Method of synthesizing magnesium silicate building material product by utilizing boron mud and coal ashes
A technology for synthesizing magnesium silicate and fly ash, which is applied in the direction of sustainable waste treatment, solid waste management, climate sustainability, etc., can solve unsatisfactory mechanical properties, limit the effective utilization rate of boron mud, and increase production cost and other issues, to achieve the effect of low price, high utilization rate, and not easy to lose
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
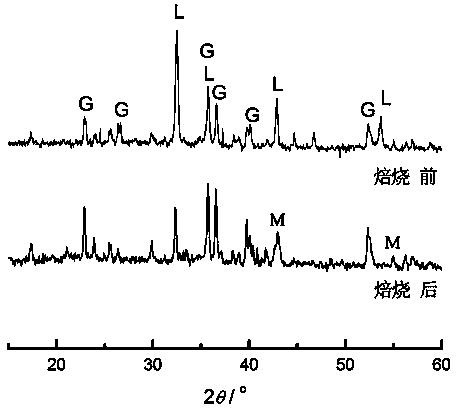
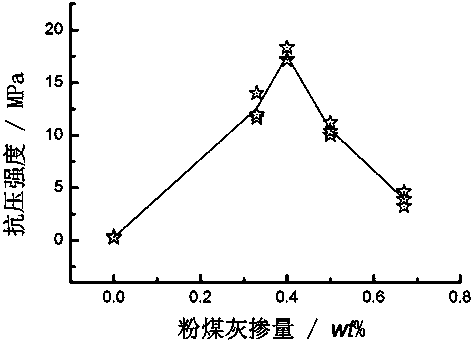
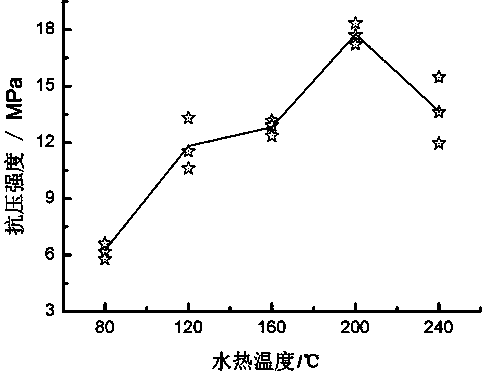
[0040] Boron mud residue from a chemical plant in Dashiqiao, containing MgCO 3 25%, roasted at 600 °C for 3 hours, crushed through a 150-mesh sieve; weighed 1 kg of roasted coal, mixed with 1 kg of fly ash (grade II, produced by Shenhai Thermal Power Plant), and then added 0.2 kg of tap water to mix well; weighed 200 g The mixture was placed in a compression mold, and a cylindrical test block with a height and a diameter of 30 mm was obtained through 20 kN pressure molding. After molding, the sample was placed in a hydrothermal reaction kettle, heated to 160°C, kept at a constant temperature for 9 hours, and then cooled naturally. The apparent density of the hydrothermally cured sample after drying is about 1.6 g / cm 3 , The average compressive strength is 10MPa. MgO in roasted boron sludge and active SiO in fly ash during hydrothermal treatment 2 with Al 2 o 3 A chemical combination reaction occurs to generate hydrated magnesium silicate (serpentine phase) and other react...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The difference from Example 1 is that the calcination temperature is increased to 850°C, the calcination time is 0.75h, and at the same time, hydrated lime is added to the reaction mixture as a strength development accelerator, and the dosage is 5% of the mass of boron mud; the average compressive strength of the obtained samples is It can be increased to about 15MPa.
Embodiment 3
[0044] The difference from Example 1 is that the hydration reaction temperature is increased to 240° C. and kept at a constant temperature for 6 hours; the average compressive strength of the obtained samples can be increased to about 18 MPa.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Apparent density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com