CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) infrared detector reading-out circuit capable of realizing element-by-element dark current suppression
An infrared detector and dark current suppression technology, applied in the direction of electric radiation detectors, etc., can solve the problem of small output swing of the circuit, achieve the effects of improving nonlinearity, ensuring repeatability, and reducing inhomogeneity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
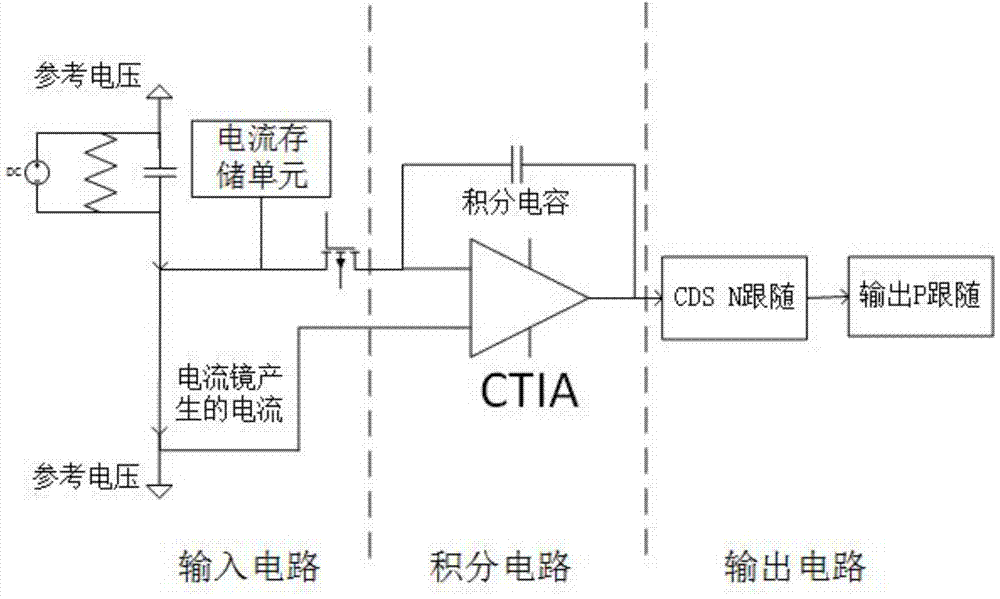
[0022] This invention adopts the combination of current storage unit and current mirror at the input end to design the medium and long-wave infrared detector line column readout circuit, and its unit structure diagram is as follows figure 1 As shown, one end of the medium and long-wave infrared detector is connected to the reference voltage, and the other end is connected to the input end of the CTIA amplifier; the reference voltage is the initial voltage of CTIA integration, which is generally set to 1.5V, and the minimum can not be lower than the threshold voltage of the NMOS tube, otherwise Distortion occurs at the low end of the signal. C i It is an integral capacitor, which can be selected according to the responsivity of the medium and long-wave infrared detectors; in order to make the detector signals of the line array read out sequentially, it is necessary to add CDS N follower to the output end of CTIA, and then connect P follower. The readout of the circuit is divid...
Embodiment approach 2
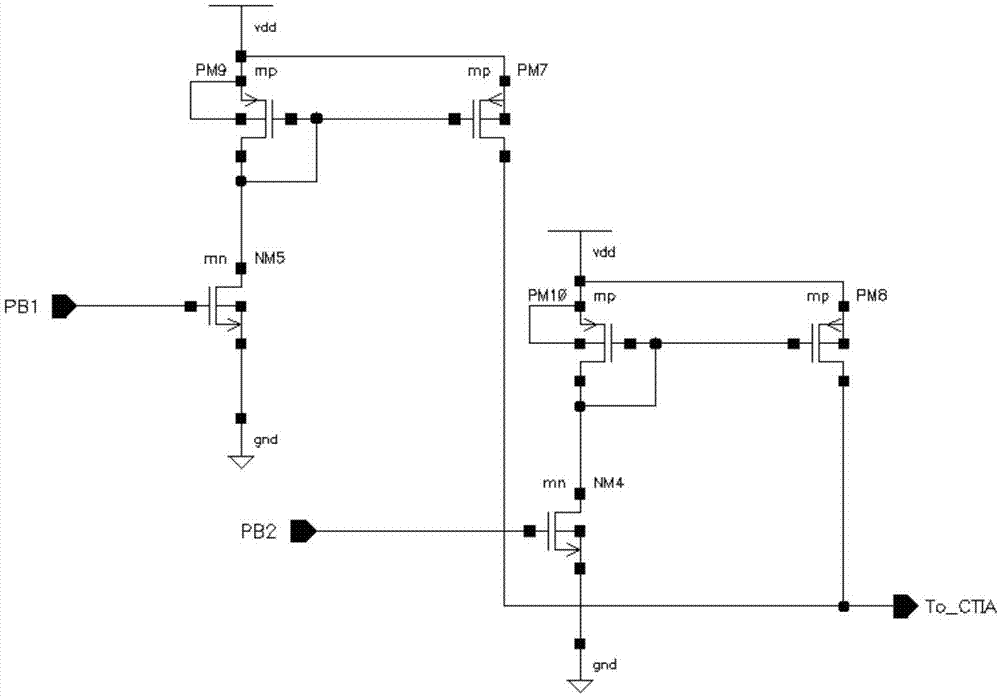
[0024] The circuit structure of the circuit in the input current mirror mode is as follows figure 2 As shown, since the width-to-length ratio of PM9 is twice that of PM10, and the width-to-length ratio of NM4 is 8 times that of NM5, PM8 and PM10 constitute the input-stage current mirror for coarse-tuning control, and PM7 and PM9 constitute the input-stage current for fine-tuning control Mirror, PB1, PB2 are fine-tuning, coarse-tuning external ports respectively. When drawing the layout, the current mirror is arranged at the left and right ends of the column circuit, and the ground wire adopts a metal wire with a width greater than 100 microns. The non-linearity of the line array 160 circuit designed by this method is less than 1%.
[0025] The tube reference size of the current mirror part is shown in the table below (unit is micron).
[0026] the pipe
Embodiment approach 3
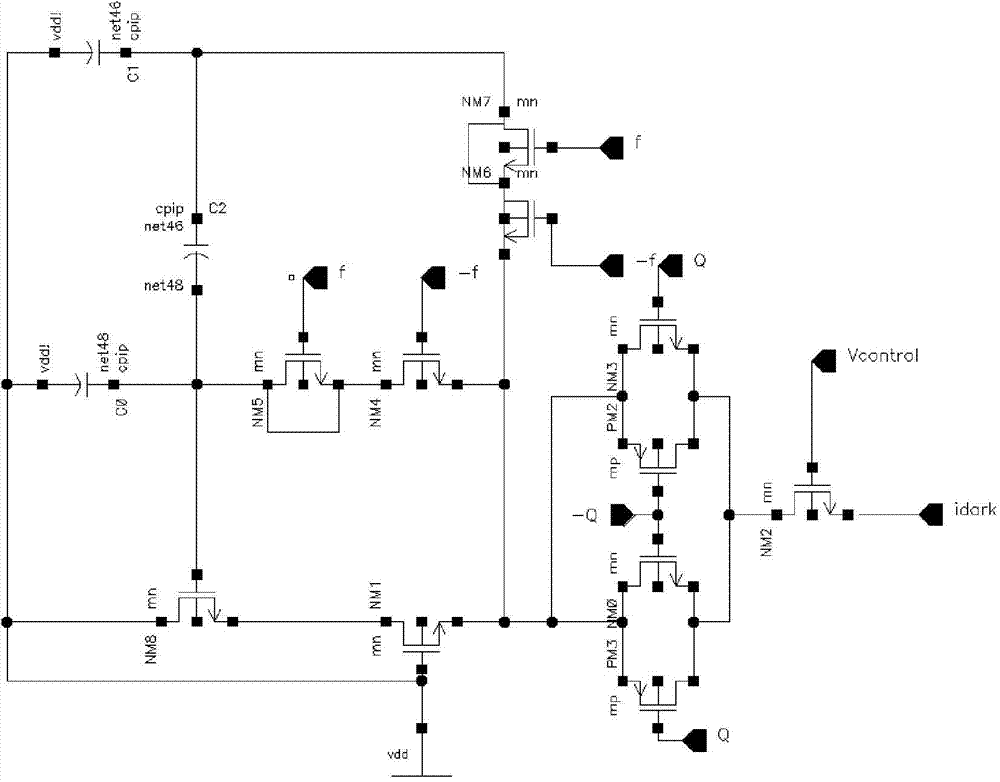
[0028] The structure of the current storage unit at the input end of the circuit is as follows: image 3 As shown, NM8 is used as a storage tube, the current flowing through it is equal to the external dark current, and the gate voltage of NM8 tube is stored by the capacitor feedback loop, so as to achieve the purpose of storing dark current. The capacitive feedback loop is composed of capacitors C0, C1, and C2, whose capacitance values are 2pF, 20fF, and 2pF respectively, which can effectively reduce the feedthrough voltage, and the rejection ratio is C0 / C1=100. NM4 / NM5 and NM6 / NM7 form two pairs of virtual switches, which are controlled by the pulse signal f / -f to reduce the influence of channel charge injection on the capacitive feedback loop. PM2 / NM3 and PM3 / NM0 form a transmission gate switch, and the reference size of each tube is shown in the table below (unit is micron).
[0029] the pipe
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com