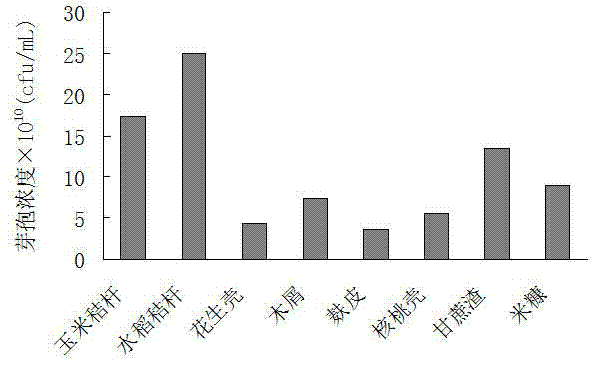Method for producing probiotics by utilizing lignocellulose hydrolysate
A technology of lignocellulose and hydrolyzate, which is applied in the directions of using microorganisms, spores, and microorganism-based methods, etc., can solve the problems of complicated fermentation process, limited production and application of Bacillus coagulans preparations, low spore formation rate, etc. To solve the problem, to achieve the effect of simple production process, good popularization and application value, and improved spore yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Embodiment 1 utilizes lignocellulose hydrolyzate to produce Bacillus coagulans
[0049] 1. Preparation of lignocellulose hydrolyzate
[0050] (1) Grinding agricultural and forestry biomass raw materials (lignocellulosic raw materials: rice straw, corn straw, peanut shells, wood chips, bagasse, walnut shells, rice bran or bran) into powder (particle size <0.05mm) , according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 10% (g / mL), mix the pulverized agricultural and forestry biomass raw materials with 1-4% sulfuric acid, react at 105-130°C for 1-2 hours, and vacuum filter to obtain the filtrate;
[0051] (2) Using Ca(OH) 2 Detoxify the filtrate: add Ca(OH) to the filtrate obtained in (1) 2 , adjust the pH of the solution to 9.0-10.0, settle for 1 hour and then extract the filtrate by suction filtration;
[0052] (3) with 2M H 2 SO 4 The pH of the filtrate obtained in (2) was adjusted to 6.0, and after standing for 1 h, the filtrate was extracted by suction filtration. The fil...
Embodiment 2
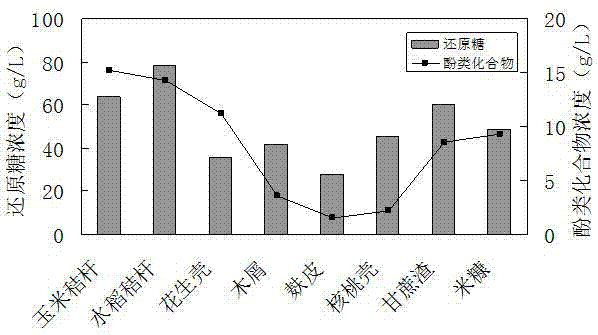
[0064] Embodiment 2 The impact of different agricultural and forestry biomass raw materials on the spore production of Bacillus coagulans
[0065] 1. Different types of agricultural and forestry biomass raw materials (lignocellulosic raw materials) have different chemical compositions, and the types and contents of five-carbon sugars, six-carbon sugars and other chemical components produced after acid hydrolysis are also different. In this study, some common and large quantities of cellulosic lignin raw materials (rice straw, corn straw, peanut shell, sawdust, bagasse, walnut shell, rice bran, bran) were selected and hydrolyzed with 2% dilute sulfuric acid for 1.5h at 121°C , through Ca(OH) 2 Detoxification and other treatments (same as Example 1) to obtain the hydrolyzate.
[0066] 2. Determining the content of reducing sugar and phenolic substances in the hydrolyzate. Reducing sugars were determined by the Fehling method (Wu Guofeng et al. "Industrial Fermentation Analys...
Embodiment 3
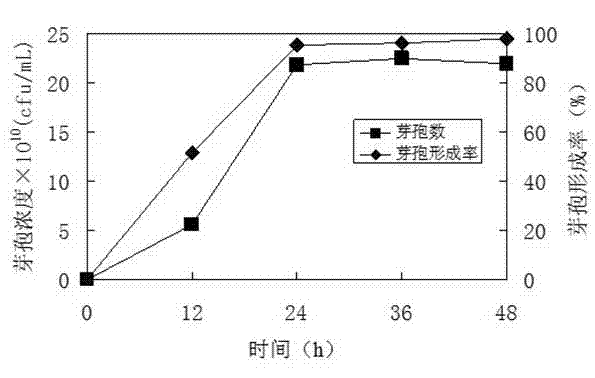
[0072] Example 3 Bacillus coagulans sporulation curve
[0073] As described in Example 2, the addition of rice straw acid hydrolyzate can effectively increase the yield of spores. The rice straw acid hydrolyzate was added at a ratio of 20% (v / v), cultivated for 48 hours according to the method of Example 2, and samples were taken at different times , Determination of spore number and sporulation rate.
[0074] The results are attached image 3 Shown, 12 hours sporulation rate reaches 51%, and 24 hours just arrived the peak period of sporulation. The sporulation rate is 95%, and the number of spores is 2×10 11 cfu / mL. The peak of spore production in the culture medium without adding lignin hydrolyzate generally takes about 48 hours. Adding lignin hydrolyzate can significantly shorten the spore-producing time of Bacillus coagulans and increase the formation rate of spores.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com