Jute fiber degumming method
A technology of jute fiber and degumming method, which is applied in the direction of producing bast fiber by chemical method, can solve the problems of failure to carry out mass production, strong itching, damage of jute fiber, etc., to avoid chemical scouring treatment, reduce pollution discharge, The effect of increasing the number of splits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
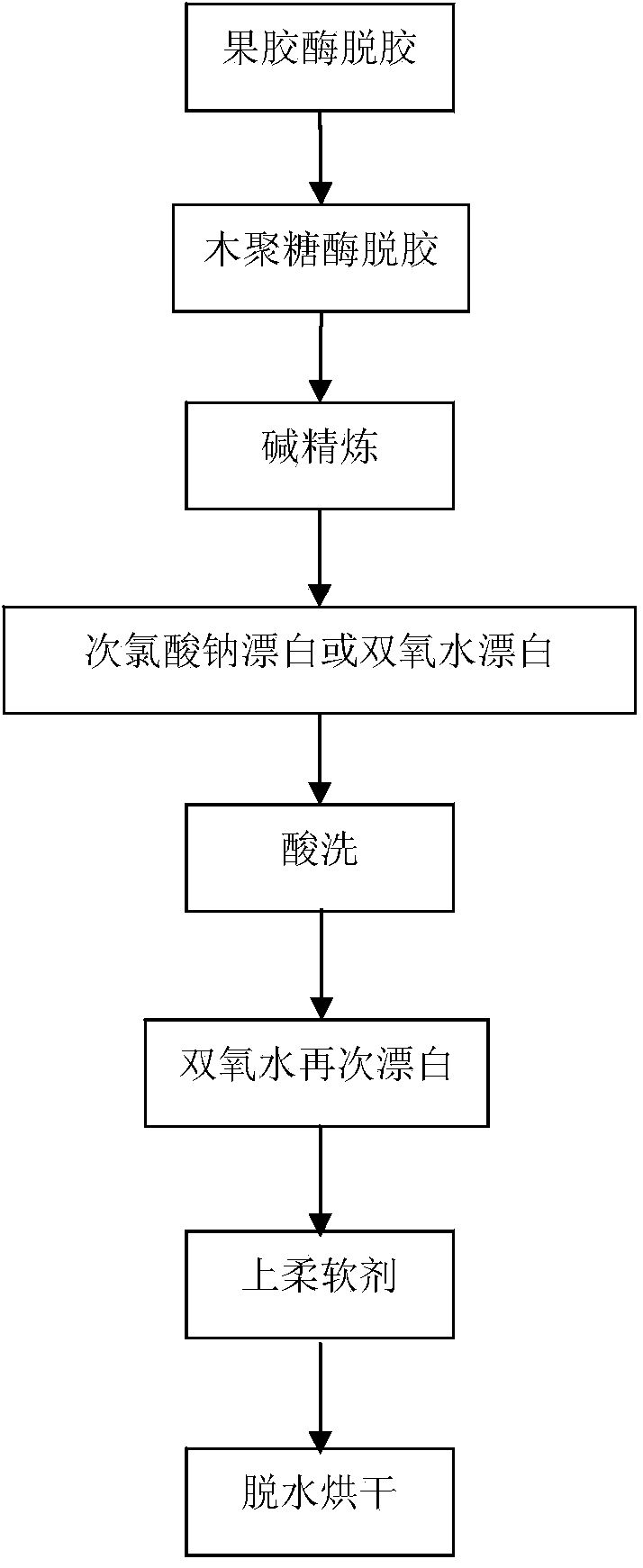
[0044] Take the degumming process of 200kg jute fiber as an example. First, the jute fiber is caged into a tank with a bath ratio of 1:15, and then the following steps are used for processing:
[0045] (1) Pectinase degumming: Use 2kg pectinase, adjust the pH to 7-8 with soda ash, and soak for 120 minutes at 50℃-55℃;
[0046] (2) Xylanase degumming: use 2 kg of xylanase, adjust the pH to 8-8.5 with soda ash, and soak for 120 minutes at 50℃-55℃;
[0047] (3) Alkali refining: use 12kg of caustic soda, 6kg of soda ash, 8kg of sodium sulfite, 4kg of refining agent (H-95), 4kg of chelating dispersant (CBI), 2kg of alkali sulfide, and treatment for 120min at 98℃-100℃;
[0048] (4) Sodium hypochlorite bleaching: use 40 kg of sodium hypochlorite solution with 10% available chlorine, and treat for 50 minutes at room temperature;
[0049] (5) Pickling: use 6kg sulfuric acid and treat at 40℃ for 30min;
[0050] (6) Hydrogen peroxide bleaching: use 26kg of 30% hydrogen peroxide, 5kg of soaking alkal...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Take the degumming process of 200kg jute fiber as an example. First, the jute fiber is caged into a tank with a bath ratio of 1:15, and then the following steps are used for processing:
[0055] (1) Pectinase degumming: Use 4kg pectinase, adjust the pH to 6-7 with soda ash, and soak for 60 minutes at 40℃-45℃;
[0056] (2) Xylanase degumming: use 4kg of xylanase, adjust the pH to 7-8 with soda ash, and soak for 60 minutes at 40℃-45℃;
[0057] (3) Alkali refining: use 16kg of caustic soda, 4kg of soda ash, 6kg of sodium sulfite, 6kg of refining agent (H-95), 6kg of chelating dispersant (CBI), 4kg of alkali sulfide, and treatment at 95℃-98℃ for 90min;
[0058] (4) Sodium hypochlorite bleaching: use 60kg of sodium hypochlorite solution with 10% available chlorine, and treat for 30min at room temperature;
[0059] (5) Pickling: Use 4kg sulfuric acid and treat at 30°C for 60min;
[0060] (6) Hydrogen peroxide bleaching: use 33kg of 30% hydrogen peroxide, 8kg of soaking alkali, 2kg of re...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Take the degumming process of 200kg jute fiber as an example. First, the jute fiber is caged into a tank with a bath ratio of 1:15, and then the following steps are used for processing:
[0065] (1) Pectinase degumming: use 1 kg of pectinase, adjust the pH to 8-8.5 with soda ash, and soak for 150 minutes at 60℃-70℃;
[0066] (2) Xylanase degumming: use 1 kg of xylanase, adjust the pH to 8.5-9.5 with soda ash, and soak for 150 minutes at 55℃-65℃;
[0067] (3) Alkali refining: use 20kg of caustic soda, 4kg of soda ash, 10kg of sodium sulfite, 4kg of refining agent (RUCO-STAB LGA), 2kg of chelating dispersant (foaming alkali), 2kg of alkali sulfide, and treatment at 95℃-100℃ 100min;
[0068] (4) Hydrogen peroxide bleaching: use 20kg of 30% hydrogen peroxide, 4kg of soaking alkali, 4kg of refining agent (H-95), 4kg of soda ash, adjust the pH to 10.5-11, and treat at 95℃-98℃ for 120min;
[0069] (5) Pickling: Use 2kg sulfuric acid and treat at 60℃ for 50min;
[0070] (6) Hydrogen per...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com