Preparation of hierarchically porous molecular sieve supported metal catalyst and application thereof in grease hydrodeoxygenation
A metal-loaded, catalytic hydrogenation technology, applied in the direction of molecular sieve catalysts, preparation of liquid hydrocarbon mixtures, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of high cetane number, low freezing point, poor stability, etc., and achieve high reactivity , large pore volume, strong anti-carbon effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1 Alkali Treatment of Molecular Sieves to Prepare Hierarchical HBEA Molecular Sieves
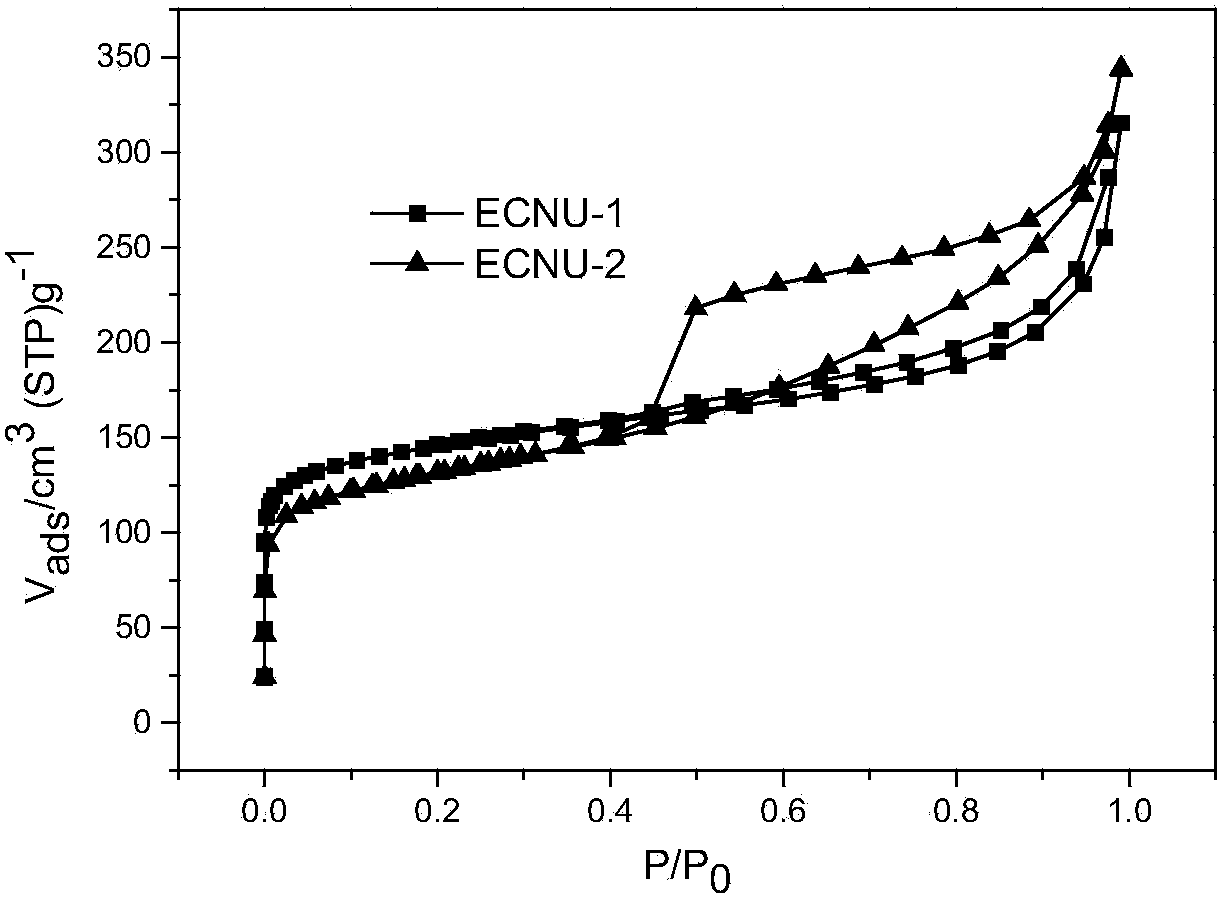
[0045] Add 4g HBEA molecular sieve and 150mL mixed alkali of sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate (molar ratio is 3 / 7) with a total concentration of 0.3mol / L into a 250ml flask, stir magnetically in an oil bath at 90°C for 2h, and cool to room temperature , the mixture was filtered, washed to neutral, and calcined after two ammonia exchanges to prepare a hierarchical porous molecular sieve. The specific surface and pore volume data of untreated HBEA molecular sieve (ECNU-1) and alkali treated (ECNU-2) are shown in Table 1, Adsorption isotherms, as figure 1 shown. From Table 1 and figure 1 The data showed that the treated carrier had a higher outer surface (from 48 to 238m 2 g -1 ) and larger mesopore volume (from 0.18 to 0.56cm 3 g -1 ).
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 Alkali Treatment of Molecular Sieves to Prepare Hierarchical Porous HZSM-5 Molecular Sieves
[0047] 4g HZSM-5 molecular sieve and 150mL total concentration of 0.5mol / L tetramethylammonium hydroxide and sodium carbonate (molar ratio is 1 / 3) mixed alkali are added in a 250mL flask, and magnetically stirred in an oil bath at 80°C for 1.5 h. After cooling down to room temperature, the mixture is filtered and washed until neutral, and after two ammonia exchanges, it is then calcined to prepare a hierarchical porous molecular sieve. The specific surface and pore volume data of HZSM-5 molecular sieve without mixed alkali treatment (ECNU-3) and mixed alkali treatment (ECNU-4) are shown in Table 1. Table 1 shows that the treated supports have higher external surface area and larger mesopore volume.
[0048] Table 1: Physicochemical properties of molecular sieves
[0049]
[0050]
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3 Preparation of Hierarchical Porous HBEA Supported Cobalt-Based Catalyst
[0052] 3g HBEA molecular sieves were dissolved in 30mL (2mol / L) sodium hydroxide solution and stirred at room temperature for 20 minutes. 10 g (16 wt%) of cetyltetramethylammonium bromide was added to the above mixture, stirred at room temperature for 20 minutes, and the above mixture was placed in a self-pressurized reactor for crystallization at 120° C. for 48 hours. After cooling down to room temperature, the pH of the mixture solution was adjusted to 10 with a certain concentration of hydrochloric acid solution, and the adjusted pH mixture was put into a self-pressurized reactor. Crystallize at 120°C for 48h, and finally the mixture is washed, filtered, dried and calcined. 0.98 g (0.0034 mol) of cobalt nitrate hexahydrate and 1 g of hierarchically porous HBEA molecular sieve were impregnated with magnetic stirring at room temperature, and after the solution was volatilized, it was c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dispersity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com