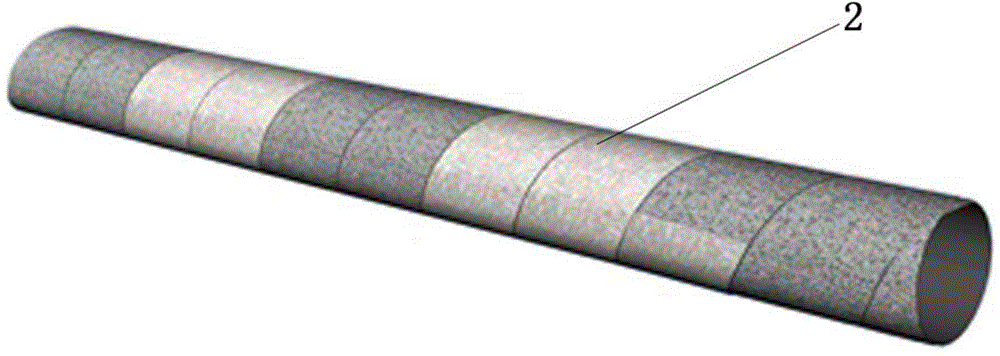
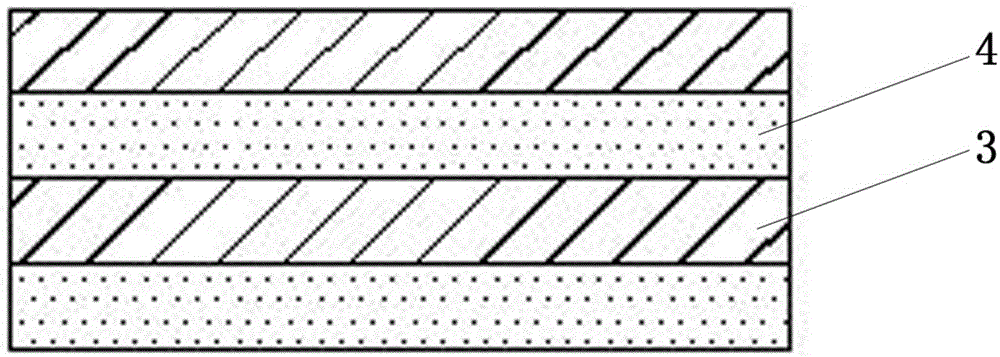
Biodegradable composite type tubular urethral stent and preparation method
A composite, tubular technology, used in the medical field, can solve the problems of easy complications, trauma, and limited material extraction at the site of the material, achieve good biocompatibility and mechanical properties, promote growth, and avoid complications. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] A preparation method of a degradable composite tubular urethral stent, the preparation method comprising the following steps:
[0031] (1) The polymer material polylactic acid PLA and polyglycolic acid PGA are mixed in a molar ratio of 50:50, and the polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer PLGA nanoscale electrospun fiber membrane is prepared by electrospinning technology. The surface of the electrospun fiber membrane was modified by grafting type I collagen to obtain the modified polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer PLGA film;
[0032] (2) Soak the small intestinal submucosa cell tissue in the decellularization solution made by mixing polyethylene glycol octylphenyl ether-100 (Triton X-100) with a volume concentration of 0.2% and ammonia water with a volume concentration of 0.03% In the above method, shake and decellularize, then freeze at -40°C and dry in vacuum to obtain the small intestine decellularized matrix SIS film;
[0033] (3) According to the diameter re...
Embodiment 2
[0037] A preparation method of a degradable composite tubular urethral stent, the preparation method comprising the following steps:
[0038] (1) The polymer materials polylactic acid PLA and polyglycolic acid PGA are mixed in a molar ratio of 75:25, and electrospinning technology is used to prepare polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer PLGA nanoscale electrospun fiber membrane with a thickness of 0.4 mm, the porosity is 90%, the electrospinning diameter is 300-450nm, and the pore diameter is 60-100μm; the surface of the prepared electrospun fiber membrane is modified by grafting type I collagen to obtain the modified polylactic acid- Glycolic acid copolymer PLGA film;
[0039] (2) Soak the small intestinal submucosa cell tissue in the decellularization solution made by mixing polyethylene glycol octylphenyl ether-100 (Triton X-100) with a volume concentration of 0.2% and ammonia water with a volume concentration of 0.03% In the method, shake and decellularize, then freeze at...
Embodiment 3
[0043] A preparation method of a degradable composite tubular urethral stent, the preparation method comprising the following steps:
[0044] (1) The polymer material polylactic acid PLA and polyglycolic acid PGA are mixed in a molar ratio of 85:15, and the polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer PLGA nanoscale electrospun fiber membrane is prepared by electrospinning technology. The surface of the electrospun fiber membrane was modified by grafting type I collagen to obtain the modified polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer PLGA film;
[0045] (2) Soak the small intestinal submucosa cell tissue in the decellularization solution made by mixing polyethylene glycol octylphenyl ether-100 (Triton X-100) with a volume concentration of 0.2% and ammonia water with a volume concentration of 0.03% In the above method, shake and decellularize, then freeze at -50°C and dry in vacuum to obtain the small intestine decellularized matrix SIS film;
[0046] (3) According to the diameter re...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com