In situ detection of abundance and diversity of marine bacteria based on laser-induced fluorescence
A laser-induced fluorescence, marine bacteria technology, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of harsh conditions, long analysis duration, complicated analysis process, etc., achieve long-term reliable work, wide application range, fast analysis easy effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
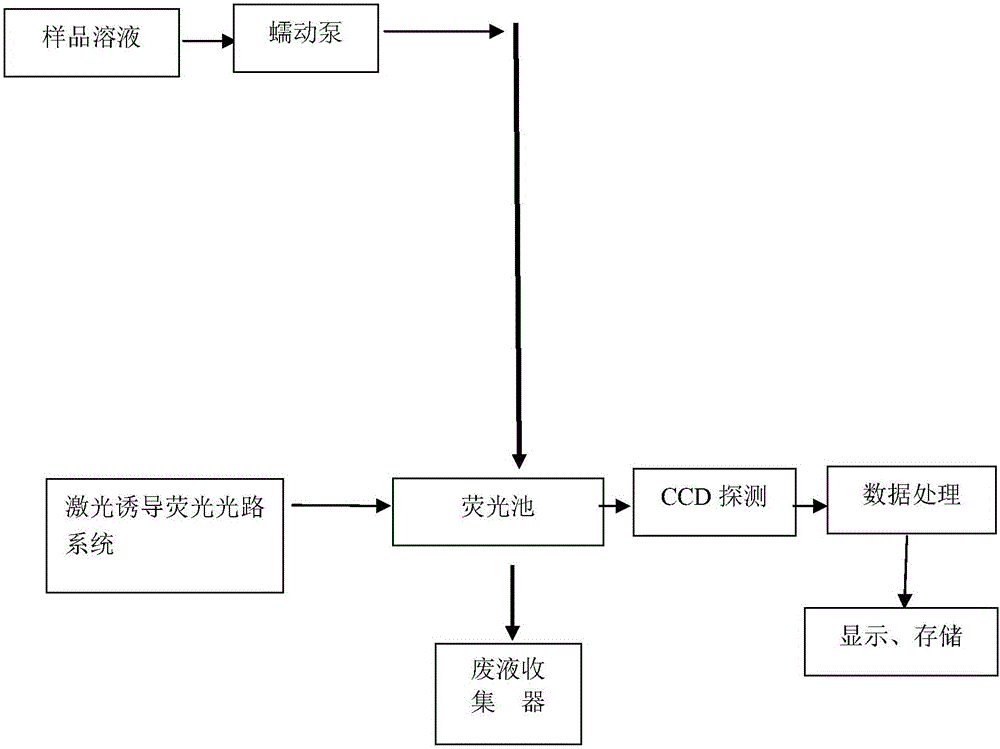
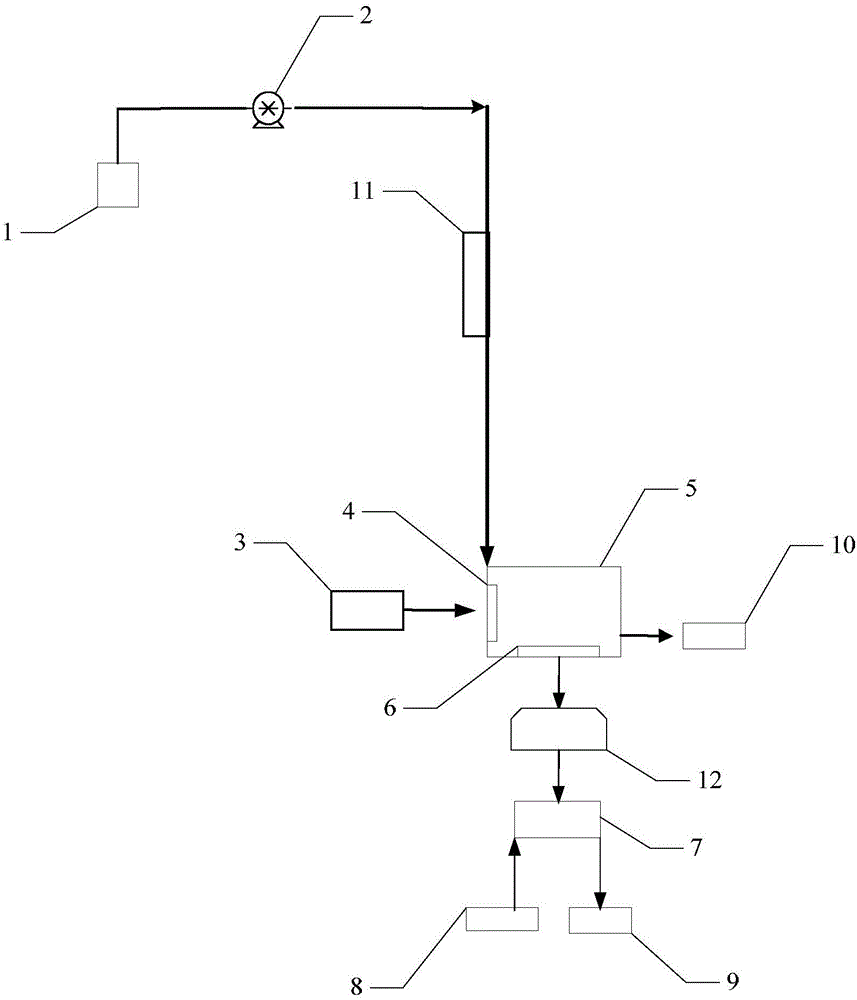
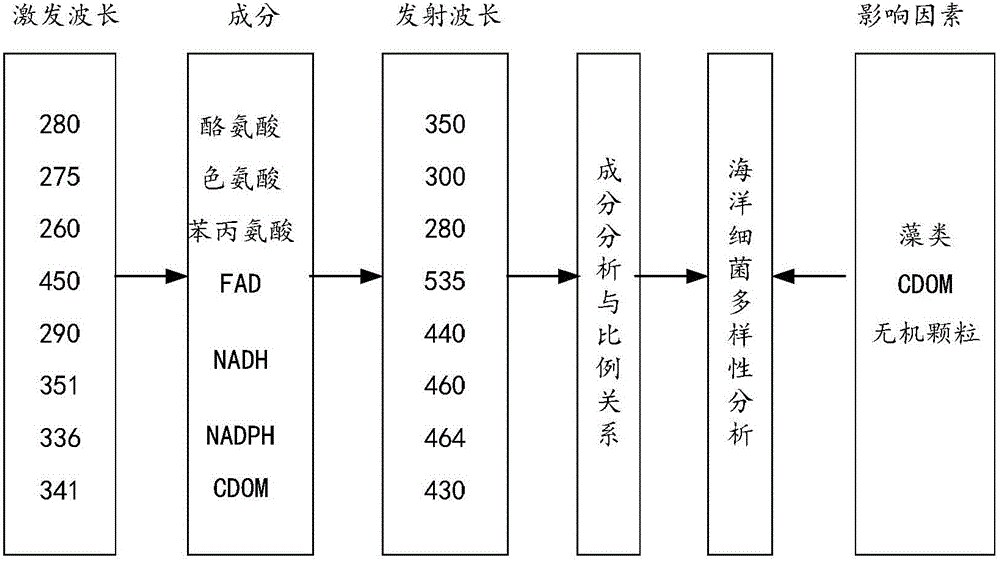
[0036] see figure 1 , figure 2 ,
[0037] Method steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0038] (1) Transport the tested water sample solution through the pump 2;
[0039] (2) The water sample solution flows through the filter column 11 under the action of the pump 2, and the inside of the filter column 11 is filled with magnesium oxide-loaded cobalt-iron metal magnetic nanomaterials, and has a temperature control device. , so the phytoplankton with large particle size can be filtered out through the filter column.
[0040] (3) The water sample flowing through the filter column enters the fluorescent pool 5, and the window material of the fluorescent pool adopts nano-diamond 4 material near the side of the excitation light source to mainly eliminate Raman scattering of the water body, and the window material near the detection window side adopts a The silicon glass 6 of the graphene thin film material mainly eliminates the fluorescence scattering of the water bod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com