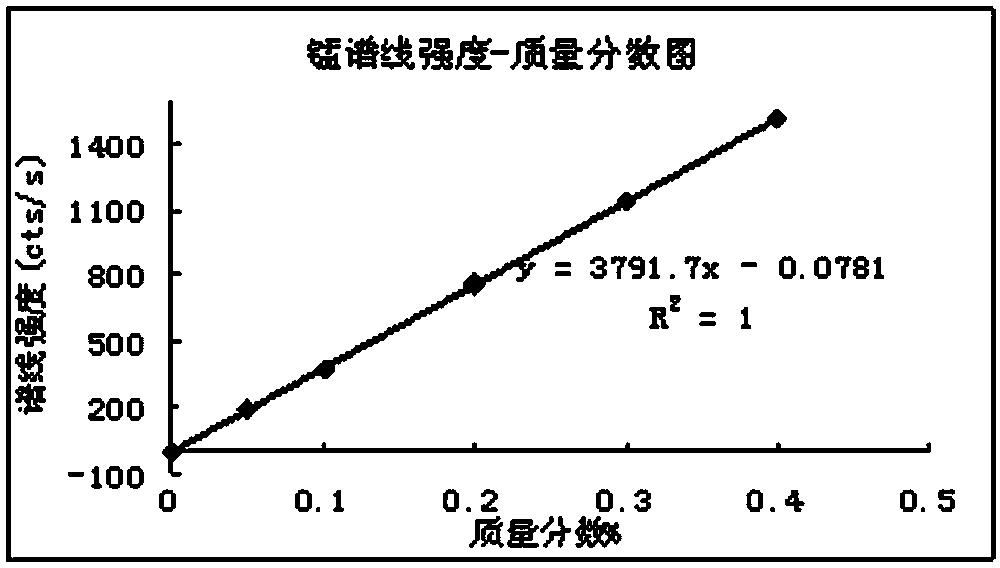
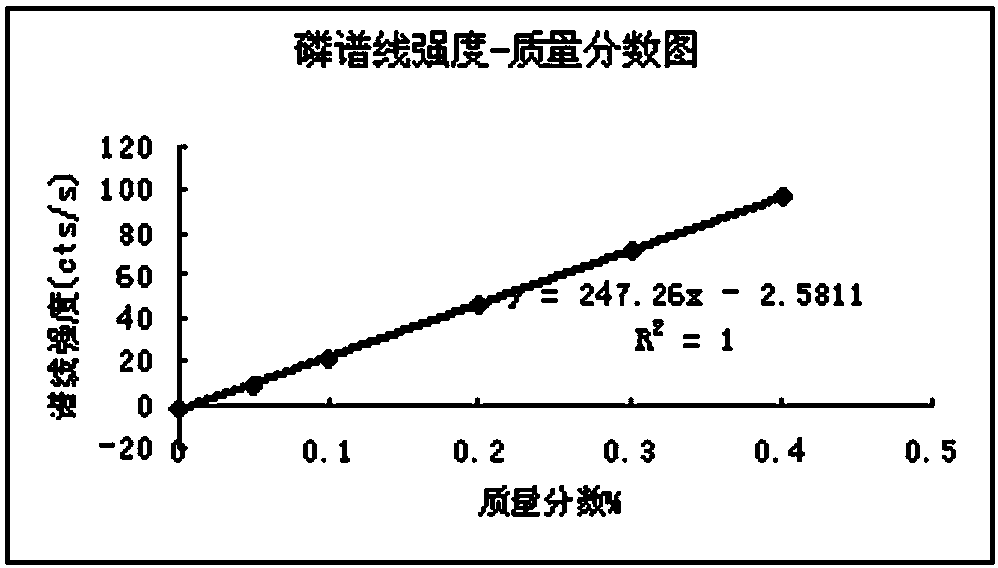
Method for determining content of six impurity elements of manganese, phosphorus, arsenic, lead, zinc and copper in permanent magnetic ferrite mixed materials
A technology for permanent magnet ferrite and impurity elements, which is applied in the field of chemical testing, can solve the problems of chemical reagents harming operators, troublesome permanent magnet composition measurement, complicated analysis steps, etc., and achieves shortened analysis period, reliable method and low analysis cost. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Add 10mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid to the test sample of the permanent magnet ferrite mixture and heat to dissolve at 70°C for about 10min; Dilute to 100 mL with distilled water and shake well.
[0057] Weigh 0.1000g of cleaned and dried electrolytic manganese (above 99.9%), put it in a 250mL beaker, add 20mL of 17.5% nitric acid to dissolve, boil to drive out nitrogen oxides, take it out and cool it to 20°C, and transfer it into a 1000mL beaker In the bottle, dilute to the mark with water, mix well, coded as a, 1mL of this solution contains 100μg manganese. Weigh 0.4393g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, which has been baked at 100°C to a constant weight and stored in a desiccator, dissolve it in an appropriate amount of water, transfer it into a 1000mL volumetric flask, dilute to the mark with water, and mix well. The code is b. 1mL of this solution contains 100μg phosphorus. Weigh 0.1320g of standard diarsenic trioxide into a 100mL beaker, slowly add about...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Add 10mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid to the permanent magnet ferrite mixture to be tested, and heat to dissolve at 80°C for about 15 minutes; add 5mL of concentrated nitric acid to the obtained sample, continue adding to dissolve completely, and cool to 25°C; Dilute the solution to 100 mL with distilled water and shake well.
[0067] Weigh 0.1000g of cleaned and dried electrolytic manganese (above 99.9%), put it in a 250mL beaker, add 20mL of 17.5% nitric acid to dissolve, boil to drive out nitrogen oxides, take it out and cool it to 25°C, and transfer it into a 1000mL beaker In the bottle, dilute to the mark with water, mix well, coded as a, 1mL of this solution contains 100μg manganese. Weigh 0.4393g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate which has been baked at 105°C to a constant weight and stored in a desiccator, dissolve it in an appropriate amount of water, transfer it into a 1000mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to the mark, mix well, and the code is b. 1m...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Add 10mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid to the permanent magnet ferrite mixture to be tested, and heat to dissolve at 90°C for about 20 minutes; add 5mL of concentrated nitric acid to the obtained sample, continue adding to dissolve completely, and cool to 30°C; Dilute the solution to 100 mL with distilled water and shake well.
[0072] Weigh 0.1000g of cleaned and dried electrolytic manganese (above 99.9%), put it in a 250mL beaker, add 20mL of 17.5% nitric acid to dissolve, boil to drive out nitrogen oxides, take it out and cool it to 30°C, and transfer it into a 1000mL beaker In the bottle, dilute to the mark with water, mix well, coded as a, 1mL of this solution contains 100μg manganese. Weigh 0.4393g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, which has been baked at 110°C to a constant weight and stored in a desiccator, dissolve it in an appropriate amount of water, transfer it to a 1000mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to the mark, and mix well. The code is b. 1mL...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com