A kind of preparation method of straw hemicellulose
A technology for hemicellulose and straw, which is applied to the field of preparation of straw hemicellulose, can solve the problems of increasing the loss and pollution of extraction residues, pollution of residue and alkali wastewater, and high cost of hemicellulose, so as to improve the concentration of target products and reduce purification The effect of burden and alkali consumption saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
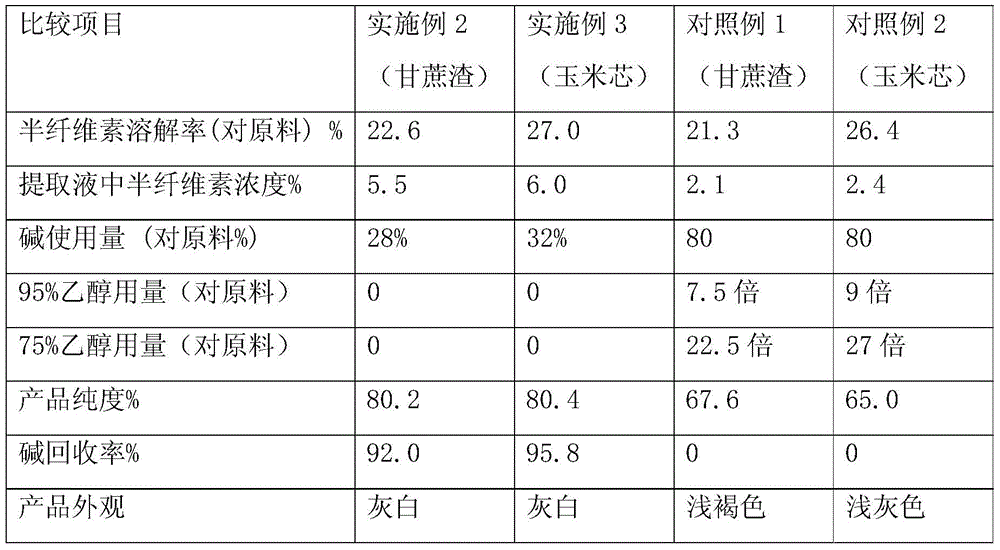
[0025] (1) Extraction: Take a 10L round bottom flask, add bagasse 1Kg to the bottle, connect it to a rotary evaporator, keep the flask at a constant temperature of 80°C in a water bath, draw a vacuum to -0.1Mpa, and inhale 3.5L of 8% (w / v) NaOH solution, continue to rotate for 30 minutes to mix the material and lye and return to normal pressure, continue to rotate and react, and the reaction time is 60 minutes;
[0026] (2) Solid-liquid separation: after the reaction finishes, the material is washed countercurrently 3 times: the first time with deionized water (total 1.2L) washing, finally obtain 3.5L primary washing liquid; the second time with deionized water (total 1.2L) 1.2L) washing to obtain 1.2L of secondary washing solution; washing with deionized water (total 1.2L) for the third time to obtain 1.2L of third-level washing solution; the 3.5L primary washing solution of the above-mentioned gained is used as alkali-containing semi-fiber The element extract enters the next...
Embodiment 2
[0030] (1) Extraction: Take a 10L round bottom flask, add bagasse 1Kg to the bottle, connect it to a rotary evaporator, keep the flask at a constant temperature of 60°C in a water bath, draw a vacuum to -0.1Mpa, and inhale 3.5L of 8% (w / v) NaOH solution, continue to rotate for 40 minutes, return to normal pressure after the material and lye are mixed, continue to rotate and react, and the reaction time is 60 minutes;
[0031] (2) Solid-liquid separation: After the reaction is over, the material is subjected to countercurrent washing for 3 times: for the first time, it is washed with the secondary washing liquid (1.2L in total) of the previous batch of materials (i.e., Example 1), and finally 4.1L of the primary Washing liquid; the second time with the third-level washing liquid (1.2L) of the last batch of materials (i.e. embodiment 1) washing, to obtain the second-level washing liquid 1.22L; for the third time with deionized water 1.2L washing, to obtain three 1.2L of first-gr...
Embodiment 3
[0035] (1) Extraction: Flatten the corn cob with a flattener (thickness is 0.8-5cm), take 1KG and put it into a 10L round-bottomed flask, connect it to a rotary evaporator, keep the temperature of the flask in a water bath at 60°C, and draw a vacuum to -0.05 Mpa, inhale 4L of 8% (w / v) NaOH solution, continue to rotate until the material and lye are mixed and return to normal pressure, continue to rotate and react, the reaction time is 60min;
[0036] (2) Solid-liquid separation: After the reaction is over, the material is subjected to countercurrent washing for 3 times: for the first time, it is washed with the secondary washing liquid (1.22 L) of the previous batch of materials (i.e., Example 2) to finally obtain 4.5 L of primary Washing liquid; the second time washes with the third-level washing liquid (1.2L in total) of the previous batch of materials (i.e. embodiment 2), to obtain the second-level washing liquid 1.2L; washes with deionized water (1.27L in total) for the thi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com