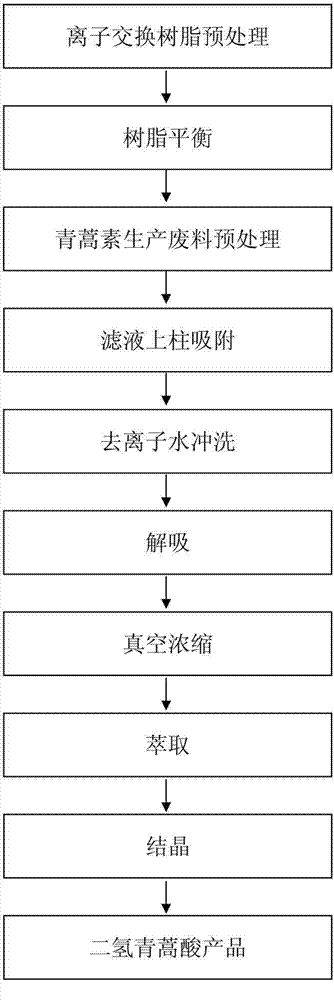
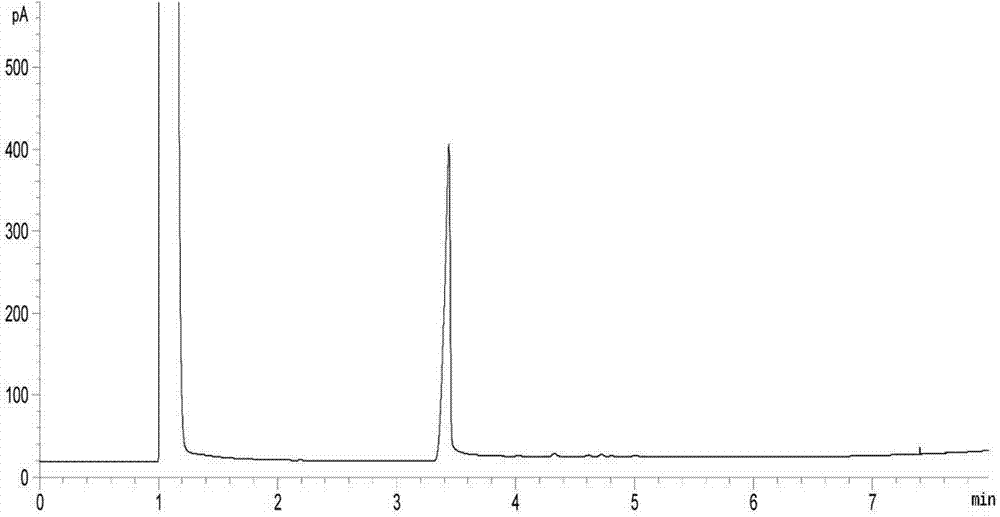
Method for separating refined dihydroartemisinic acid from artemisinin production waste through ion-exchange resin method
A technology of ion exchange resin and dihydroartemisinic acid, applied in the separation/purification of carboxylic acid compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of resource waste, achieve high recovery rate, reduce concentration time and energy consumption, and facilitate operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Take 100g of completely dried artemisinin production waste, add 450mL of 0.3% (W / V) sodium hydroxide solution, crush the artemisinin production waste, adjust the pH value to 8.0, soak at 50°C for 30min, and centrifuge at 2500rpm at room temperature 15min, take the supernatant. Open the lower end plug of the chromatography column and load it on the column at a speed of 1.5BV / h (the initial processing capacity of 717 anion exchange resin is 100mL). After loading the column, close the lower end plug of the chromatography column and statically adsorb to saturation. After the adsorption is complete, open the plunger at the lower end of the chromatographic column and rinse with 500 mL of deionized water at a rate of 6 BV / h. Take 10% (W / V) ammonium chloride solution and 60% (V / V) edible alcohol mixed in a 1:1 volume ratio, add the mixed solution to the chromatographic column, and elute at a speed of 3BV / h, collect the eluted A total of 350mL was removed. At 40°C, concentrate...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Take 725g of completely dried artemisinin production waste, add 2200mL of 0.3% (W / V) sodium hydroxide solution, crush the artemisinin production waste, adjust the pH value to 9.0, soak at 60°C for 20min, and centrifuge at 3000rpm at room temperature 15min, take the supernatant. Open the lower end piston of the chromatography column and load it on the column at a speed of 1BV / h (the initial processing capacity of 717 anion exchange resin is 500mL). After the adsorption is completed, open the plunger at the lower end of the chromatographic column, and rinse with 3000 mL of deionized water at a rate of 4 BV / h. Get the mixed solution of 6% (W / V) ammonium chloride solution and 85% (V / V) edible alcohol mixed by 1:1 volume ratio, add the chromatographic column, carry out elution with the speed of 2BV / h, collect and wash A total of 1500mL was removed. At 35°C, the eluate was concentrated in vacuo to 1 / 3 volume, then extracted twice with 500mL of dichloromethane, the extracts ...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Take 1.2kg of completely dry artemisinin production waste, add 4.8L of 0.3% (W / V) sodium hydroxide solution, crush the artemisinin production waste, adjust the pH value to 8.5, soak at 55°C for 26min, and Centrifuge at 2800rpm for 15min, and take the supernatant. Open the lower plug of the chromatography column, and load the column at a rate of 1.2BV / h (the initial processing capacity of 717 anion exchange resin is 1000mL). After loading the column, close the lower plug of the chromatography column, and statically adsorb to saturation. After the adsorption is completed, open the lower end piston of the chromatography column and wash with 5.5L deionized water at a washing speed of 5BV / h. Take 8% (W / V) ammonium chloride solution and 70% (V / V) edible alcohol mixed in a 1:1 volume ratio, add the mixed solution to the chromatography column, and elute at a speed of 2.5BV / h, collect A total of 3.3L of eluate. At 38°C, the eluate was concentrated in vacuo to 1 / 3 volume, then ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com