Ultrasonic extraction method of heavy metal elements in vegetables
An extraction method and heavy metal technology, which is applied in the field of ultrasonic extraction of chromium, lead, cadmium, nickel, and zinc five heavy metal elements in vegetables, can solve the problem of less application of heavy metal extraction, and reduce the emission of toxic, harmful and corrosive gases , The reaction is mild and safe, and the effect of less reagent consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] (1) Take GBW10015 spinach, rinse it with running water first, then wash it with distilled water and deionized water, air-dry it, weigh it, and dry it in an oven at 60°C for 72 hours. The dried sample is homogenized with an agate mortar and passed through 200 mesh (74μm) Sieve and store in a polyethylene bottle in a desiccator at room temperature for later use.
[0038] (2) Wet digestion method: Weigh 1.0g of the sample into a tall beaker, put a few glass beads, add 10mL of 65% HNO 3 -70% HClO 4 (9:1, V / V) cover and soak overnight, heat and digest on the electric heating plate, if it turns brown-black, add mixed acid until white smoke, until the digestive juice is colorless, transparent or slightly yellow, and the excess The acid was evaporated to nearly dryness, cooled, and the digestive juice was washed into a 25mL volumetric flask with a dropper, and the tall beaker was washed several times with a small amount of water. Blank test.
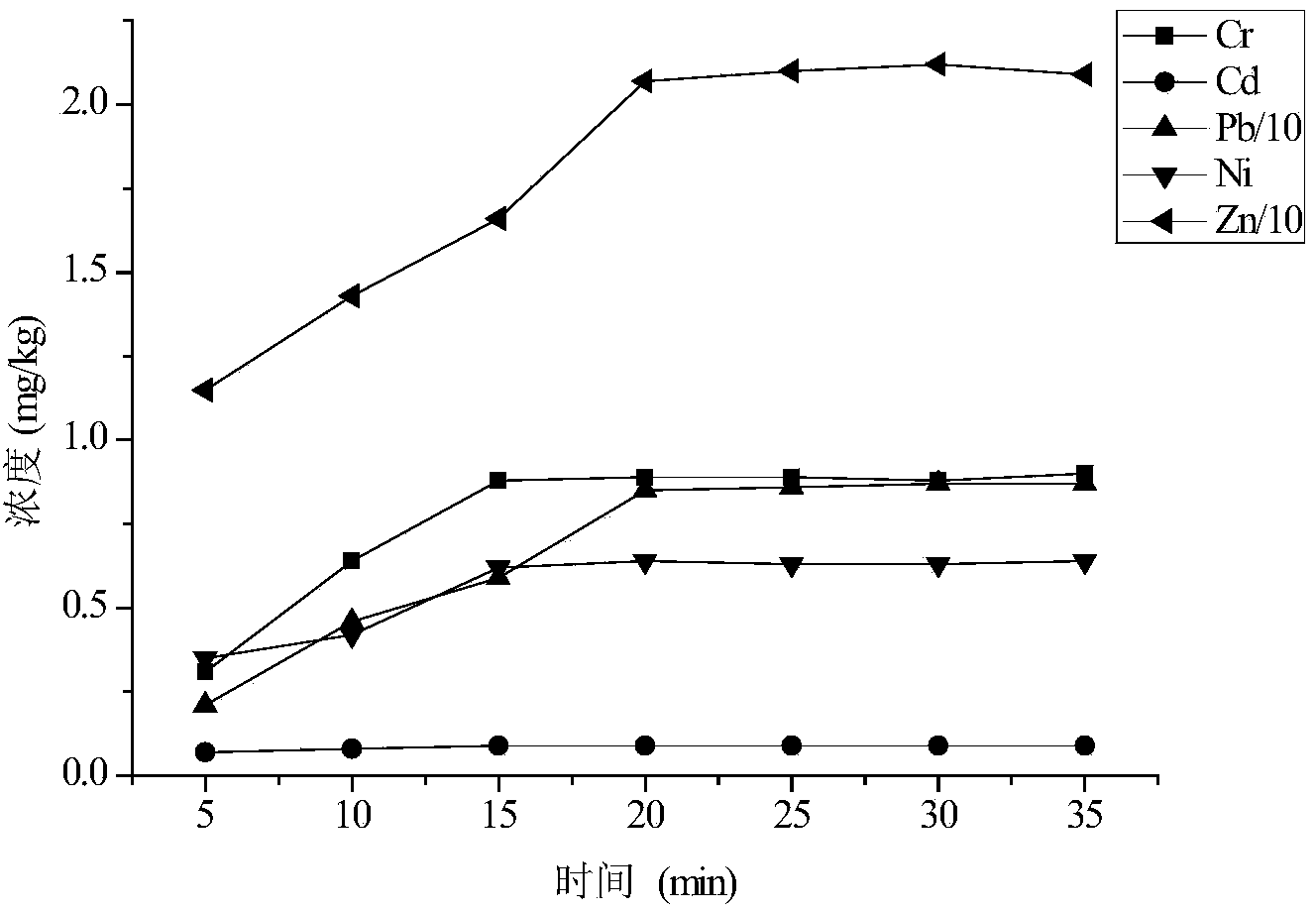
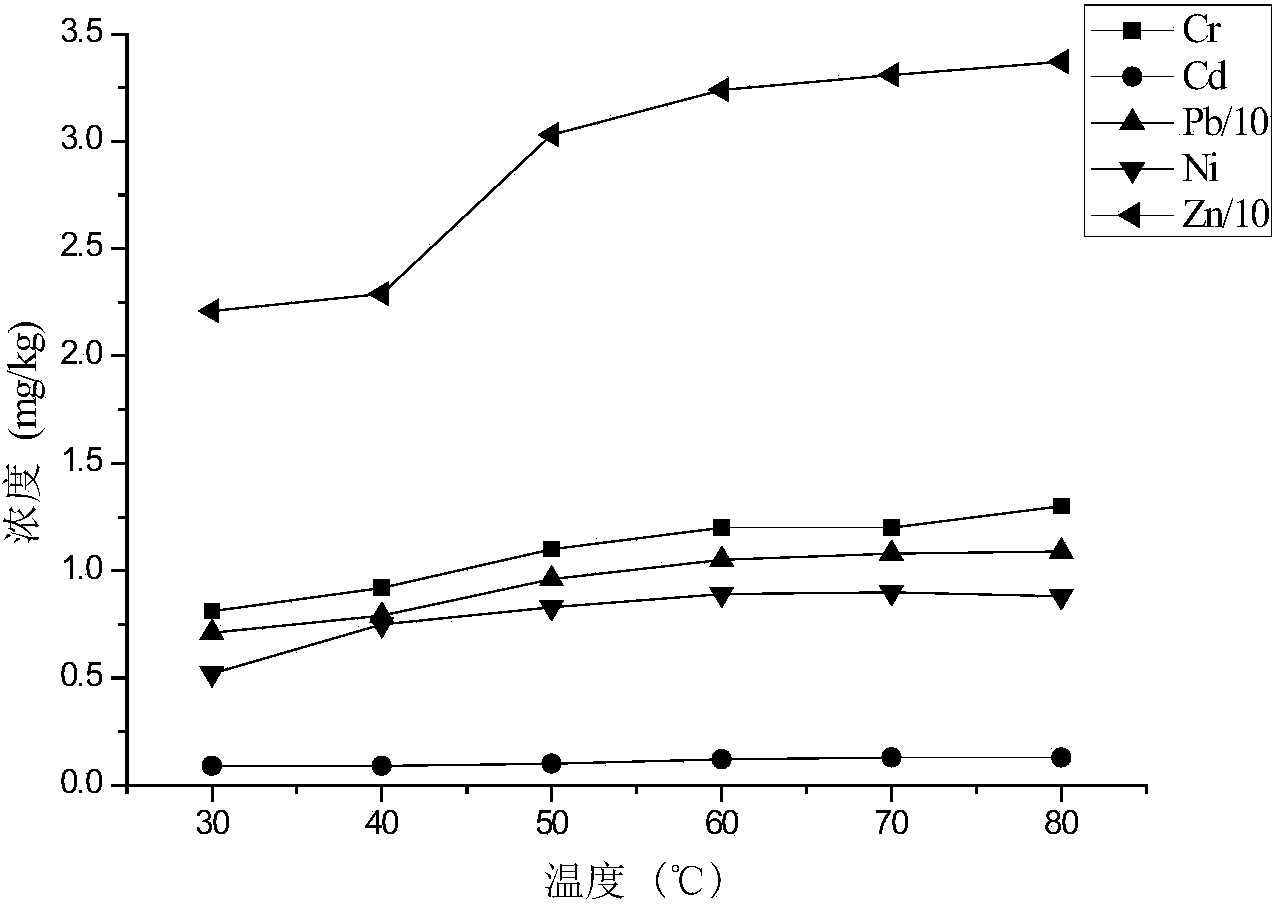
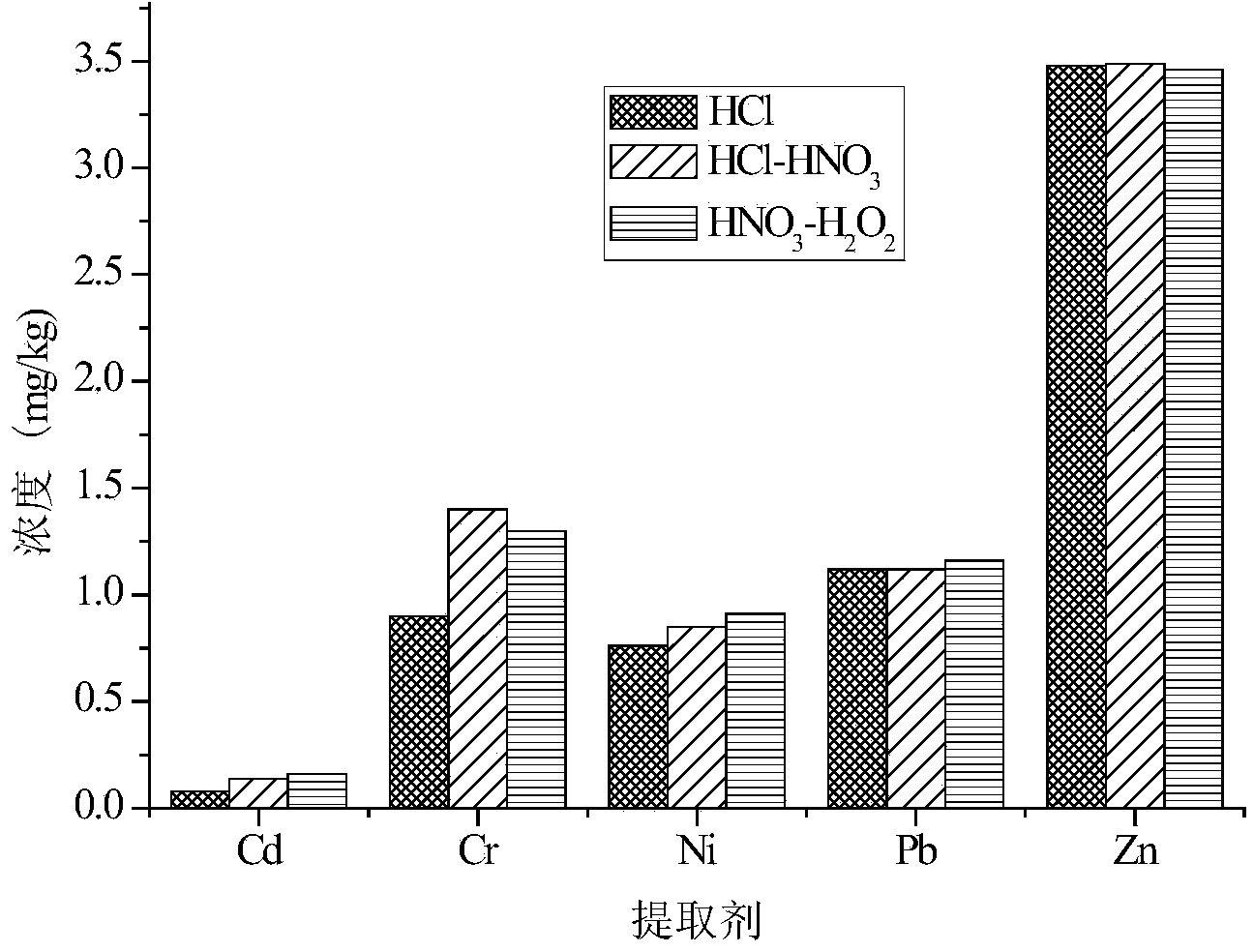
[0039] (3) Ultrasonic extractio...
Embodiment 2
[0042] (1) Take spinach, rinse it with running water first, then wash it with distilled water and deionized water, air-dry it, weigh it, and dry it in an oven at 70°C for 48 hours. The dried sample is homogenized with an agate mortar and passed through a 150-mesh (104 μm) sieve , stored in a polyethylene bottle in a desiccator at room temperature for later use.
[0043] (2) Dry ashing: Weigh 1.0g of the sample into a porcelain crucible, add 1mL of phosphoric acid (1+10), soak for more than 1h, place the crucible on a heating plate, carbonize on low heat until smokeless, and then transfer it into a muffle furnace In medium temperature, ash at 500±25°C for about 8 hours, until the sample is grayish white, take it out and let it cool, then add a small amount of hydrochloric acid (1+11), heat on low heat, do not make it dry, add a little mixed acid if necessary, and repeat the treatment like this , until there is no carbon particle in the residue, add 10mL hydrochloric acid (1+11)...
Embodiment 3
[0047] (1) Take samples of celery, cabbage, leek and garlic sprouts, rinse them with running water first, then wash them with distilled water and deionized water, air-dry them, weigh them, and dry them in an oven at 65°C for 60 hours. The dried samples are homogenized with an agate mortar. Pass through a 170-mesh (88 μm) sieve, and store in a polyethylene bottle in a desiccator at room temperature for later use.
[0048] (2) Microwave digestion method: Weigh 0.5g of the sample into a polytetrafluoroethylene digestion tank, add 5mL of 65% nitric acid and 1mL of 30% hydrogen peroxide, place it in a microwave digestion device, and digest according to the program: 0.2MPa, 2min; 0.5 MPa, 2min; 1.0MPa, 2min; 1.5MPa, 5min; 2.0MPa, 5min; cooling for 10min. After the digestion is completed, cool to room temperature, heat on an electric heating plate until nearly dry, and dilute the solution in a 50-100mL volumetric flask after cooling. At the same time as a blank test.
[0049] (3) U...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com