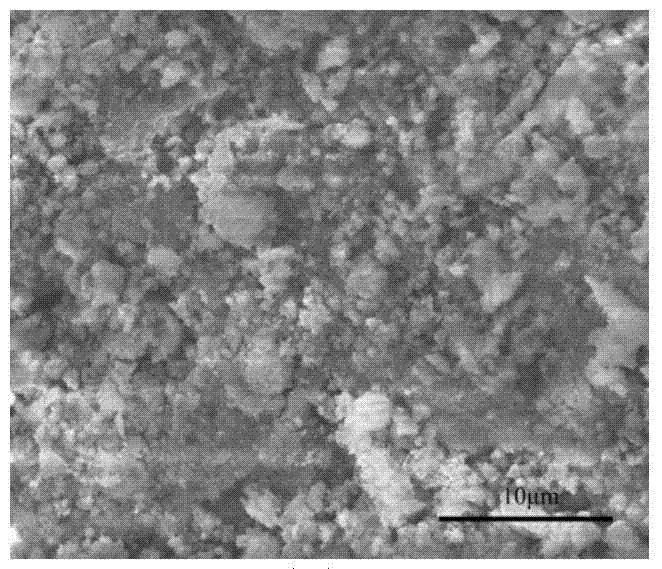
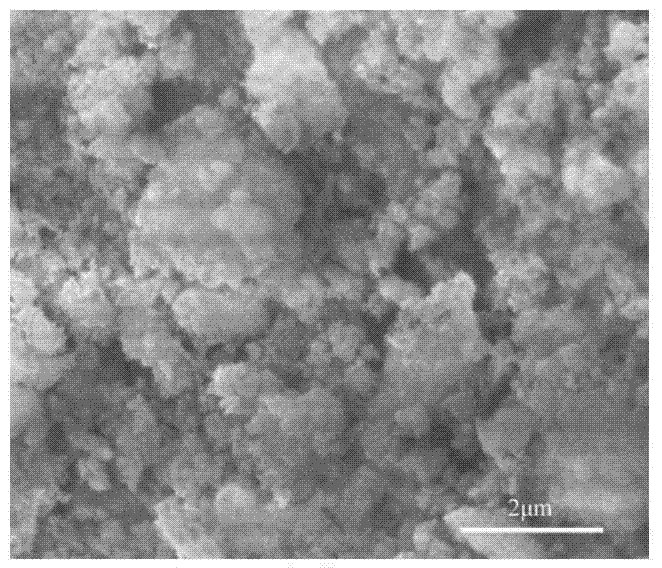
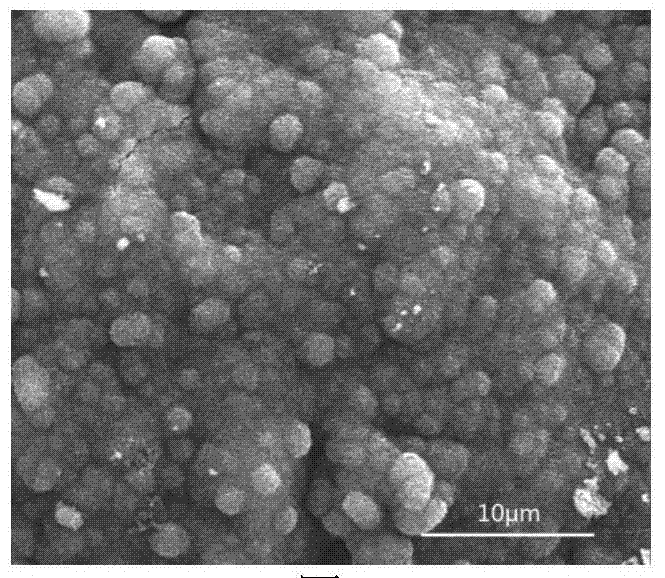
Preparation method of micron or nanometer calcium phosphate/catechol-based polymer bone repair scaffold
A nano-calcium phosphate and catechol-based technology, applied in the fields of medical science and prostheses, can solve the problems of uniform distribution of fibers and carbon nanotubes, inability to use 3D printing methods, and limited improvement of material mechanical properties, etc., to achieve Avoid adverse effects, good biocompatibility, and improve the effect of mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A method for preparing micro- and nano-calcium phosphate / catechol-based polymer bone repair scaffolds, the steps are:
[0034] A. Combine 85 parts by weight of alpha tricalcium phosphate with an average particle diameter of 500 μm, 10 parts by weight of dibasic calcium phosphate dihydrate with an average particle diameter of 500 μm, and 5 parts by weight of hydroxyapatite with an average particle diameter of 500 μm. One part by weight of pore former—mannitol is mixed with 20 parts by weight of polydopamine, and trihydroxyaminomethane-hydrochloric acid buffer is added to obtain a slurry mixture;
[0035] B. The slurry mixture of step A is molded by molding, and then placed in a 37°C water bath for curing for 24 hours.
[0036] The polydopamine of this example was prepared by the following method:
[0037] Dopamine was added to the potassium hydroxide solution of pH 8.5, stirred for 24 hours under the condition of oxygen gas, and then the solution was centrifuged and freeze-dried...
Embodiment 2
[0041] A method for preparing micro- and nano-calcium phosphate / catechol-based polymer bone repair scaffolds, the steps are:
[0042] A. Mix 100 parts by weight of α-type tricalcium phosphate with an average particle size of 1μm, 40 parts by weight of pore former-hydrogen peroxide and 0.1 part by weight of polydopamine, and then add trihydroxyaminomethane-hydrochloric acid buffer to obtain a slurry mixture;
[0043] B. The slurry mixture of step A is molded by pouring, and then placed in a 35°C water bath for curing for 20 hours after molding.
[0044] The polydopamine of this example was prepared by the following method:
[0045] Add dopamine to the pH10 sodium hydroxide solution, stir for 24h under UV irradiation, and then centrifuge and freeze-dry the solution.
Embodiment 3
[0047] A method for preparing micro- and nano-calcium phosphate / catechol-based polymer bone repair scaffolds, the steps are:
[0048] A. Mix 100 parts by weight of β-tricalcium phosphate with an average particle size of 500μm, 1 part by weight of pore former-degradable polymer and 45 parts by weight of polydopamine, and then add trihydroxyaminomethane-hydrochloric acid buffer to obtain Slurry mixture
[0049] B. The slurry mixture of step A is molded by molding, and then placed in a 40°C water bath for curing for 30 hours.
[0050] The polydopamine of this example was prepared by the following method:
[0051] Add dopamine to the pH7.4 sodium hydroxide solution, add sodium periodate, stir for 24h, then centrifuge the solution and freeze-dry it to obtain.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com