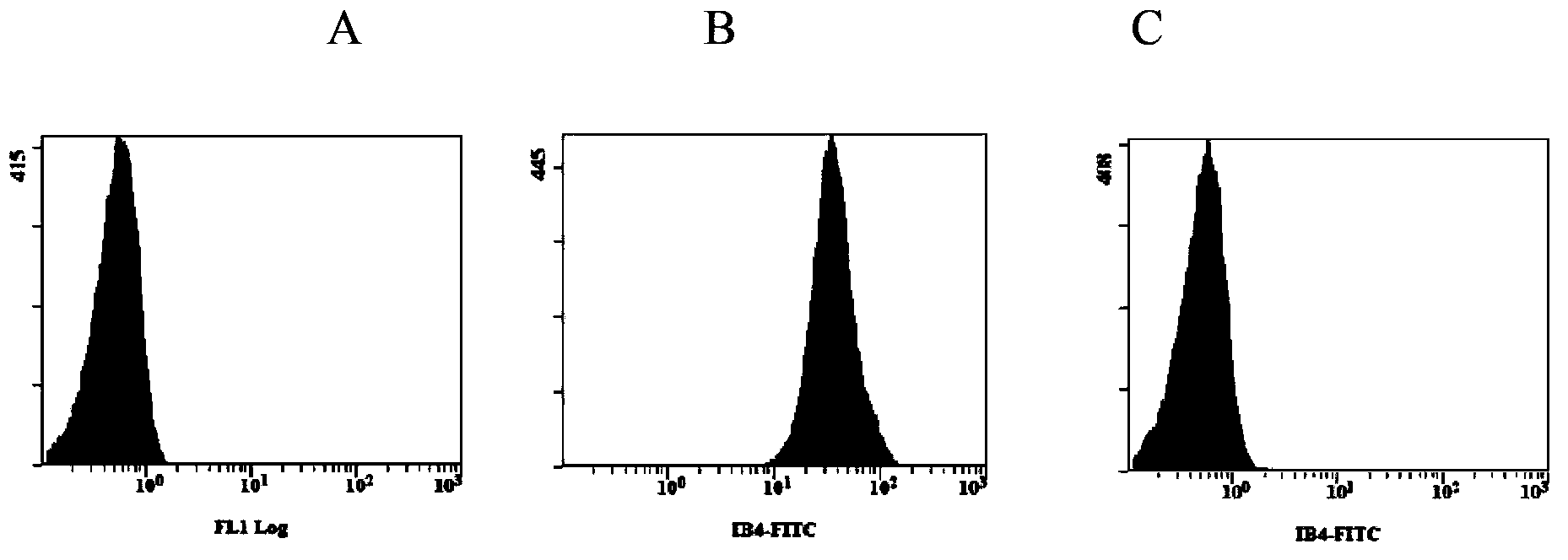
[0065] Embodiment 3, the detection of enzymatic hydrolysis experiment of bovine erythrocyte and α-Gal antigen clearance rate
[0066] The same operation as in Example 2, using bovine erythrocytes to carry out the enzymatic hydrolysis experiment.
[0067] The results of flow cytometry were as image 3 (A. blank (blank, unlabeled bovine erythrocytes), B. non-enzymolyzed bovine erythrocytes (positive control), C. enzymatically treated bovine erythrocytes), the test results show that the α-Gal antigen on the surface of bovine erythrocytes It can be cleared by α-galactosidase, and the clearance rate is greater than 99%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com