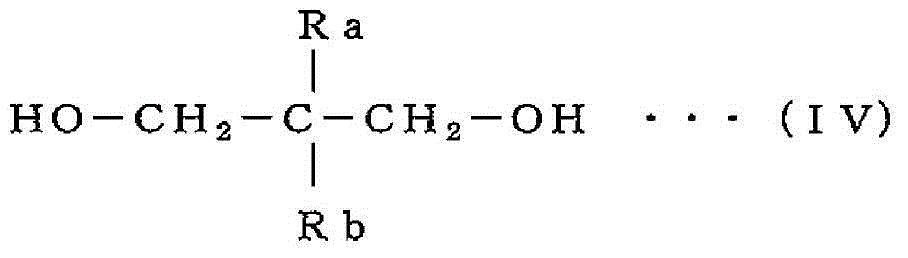Production method for aromatic polycarbonate resin having increased molecular weight
A polycarbonate resin, high molecular weight technology, applied in the field of aromatic polycarbonate resin manufacturing, can solve the problems such as the inability to increase the molecular weight of polycarbonate, difficulty in removing aromatic monohydroxy compounds, and reduced reaction speed, etc., to achieve thermal good stability effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0198] Hereinafter, the present invention will be described by way of examples, but the present invention is not limited by these examples. However, the measured values in the Examples were measured using the following methods or devices.
[0199] 1) Polystyrene-equivalent weight-average molecular weight (Mw): Using GPC, chloroform was used as a developing solvent, and standard polystyrene (manufactured by Tosoh Corporation, "PStQuick MP-M" with known molecular weight (molecular weight distribution=1) was used. ) to make a standard curve. The dissolution time and molecular weight value of each peak were plotted from the measured standard polystyrene, and the approximate calculation was performed using the cubic formula to prepare a calibration curve. The weight average molecular weight (Mw) was calculated|required by the following calculation formula.
[0200] [calculation formula]
[0201] Mw=Σ(W i × M i )÷Σ(W i )
[0202] Among them, i represents the ith split point...
manufacture example 1
[0245]
[0246] 10,000.6 g (43.808 moles) of 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl) propane, 10,557 g (49.295 moles) of diphenyl carbonate, and 1.0 μmol / mol-BPA of cesium carbonate as a catalyst (catalyst as relative to 2 , calculated by the number of moles of 2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane) was put into a 50 L SUS reactor equipped with a stirrer and a distillation device, and the system was replaced with a nitrogen atmosphere. The degree of reduced pressure was adjusted to 27 kPaA (200 torr), the heating medium was set to 205° C., and the raw materials were heated and melted, followed by stirring.
[0247] Then, gradually increase the temperature of the heat medium while reducing the decompression degree, and use the cooling tube to condense and remove the phenol distilled from the reaction system to carry out the transesterification reaction. After about 4 hours, the inside of the system was finally adjusted to 260° C., the degree of reduced pressure was reduced to 0.13 kPaA (1 torr), an...
Embodiment 2
[0253] Put 33.3000 g of the above polycarbonate prepolymer into a 300 cc four-necked flask equipped with a stirrer and a distillation device, and heat and melt at 280°C. Add 0.2840 g (0.001772 mol) of 2-butyl-2-ethyl-propane-1,3-diol as an aliphatic diol compound, add at a jacket temperature of 280°C under normal pressure, and stir and knead for 3 minute. Next, the pressure was adjusted to 0.04 kPaA (0.3 torr) at 280° C., stirred and kneaded for 60 minutes, and a transesterification reaction was performed. Use the cooling tube to distill the phenol, cyclic carbonate (5-butyl-5-ethyl-1,3-dioxan-2-one) and unreacted 2-butyl-2- Ethyl-propane-1,3-diol was coagulated and removed to obtain a cyclic carbonate (5-butyl-5- ethyl-1,3-dioxan-2-one) polycarbonate resin.
[0254] 1 g of the obtained sample resin was put into a test tube, and dried for 2 hours by a cylinder heater set at 120° C. in a glove box (oxygen concentration: 0.0%) substituted with nitrogen. Next, in the same glo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com