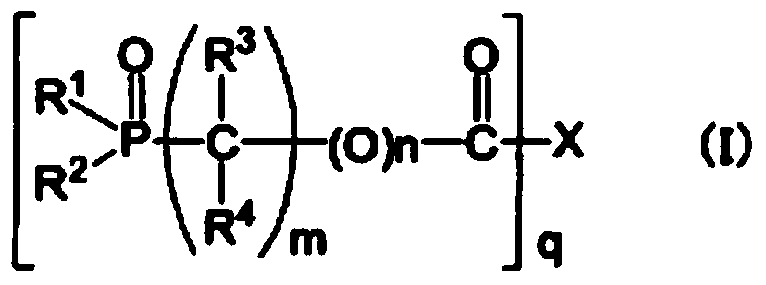Non-aqueous electrolyte solution and electricity-storage device using same
A technology for non-aqueous electrolytes and power storage devices, applied in the field of organophosphorus compounds, can solve the problems of reduced battery characteristics such as cycle characteristics, reduced battery performance such as battery capacity or cycle characteristics, and hindered movement of lithium ions, so as to improve electrochemical performance. Effects of Features
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
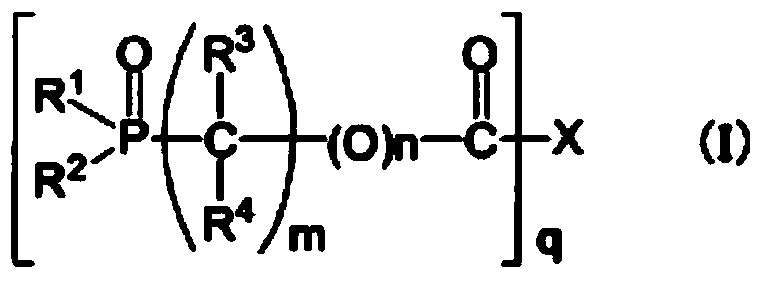
[0192] Synthesis examples of organophosphorus compounds used in the present invention are shown below, but are not limited to these synthesis examples.
Synthetic example 1
[0193] Synthesis Example 1 [Synthesis of 2-propynyl 2-(diethoxyphosphoryl) acetate (synthesis of compound 1)]
[0194] Stir 100.0g (0.51mol) of 2-(diethoxyphosphoryl)acetic acid, 400mL of toluene, and N,N-dimethylformamide (0.1g) at 50°C, and add 95% chloride solution dropwise over 20 minutes. Thionyl 67.7g (0.54mol). After stirring at 63°C for 90 minutes, the solvent was distilled off to prepare 2-(diethoxyphosphoryl)acetyl chloride.
[0195] 31.4 g (0.56 mol) of the above-mentioned 2-(diethoxyphosphoryl) acetyl chloride and propynyl alcohol were dissolved in 100 mL of toluene, and cooled to 5°C. After adding 67.1 g (0.66 mol) of triethylamine dropwise to this solution at 15° C. or lower, it was stirred at room temperature for 90 minutes, and the disappearance of the raw material was confirmed by gas chromatography. The generated salt was filtered and washed with 30 ml of saturated brine. The organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the resulting residue wa...
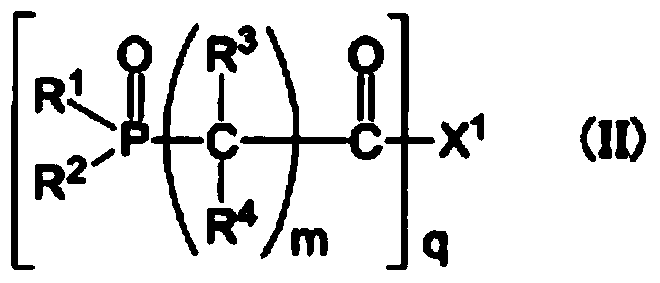
Synthetic example 2
[0214] Synthesis Example 2 [Synthesis of 2-(2-(diethoxyphosphoryl)acetoxy)ethyl methyl oxalate (synthesis of compound 7)]
[0215] Dissolve 2.0 g (13.51 mmol) of 2-hydroxyethyl methyl oxalate and 1.7 g (16.8 mmol) of triethylamine in 50 mL of ethyl acetate, and add diethyl (2- Chloro-2-oxyethyl) phosphonate 3.1 g (14.5 mmol). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour, and the disappearance of the raw material was confirmed by gas chromatography. The reaction solution was washed with water, the organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the resulting residue was purified by silica gel chromatography (eluted with ethyl acetate) to obtain the target 2-(2-(diethoxyphosphoryl)acetoxy ) ethyl methyl oxalate 1.8g (yield is 42%).
[0216] The resulting 2-(2-(diethoxyphosphoryl) acetoxy) ethyl methyl oxalate 1 The structure was confirmed by H-NMR measurement. The results are shown below.
[0217] 2-(2-(Diethoxyphosphoryl)acetoxy)ethylmethyl oxalate
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com