Carbon-series/active-substance compound and preparation method thereof
A manufacturing method and composite technology, which can be applied to electrical components, electrochemical generators, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of inability to reduce tin dioxide, electrical decay, and inability to effectively reduce the irreversible capacitance of the first cycle.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
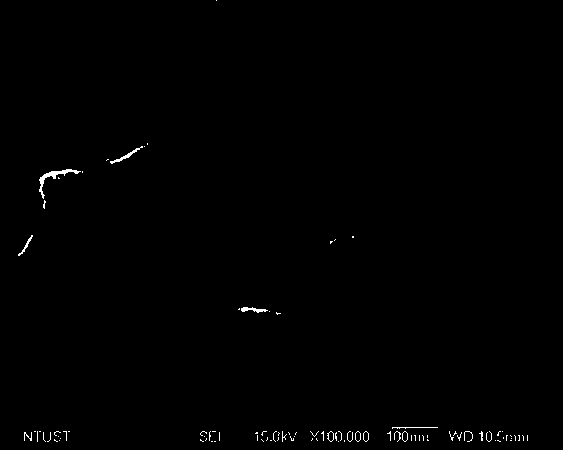
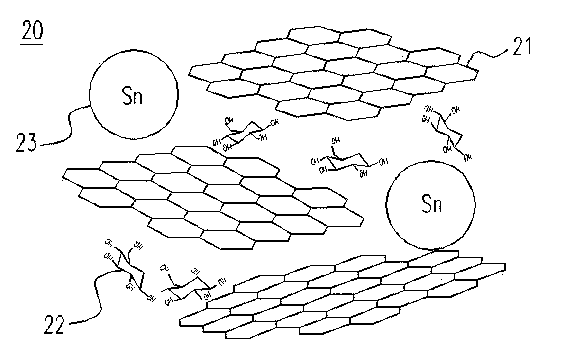
[0046] First, 2.5 grams of graphite (Graphite), 2.5 grams of sodium nitrate (Sodium nitrate, NaNO 3 ) with 115 ml of sulfuric acid (Sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4 ), uniformly mixed in a 500 ml ice-bath reaction flask, and stirred with a magnet. Then slowly add 7.5 grams of potassium permanganate (Potassium Permanganate, KMnO 4 ) and avoid the reaction temperature exceeding 20°C. Then the reaction bottle was moved to a 35°C water bath for 30 minutes of reaction. After the reaction was completed, 115 ml of deionized water was slowly added to the bottle, and the reaction temperature was raised to 98°C for 15 minutes of reaction. Then inject 350 ml of deionized water and 23 ml of 35% hydrogen peroxide (Hydrogen peroxide, H 2 o 2 ), and after waiting for natural cooling, the reactant was washed to neutrality by dialysis water washing to prepare a graphene oxide aqueous solution 21 (as shown in Figure 2(a) and 2(b)). Take 10 ml of 1 wt% graphene oxide aqueous solution 21, add 3.6 g ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Add 3.6 g of glucose (>99.5%; preferably D(+) glucose) to 10 mL of deionized water, and stir with a magnet for 90 minutes to fully dissolve the glucose, then add 1 g of micron tin powder (>99%; Sigma -Aldrich) stirred for half an hour. After mixing evenly, the mixed solution was transferred into a 100 ml reaction kettle, and the pressure was 10 bar (Bar) and the temperature was 180° C., and the oil bath was continuously heated and stirred for 5 hours. After the reactor was naturally cooled, the black powder was taken out, rinsed with 500 ml of deionized water, and dried overnight in an oven at 80°C. Move 2.25 g of the dried powder to a place containing an inert gas (N 2 ), and controlled calcination at 400°C for 4 hours to produce nanoscale tin dioxide carbon composites.
Embodiment 3
[0052] Add 3.6 g of glucose (>99.5%; preferably D(+) glucose) to 10 ml of deionized water, and stir with a magnet for 90 minutes to fully dissolve the glucose, followed by adding 1 g of micron tin powder (>99%; Sigma -Aldrich) stirred for half an hour. After mixing evenly, the mixture was transferred into a 100 ml reaction kettle, and the mixture was continuously heated and stirred for 5 hours in an oil bath with a pressure of 10 bar (Bar) and a temperature of 180°C. After waiting for the reactor to cool down naturally, the black powder was taken out, rinsed with 500 ml of deionized water, and dried overnight in an oven at 80°C. Move the dried powder (about 2.25 g) to an inert gas mixture (5% H 2 & 95% Ar) and calcined at 600 °C for 4 hours to produce nanoscale metallic tin / carbon composites.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com