Method for degrading enteromorpha prolifera polysaccharides by enzymic method
A technology for enzymatic degradation of E. prolifera polysaccharide, applied in the field of food biology, can solve the problems of difficulty and few reports of enzymatic degradation of E. prolifera polysaccharide, and achieves mild action conditions, good in vitro antioxidant activity, and short reaction time. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-1
[0041] Embodiment 1-1, the method for enzymatic degradation of enteromorpha polysaccharide:
[0042] The crude polysaccharide of Enteromorpha enteromorpha with a purity of 75.45% is dissolved into a crude polysaccharide solution of 5 mg / mL with the acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer (the total concentration of acetic acid and sodium acetate is 0.1mol / L) with a pH of 4.5 .
[0043] 10×10 4 U / mL glucoamylase (glucoamylase) was diluted to 100 U / mL with pH 4.5 acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer (the total concentration of acetic acid and sodium acetate was 0.1 mol / L) to obtain a glucoamylase enzyme solution. Take 710 μL of glucoamylase enzyme solution and make up to 1 mL with distilled water to obtain the diluted glucoamylase enzyme solution.
[0044] Then add 1ml diluted glucoamylase enzyme solution to 4mL crude polysaccharide solution, so that the concentration of glucoamylase is 14.2U / mL, and the concentration of Enteromorpha crude polysaccharide is 4mg / mL; at this time, the pH...
Embodiment 1-2
[0050]Embodiment 1-2, enteromorpha polysaccharide is enzymatically hydrolyzed with glucoamylase:
[0051] The reaction time among the embodiment 1-1 is changed into 4 hours from 2 hours, all the other are the same as embodiment 1-1.
[0052] Enzymatically hydrolyzed Enteromorpha polysaccharides with a degradation rate of 11.6% were obtained.
[0053] Experiment 1,
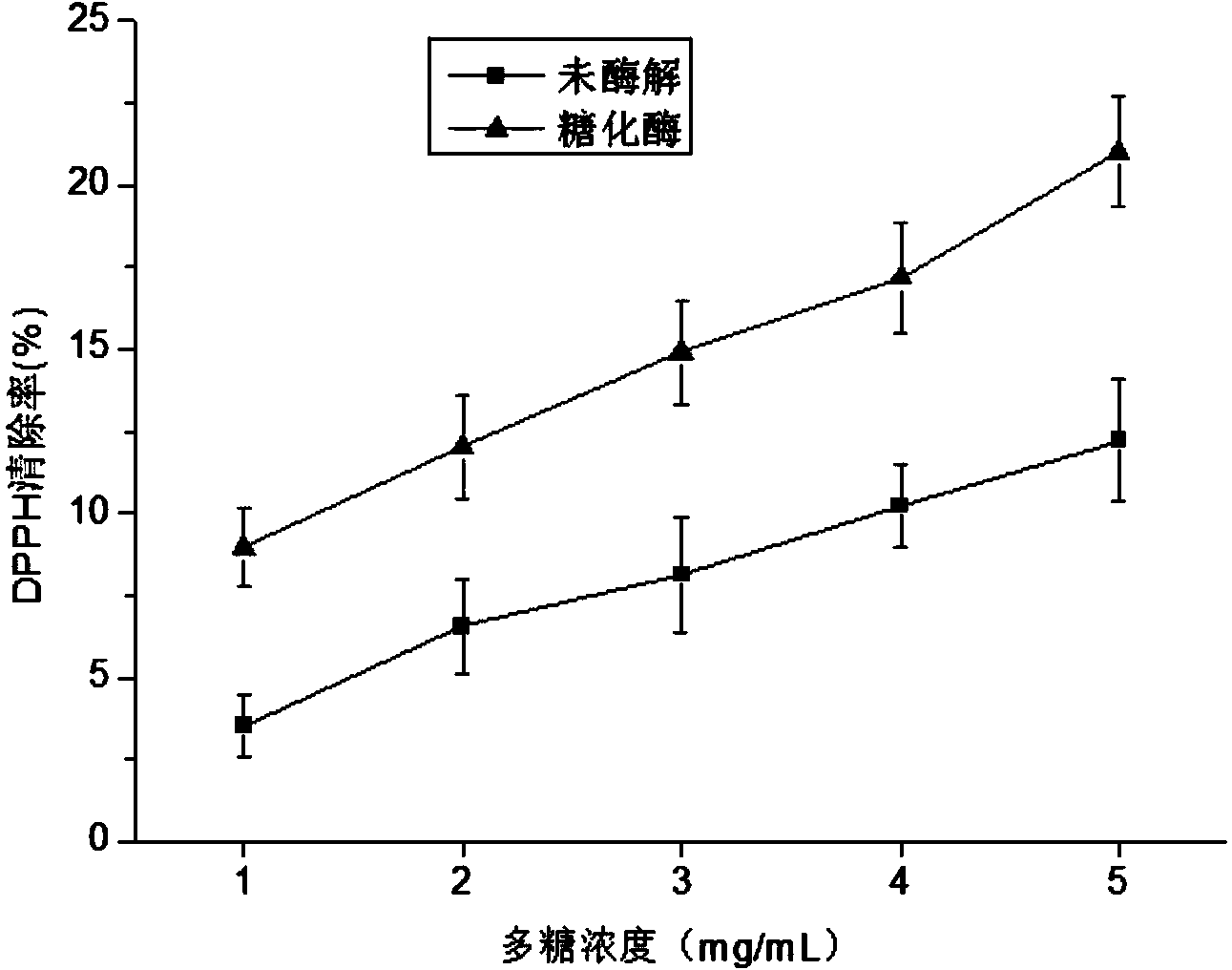
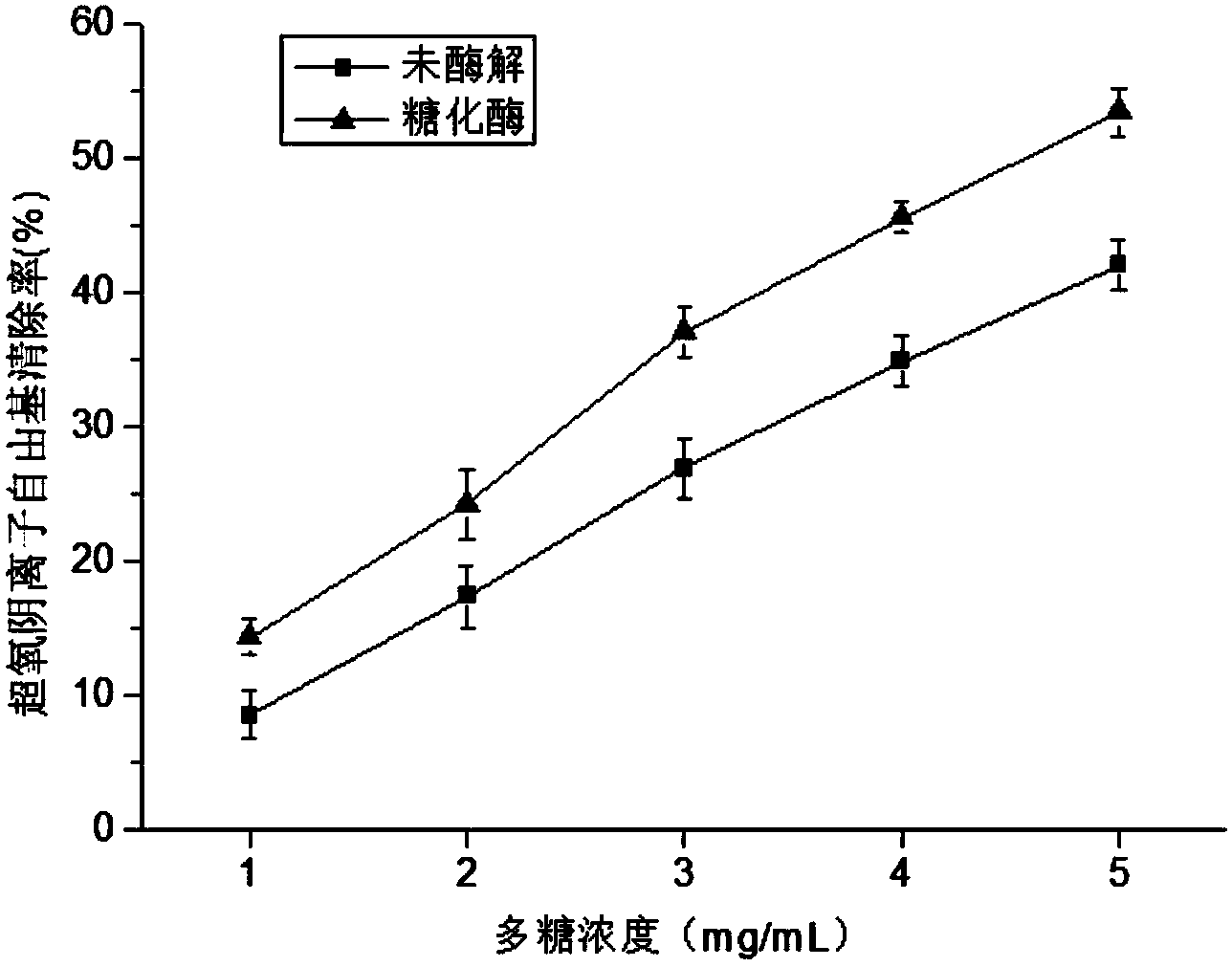
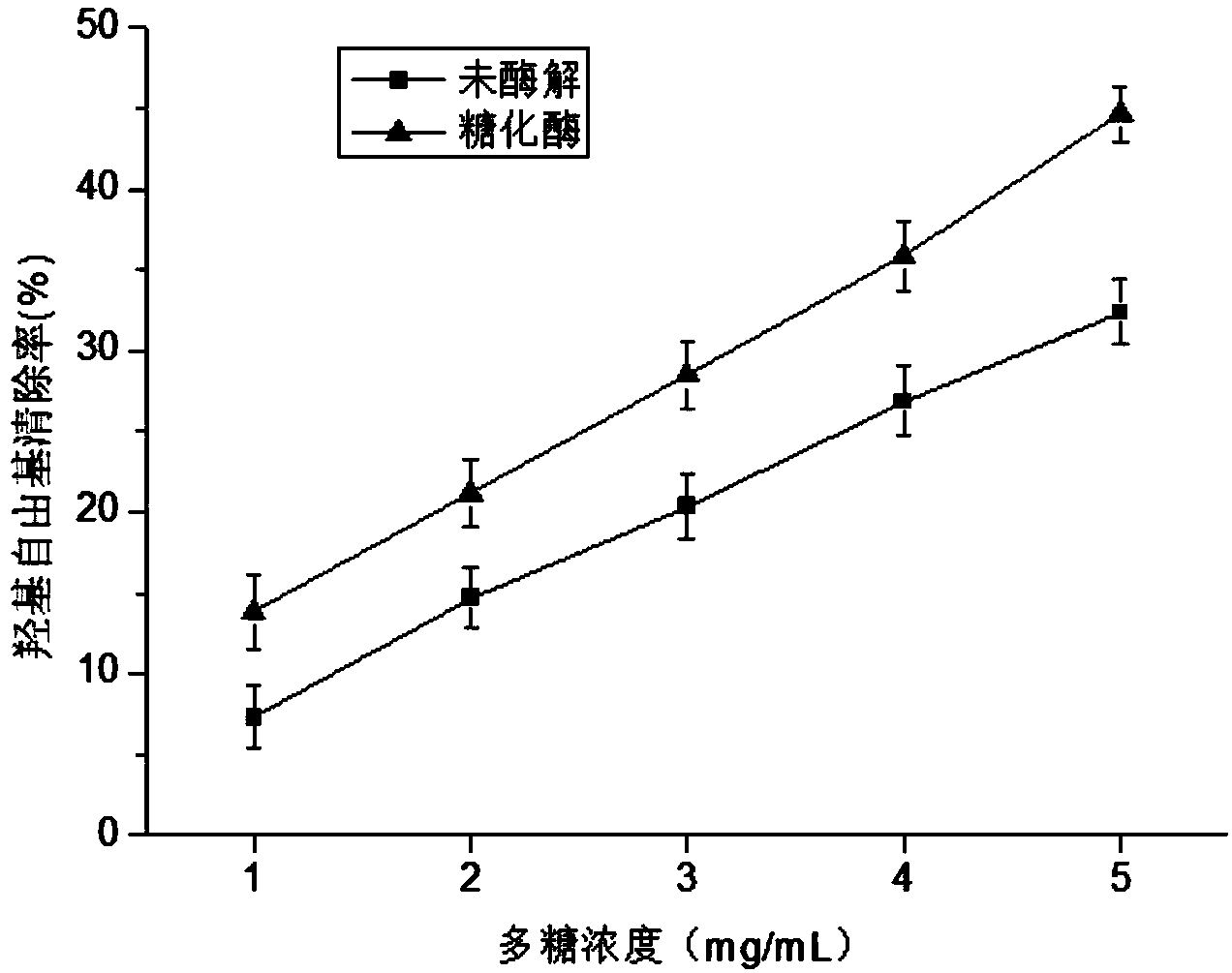
[0054] Using literature (Espin J C, Soler-Rivas C, Wichers H J, et al. Anthocyanin-based natural colorants: a new source of antiradical activity for foodstuff [J]. Journal Agricultural Food Chemistry, 2000, 48 (5): 1588-1592. ) report method, the enzymolysis Enteromorpha polysaccharide obtained in Example 1-1 is carried out the test of DPPH free radical scavenging ability, and compares with undegraded polysaccharide. Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that after the enzymatic hydrolysis of Enteromorpha polysaccharides, the scavenging ability of DPPH free radicals has been significantly improved. When the concent...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Embodiment 2, the method for enzymatic degradation of enteromorpha polysaccharide
[0068] Enteromorpha crude polysaccharides with a purity of 75.45% were dissolved in acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution (0.1 mol / L) at pH 4.5 to form a crude polysaccharide solution with a concentration of 5 mg / mL.
[0069] 10×10 4 U / mL glucoamylase (glucoamylase) was diluted to 100 U / mL with pH 4.5 acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer (0.1 mol / L) to obtain a glucoamylase enzyme solution.
[0070] Dilute 156 mg of pectinase (enzyme activity: 30 U / mg) to 100 mL with pH 4.5 acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer (0.1 mol / L); obtain pectinase enzyme solution.
[0071] Then add 1ml diluted glucoamylase enzyme solution to 4mL crude polysaccharide solution, so that the enzyme concentration is 14.2U / mL, and the concentration of Enteromorpha crude polysaccharide is 4mg / mL; at this time, the pH is 4.5, and the reaction time is 49°C 2 hours.
[0072] Boil the polysaccharide solution after enzymo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com