Method for preparing mimic enzyme molecularly imprinted polymer microsphere for hydrolyzing organophosphorus
A technology of molecular imprinting and imitating enzymes, which is applied in the fields of alkali metal compounds, chemical instruments and methods, and inorganic chemistry. It can solve the problems of too deep embedding of template molecules, difficulty in removing template molecules, and low activity of imitating enzymes, and achieve low cost. , large surface area, large adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
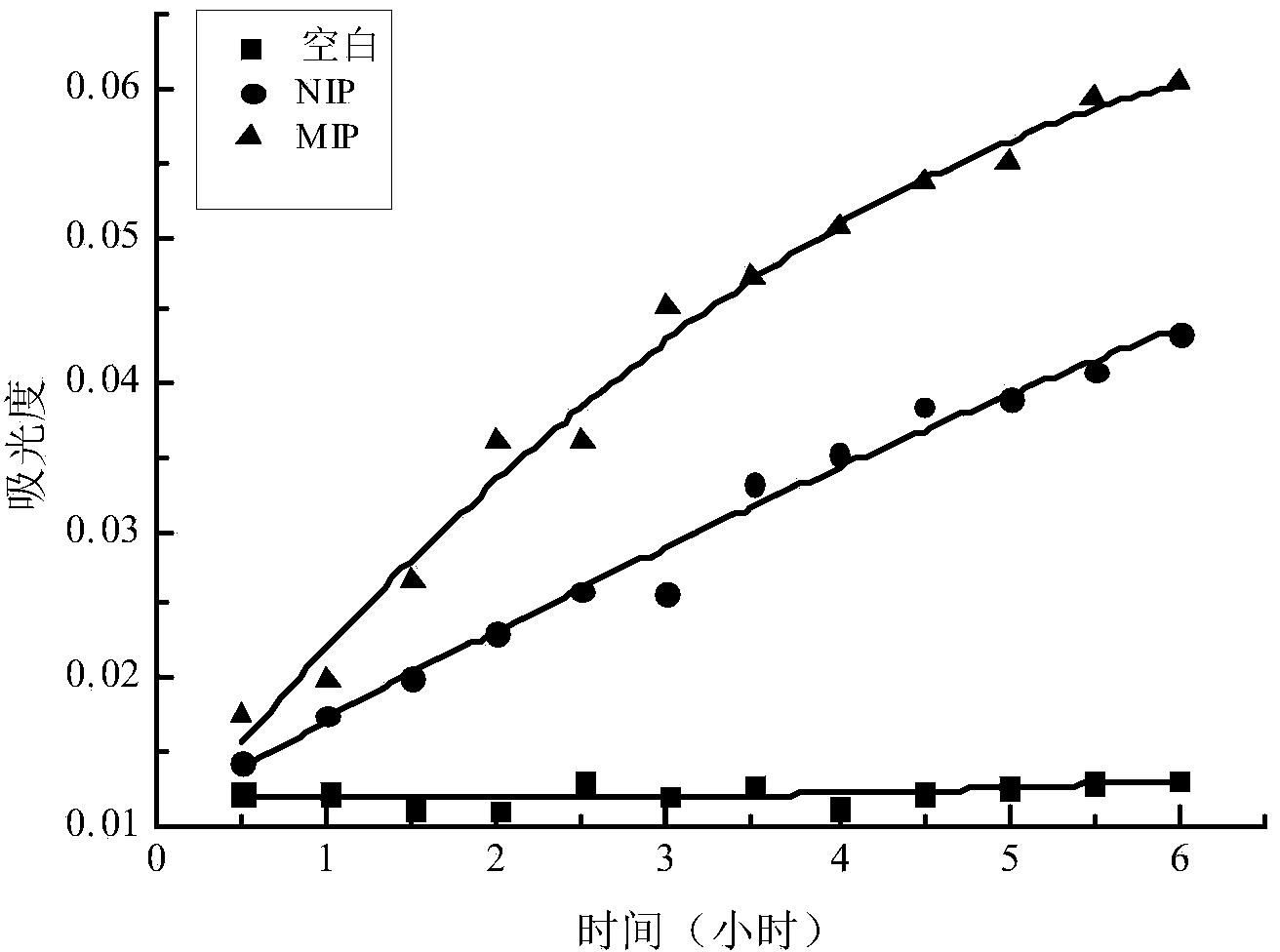
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] 0.1530g (1.125mmol) ZnCl 2 , 96 μL (1.125 mmol) methacrylic acid, 408 μL (4.5 mmol) 1-vinylimidazole and 99 μL (0.45 mmol) (4-nitrobenzyl) diethyl phosphate were dissolved in 80 mL of acetonitrile and methanol with a volume ratio of 9: 1, add 2.4mL (16.8mmol) divinylbenzene and 0.2624g (1.6mmol) 2,2'-azobisisobutyronitrile, and then use a wavelength of 365nm under nitrogen protection and room temperature Ultraviolet light irradiation for 12 hours, then centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 minutes with a centrifuge, and the resulting solid was shaken and washed with 100 mmol / L bipyridyl methanol solution for 7 hours to remove (4-nitrobenzyl) diethyl phosphate ester, and then washed 3 times with methanol, each time for 30 minutes, and then washed with 100mmol / L ZnCl 2 The methanol solution was incubated for 4 hours, centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 minutes, the supernatant was discarded, and vacuum-dried at 45°C to obtain molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres of organophosp...
Embodiment 2
[0025] 0.1224g (0.9mmol) ZnCl 2 , 77 μL (0.9 mmol) of methacrylic acid, 326 μL (3.6 mmol) of 1-vinylimidazole and 99 μL (0.45 mmol) of (4-nitrobenzyl) diethyl phosphate were dissolved in 50 mL of acetonitrile and methanol at a volume ratio of 9: 1, add 1.9mL (13.5mmol) divinylbenzene and 0.2214g (1.35mmol) 2,2'-azobisisobutyronitrile, and then under nitrogen protection and room temperature, use a wavelength of 365nm Ultraviolet light irradiation for 12 hours, then centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 minutes with a centrifuge, and the resulting solid was shaken and washed with 100 mmol / L bipyridyl methanol solution for 7 hours to remove (4-nitrobenzyl) diethyl phosphate ester, and then washed 3 times with methanol, each time for 30 minutes, and then washed with 100mmol / L ZnCl 2 The methanol solution was incubated for 4 hours, centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 minutes, the supernatant was discarded, and vacuum-dried at 45°C to obtain molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres of organo...
Embodiment 3
[0027] 0.1836g (1.35mmol) ZnCl 2 , 115 μL (1.35 mmol) of methacrylic acid, 612 μL (6.75 mmol) of 1-vinylimidazole and 99 μL (0.45 mmol) of (4-nitrobenzyl) diethyl phosphate were dissolved in 100 mL of acetonitrile and methanol at a volume ratio of 9: 1, add 3.2mL (22.5mmol) of divinylbenzene and 0.3690g (2.25mmol) of 2,2'-azobisisobutyronitrile, and then use a wavelength of 365nm under nitrogen protection and room temperature Ultraviolet light irradiation for 24 hours, then centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 minutes with a centrifuge, and the resulting solid was shaken and washed with 100 mmol / L bipyridyl methanol solution for 7 hours to remove (4-nitrobenzyl) diethyl phosphate ester, and then washed 3 times with methanol, each time for 30 minutes, and then washed with 100mmol / L ZnCl 2The methanol solution was incubated for 4 hours, centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 minutes, the supernatant was discarded, and vacuum-dried at 45°C to obtain molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com