Edible agar utilized double-coated lactobacillus powder and preparation method thereof
A lactic acid bacteria powder, lactic acid bacteria technology, applied in food preparation, microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient effect and limited application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1 utilizes the preparation of the double coating lactic acid bacteria powder of edible agar
[0047] First, in order to produce Lactobacillus casei (Lactobacillus casei CBT-LC) lactic acid bacteria coated with protein alone, the following experiment was performed.
[0048] Specifically, 5% glucose was added as a sugar component, 2% yeast extract, 3% soybean peptone, 0.1% edible agar, 0.2% potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.2% ammonium citrate, 0.2% sodium acetate, and 0.01% magnesium sulfate were added as The ionic components were then dissolved, transferred to an anaerobic fermentation tube with a capacity of 200L, sterilized at 121°C for 15 minutes, inoculated with 2L of bacteria, maintained pH with ammonia, and fermented for 12 hours. After the above-mentioned fermentation, the fermented liquid was transferred to a continuous centrifugal separator at a flow rate of 60 L / hr to precipitate bacteria and edible agar jelly, thereby forming a concentrated aqueous...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2 Preparation of Lactic Acid Bacteria Double-coated with Proteins and Polysaccharides Containing Edible Agar
[0054] First, the following experiments were conducted in order to produce Bifidobacterium lactis CBT-BL lactic acid bacteria coated with edible agar and protein.
[0055] Specifically, 5% glucose was added as a sugar component, 3% yeast extract, 2% soybean protein isolate as a protein component, 0.3% edible agar, 0.2% potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.2% ammonium citrate, 0.2% sodium acetate, 0.01 % magnesium sulfate as ionic components, then dissolve them, transfer to a 200L capacity anaerobic fermentation tube, sterilize at 121°C for 15 minutes, inoculate 2L of bacteria, maintain pH with ammonia, and ferment for 15 hours. After the above-mentioned fermentation, the fermented liquid was transferred to a continuous centrifugal separator at a flow rate of 60 L / hr to precipitate bacteria and edible agar jelly, thereby forming a concentrated aqueous solut...
experiment example 1
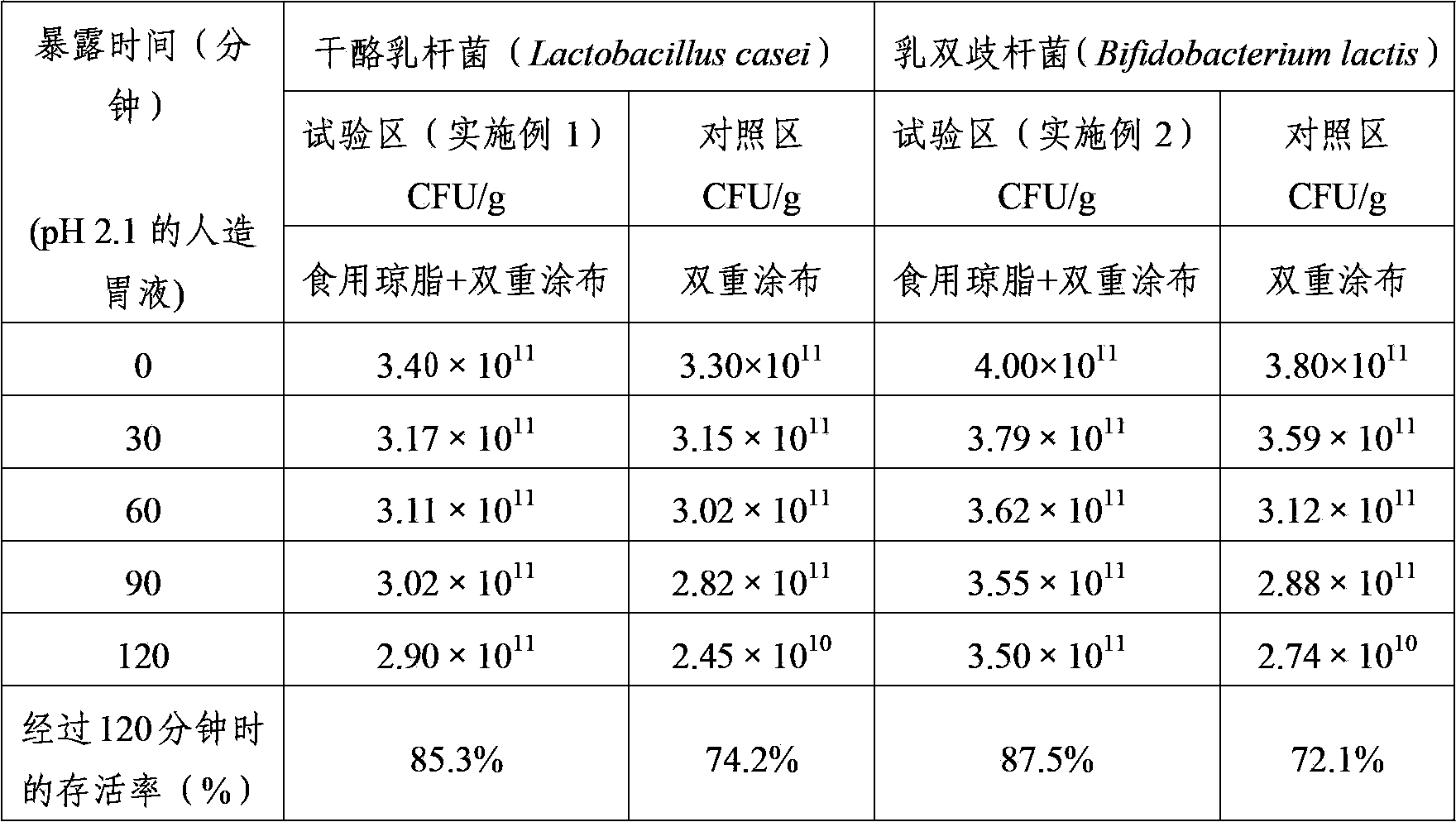
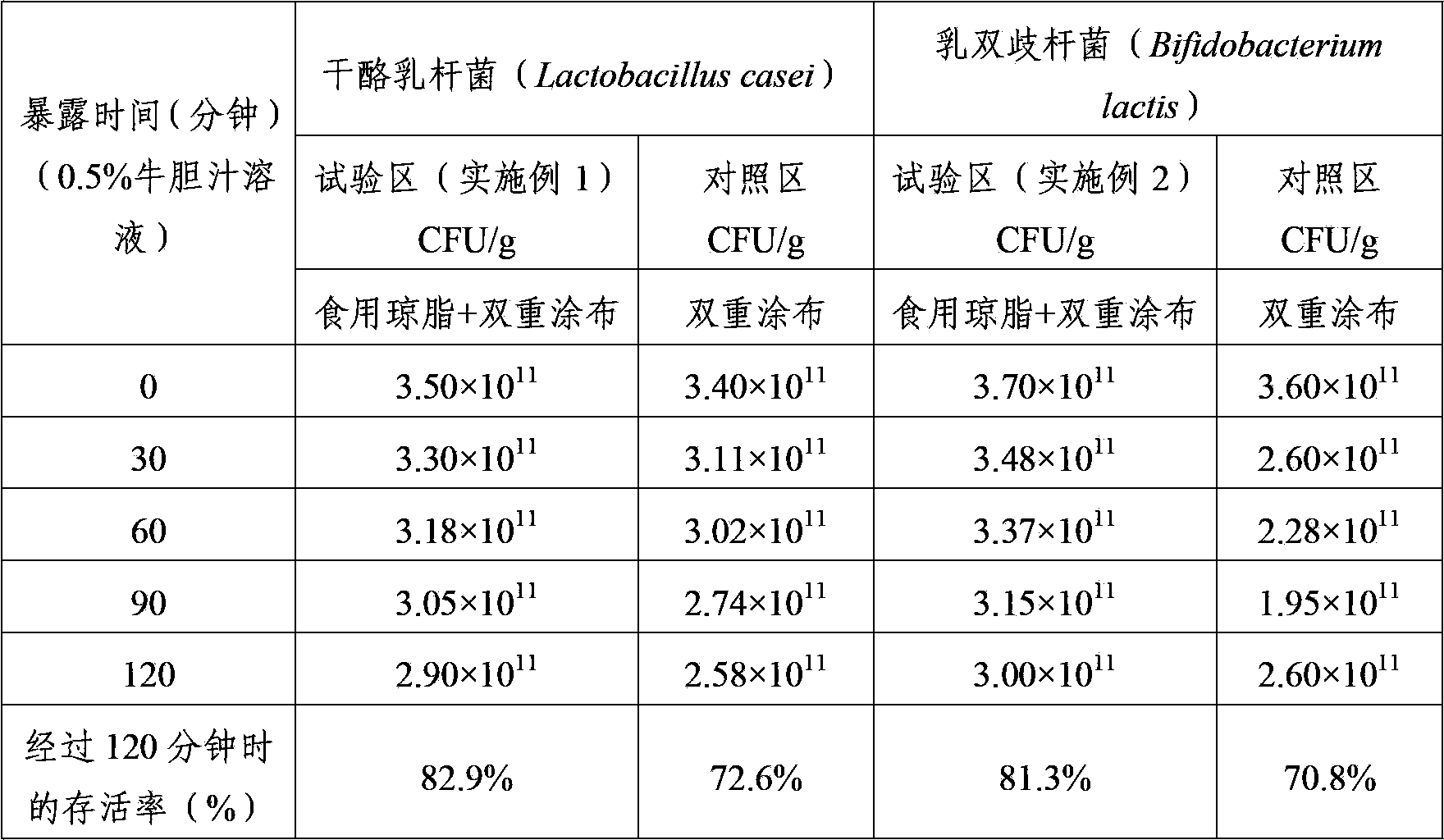
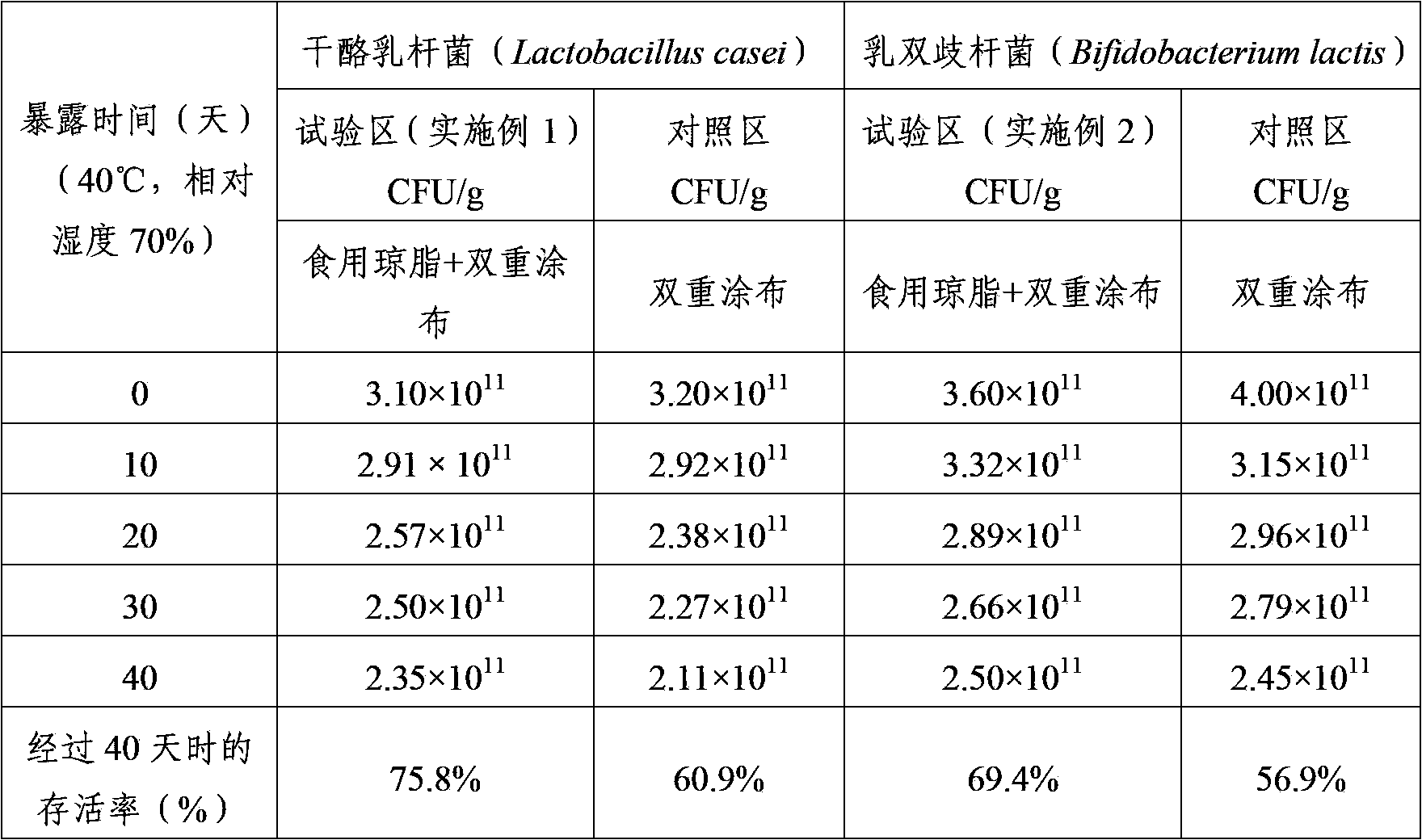
[0059] Experimental Example 1 Utilizes the Acid Resistance Comparison of the Double Coated Lactic Acid Bacteria Powder of Edible Agar
[0060] After measuring the acid resistance of the double-coated lactic acid bacteria powder utilizing edible agar prepared in the above-mentioned Example 1 and Example 2, its structure is shown in Table 1.
[0061] React the lactic acid bacteria powder prepared in the above-mentioned Example 1 and Example 2 in the artificial gastric juice of pH 2.1 for 30, 60, 90 and 120 minutes respectively, dilute the water with physiological saline or phosphate-buffer solution (Phosphate-buffer), pass After dilution by the decimal dilution method, spread on a solid medium (agar plate) and count the lactic acid bacteria.
[0062] Table 1
[0063]
[0064] In the above-mentioned Table 1, each control area shows that it is prepared according to the same method as that of Example 1 and Example 2, and forms double-coated lactic acid bacteria powder of protei...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com