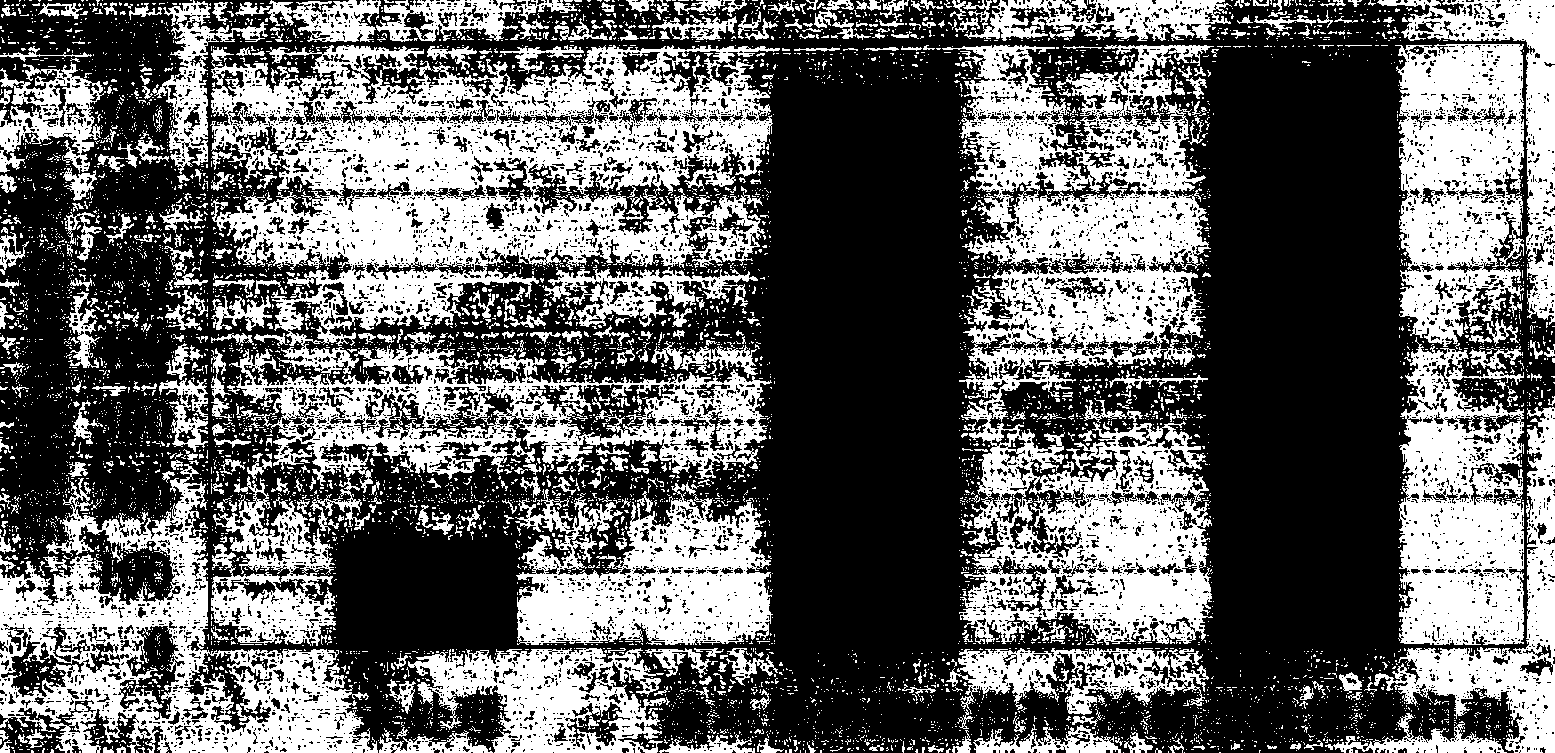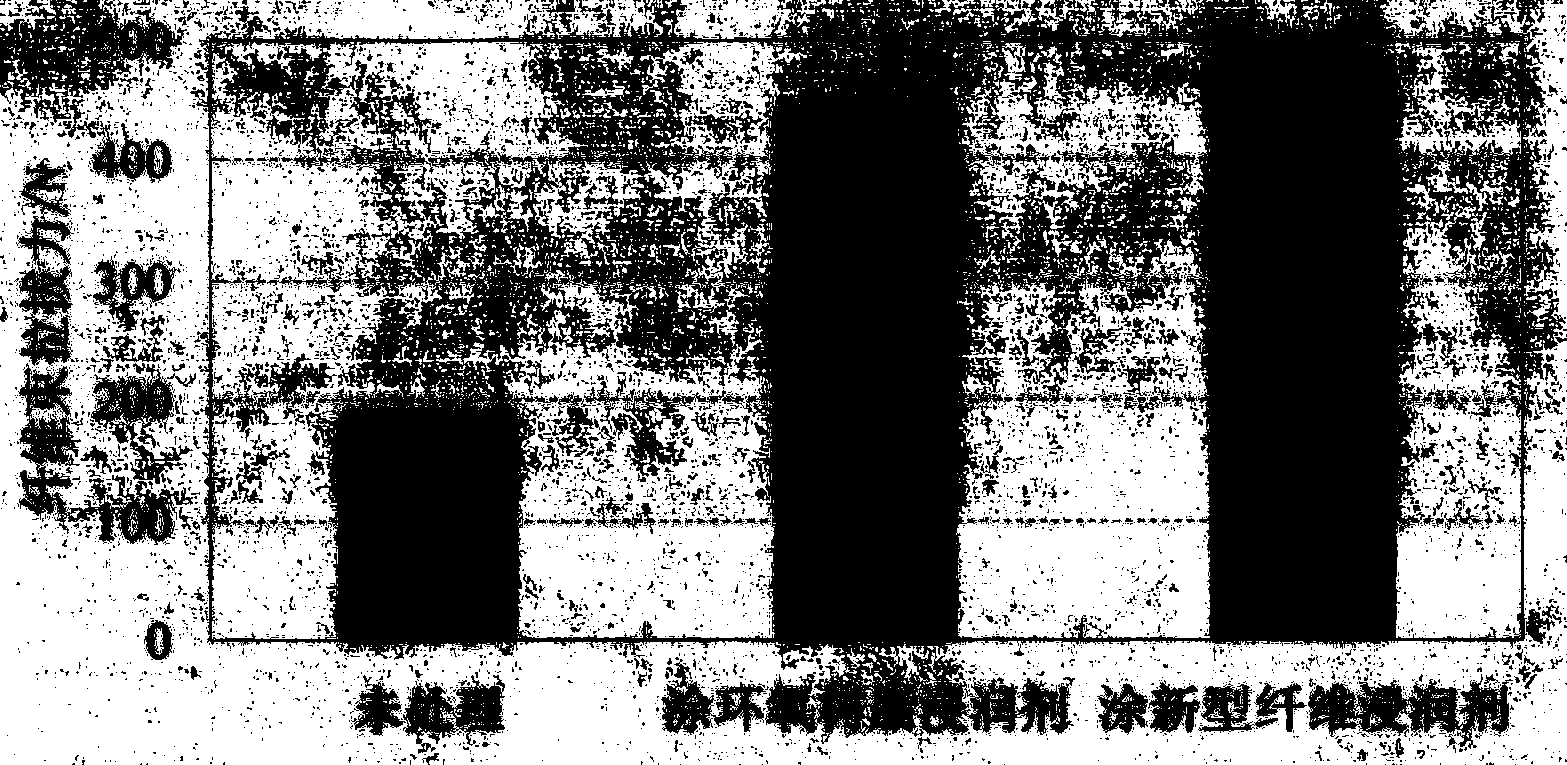Method of improving bonding performance of fiber bundle and potassium magnesium phosphate cement-based material
A technology of potassium magnesium phosphate cement and bonding performance, which is applied in the manufacture of fiber-reinforced potassium magnesium phosphate cement composite materials, and in the field of improving the bonding performance of fiber bundles and potassium magnesium phosphate cement-based materials, and can solve problems such as fiber bundle breakage and achieve Fast curing, high bond strength, and strong permeability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1: Get the sodium fluorosilicate of 2 mass parts, the dead-burned magnesium oxide powder of 10 mass parts and the sodium silicate aqueous solution (modulus is 3.0, Baume degree is 50.3) of 100 mass parts, with planetary liquid mixer Stir the mixed solution at a speed of 60-90 r / min for 3-5 minutes to obtain a new fiber sizing with controllable curing speed. Use a new fiber sizing agent to evenly brush the surface of the glass fiber bundles, fully soak the glass fiber bundles, and after the glass fiber bundles have been treated for 3 days (cured), use the DL-5000 electronic tensile testing machine to conduct an axial tensile test. The treated glass fiber bundles and the glass fiber bundles treated with epoxy resin sizing agent were subjected to axial tensile test; the MPC-based material slurry was prepared according to a certain proportion, poured and compacted, and glass fibers treated in different ways were supplemented. Fiber-reinforced MPC-based composite ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2: get the sodium fluosilicate of 8~10 mass parts, the dead burnt magnesia powder of 15~20 mass parts and the sodium silicate aqueous solution of 100 mass parts (modulus is 2.6~2.8, Baume degree is 38.4~ 48.3), use a planetary liquid mixer to stir the mixed solution at a speed of 60-90r / min for 2-3 minutes to obtain a new type of fiber sizing with controllable curing speed. Use a new fiber sizing agent to evenly brush the surface of the carbon fiber bundles, fully infiltrate the carbon fiber bundles, and after the carbon fiber bundles have been treated for 3 days (cured), perform an axial tensile test with a DL-5000 electronic tensile testing machine. The carbon fiber bundles treated with epoxy resin sizing agent are subjected to axial tensile test; the MPC-based material slurry is prepared according to a certain proportion, poured and compacted, and carbon fiber bundles treated in different ways are supplemented to prepare fiber-reinforced MPC-based composit...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3: get the sodium fluosilicate of 8~10 mass parts, the dead burnt magnesia powder of 15~20 mass parts and the sodium silicate aqueous solution of 100 mass parts (modulus is 2.6~2.8, Baume degree is 38.4~ 48.3), use a planetary liquid mixer to stir the mixed solution at a speed of 60-90r / min for 2-3 minutes to obtain a new type of fiber sizing with controllable curing speed. Brush the surface of the basalt fiber bundle evenly with a new type of fiber sizing agent, and fully soak the basalt fiber bundle. The treated basalt fiber bundles and the basalt fiber bundles treated with epoxy resin sizing agent were subjected to axial tensile test; MPC-based material slurry was prepared according to a certain mix ratio, poured and compacted, and basalt fibers treated in different ways were supplemented. The bundles were prepared into fiber-reinforced MPC-based composite material pull-out specimens, and the basalt fiber bundles with different treatment methods of untreat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com