Device based on microorganism electrolytic tank technique for on-line biochemical oxygen demand measurement
A technology of microbial electrolysis cell and biochemical oxygen demand, which is applied in measuring devices, material analysis through electromagnetic means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of reducing Coulombic efficiency of anode anaerobic microorganisms, long sensor detection time, and decreased sensor sensitivity. It achieves the effects of short detection time, low detection limit concentration and improved monitoring level
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
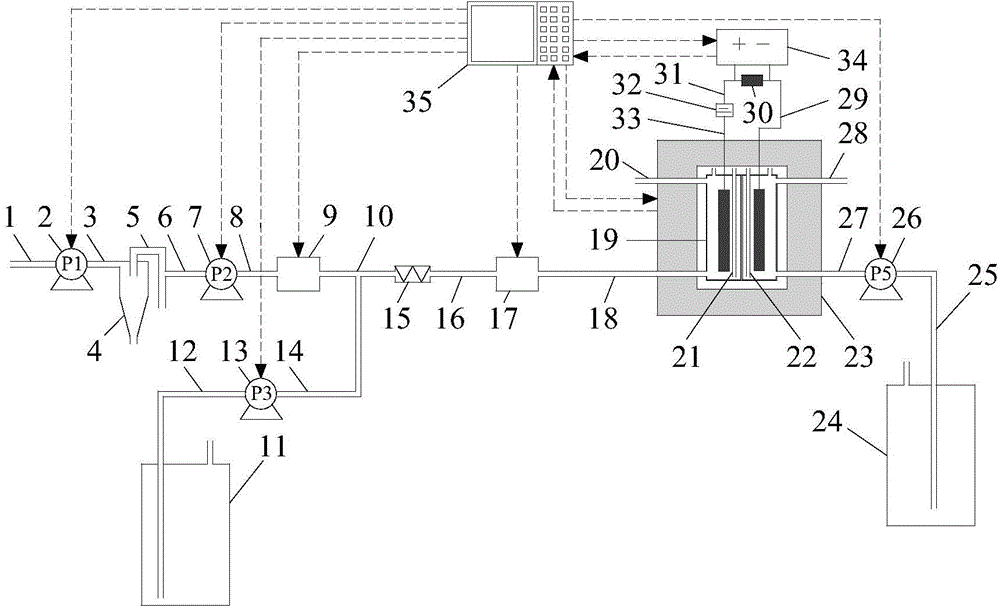
[0032] 1. The structure of the device for on-line determination of biochemical oxygen demand and the design and assembly of the microbial electrolytic cell sensor
[0033] figure 1 It is a graphic illustration of the device used for the on-line measurement of biochemical oxygen demand. The device includes: connecting pipe 1, sampling pump 2, connecting pipe 3, hydrocyclone 4, hydrocyclone overflow pipe 5, connecting pipe 6 , peristaltic pump 7, connecting pipe 8, automatic sample diluter 9, connecting pipe 10, liquid storage tank 11, connecting pipe 12, peristaltic pump 13, connecting pipe 14, static mixer 15, connecting pipe 16, online degasser 17. Connecting pipe 18, microbial electrolytic cell 19, drain pipe 20, air guide pipe 21, air guide pipe 22, thermostat box 23, liquid storage tank 24, connecting pipe 25, peristaltic pump 26, connecting pipe 27, liquid drain pipe 28, Titanium wire 29 , resistor 30 , wire 31 , potentiostat 32 , titanium wire 33 , data acquisition sys...
Embodiment 2
[0045] 1. The structure of the device for on-line determination of biochemical oxygen demand and the design and assembly of the microbial electrolytic cell sensor
[0046] The device of embodiment 2 is the same as embodiment 1.
[0047] 2. Enrichment of oligotrophic electroactive microorganisms on the surface of the anode electrode of the microbial electrolysis cell
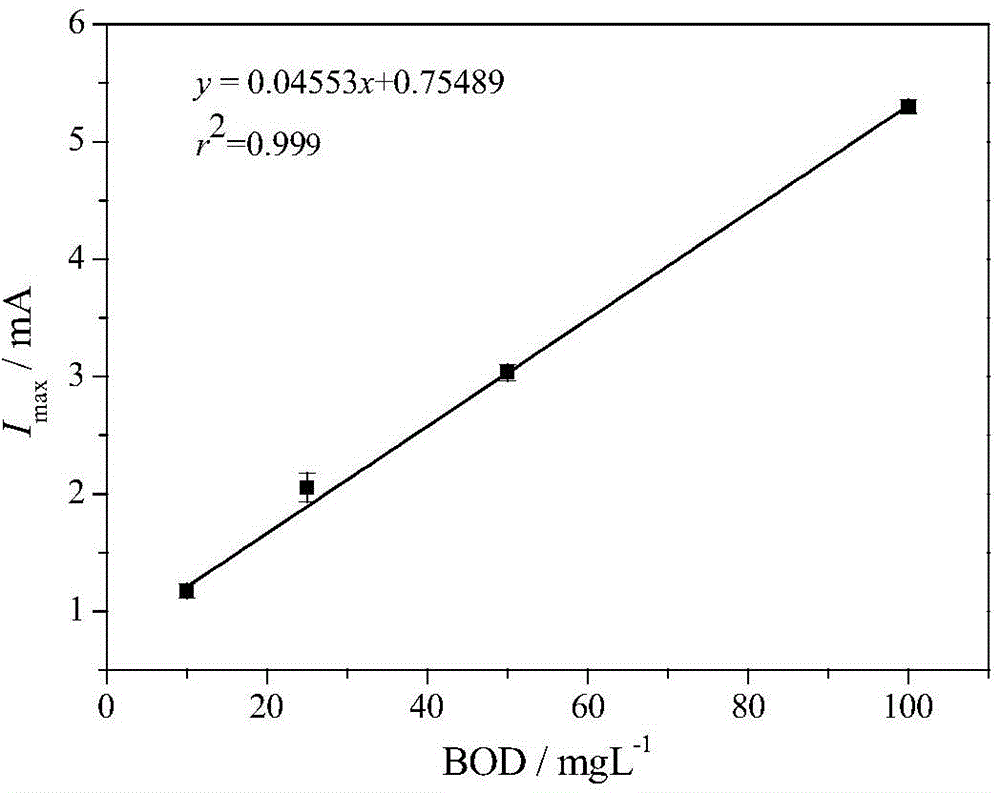
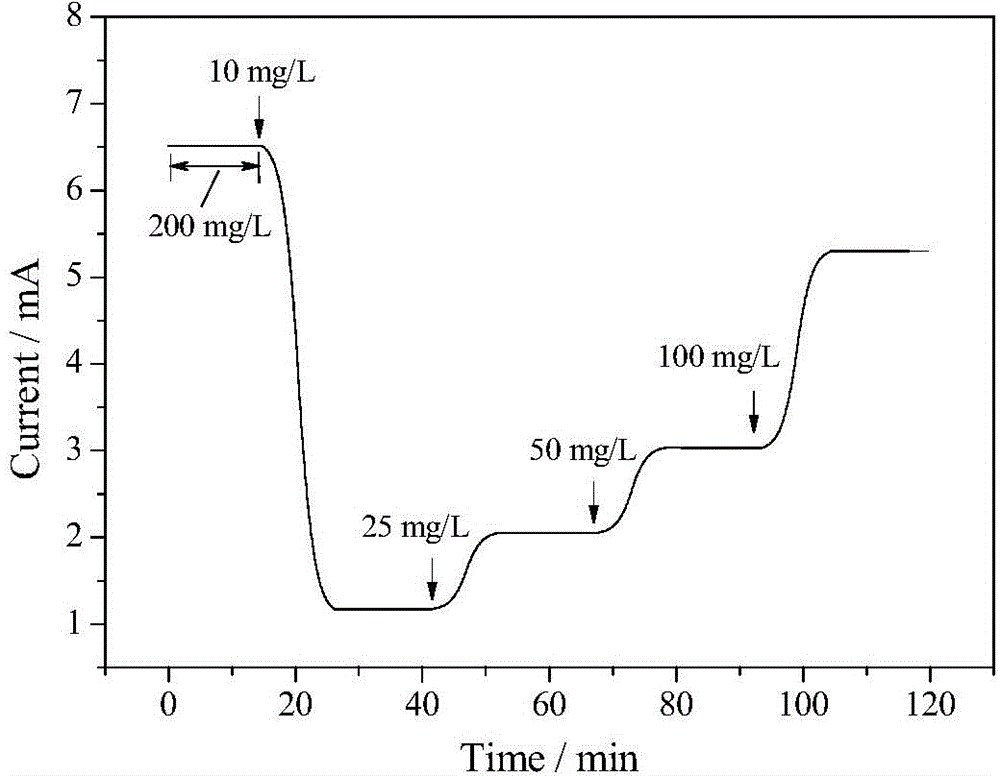
[0048] Glucose-glutamic acid simulated artificial wastewater medium (BOD=5.0 mg / L, pH=7.0) was prepared as in Example 1, and then sodium azide was added to the prepared simulated artificial wastewater medium to 1 mmol / L ( final sodium azide solution concentration).
[0049] The anode chamber of the microbial electrolysis cell 19 is inoculated with the river bottom sediment as the inoculum and the glucose-glutamic acid simulated artificial wastewater as the nutrient solution to enrich the electricity-producing microorganisms. Simulated artificial waste water passes through connecting pipe 1, sampling pump 2, con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com