Method for reducing content of nitrite in pickled vegetables
A nitrite and content technology, which is applied in the field of food processing, can solve the problems affecting the quality of pickled vegetables and the nitrite content exceeds the standard, and achieves the effects of speeding up reproduction, excellent quality and reducing content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
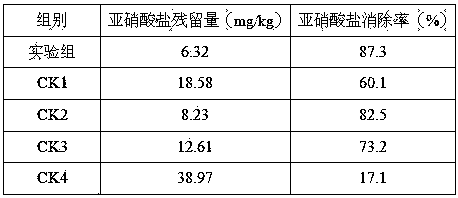
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1 Processing of pickled cauliflower with low nitrite content
[0042] 1. Pickling method
[0043] S1. Select cauliflower raw materials, wash and organize.
[0044] S2. Put the cauliflower raw material pretreated in S1 on a drying field in a clean place for drying; the drying time is controlled at 1 day, so that the moisture content of the material is reduced by 3%.
[0045] S3. Put the air-dried cauliflower into a clean pickling pool equipped with a pickling liquid circulation and spraying device, and add auxiliary materials to pickle together. The auxiliary materials are edible salt, edible lactic acid, disodium edetate and fresh radish slices. The amount of auxiliary materials added is 13kg of edible salt, 0.28kg of edible lactic acid, 0.018kg of disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (disodium EDTA) and 8kg of fresh radish slices (thickness 1cm) per 100kg of cauliflower raw materials. The said joint pickling is to put a layer of pickled auxiliary mate...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2 Processing of low nitrite content plum vegetables
[0056] 1. Pickling method
[0057] S1. Select the raw materials of preserved vegetables, clean and arrange them;
[0058] S2. Put the raw materials of plum vegetables pretreated in S1 on a shelf in the drying yard for drying. The drying time is controlled at 1.5 days to reduce the moisture content of the material by 6%.
[0059] S3. Put the sun-dried plum vegetable raw materials into a clean pickling pool with a pickling liquid circulation and spraying device, and add auxiliary materials to pickle together. The auxiliary materials are edible salt, edible lactic acid, disodium edetate and fresh radish slices. The amount of auxiliary materials added is 12kg of edible salt, 0.32kg of edible lactic acid, 0.020kg of disodium edetate (disodium EDTA) and 6.5kg of fresh radish slices (thickness 1.1cm) per 100kg of raw materials. The said pickling together is to pickle with a layer of preserved vegetables (thic...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3 Processing of low nitrite content kohlrabi
[0070] 1. Pickling method
[0071] S1. Select raw materials of kohlrabi, clean and organize;
[0072] S2. The kohlrabi raw material pretreated in S1 is placed on a shelf in the drying yard for drying. The drying time is controlled at 1.5 days, which reduces the moisture content of the material by 9%.
[0073] S3. Put the sun-dried kohlrabi raw materials into a clean pickling pool equipped with a pickling liquid circulation and spraying device, and add auxiliary materials to pickle together. The auxiliary materials are edible salt, edible lactic acid, disodium edetate and fresh radish slices. The amount of auxiliary materials added is 11kg of edible salt, 0.30kg of edible lactic acid, 0.022kg of disodium edetate (disodium EDTA) and 7kg of fresh radish slices (thickness 0.9cm) per 100kg of raw materials. The said joint pickling is to put a layer of pickled auxiliary materials on one layer of kohlrabi (thickness 7....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com