Catalyst for preparing methyl nitrite by reducing dilute nitric acid through methanol and preparation thereof
A technology of methyl nitrite and catalyst, which is applied in the direction of nitrite preparation, physical/chemical process catalyst, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalyst, etc., to achieve the effect of high strength and high activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] 1g of SiO with a particle size of 5 mesh 2 The pellets were dispersed in 10ml of 15wt% glucose aqueous solution, added with 0.6g of concentrated sulfuric acid, left at room temperature for 12h, then dried under vacuum at 50°C for 2h; 2 Under the atmosphere, the temperature is programmed from room temperature to the calcination temperature, and the calcination is carbonized. The temperature programming rate is 1°C / min, the calcination temperature is 600°C, and the calcination time is 1h, and the carbon-coated SiO is obtained. 2 Pellets, named SiO 2 5gC-15wt%.
[0017] Subsequently, 1 g of the obtained carbon-coated SiO 2 Pellet SiO 2 5gC-15wt%, dispersed in 10ml containing 0.16g ZrOCI 2 ·8H 2 In aqueous solution of O, place at room temperature for 12h, then in N 2 Under the atmosphere, the temperature was programmed from room temperature to the roasting temperature, roasted and carbonized, the programmed temperature increase rate was 1°C / min, the roasting temperatu...
Embodiment 2
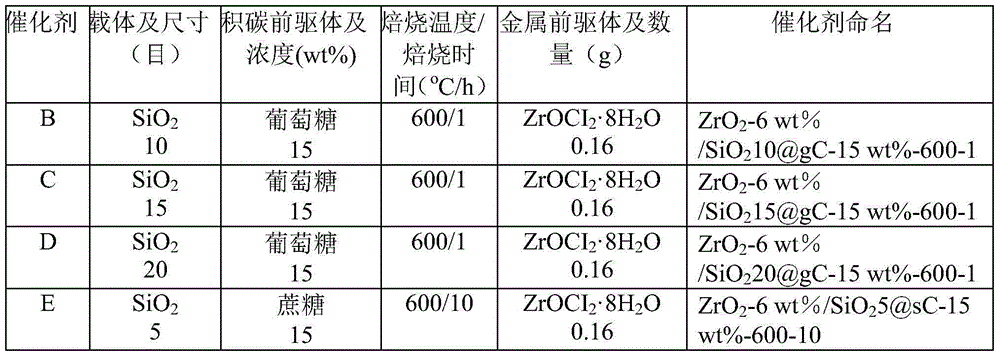
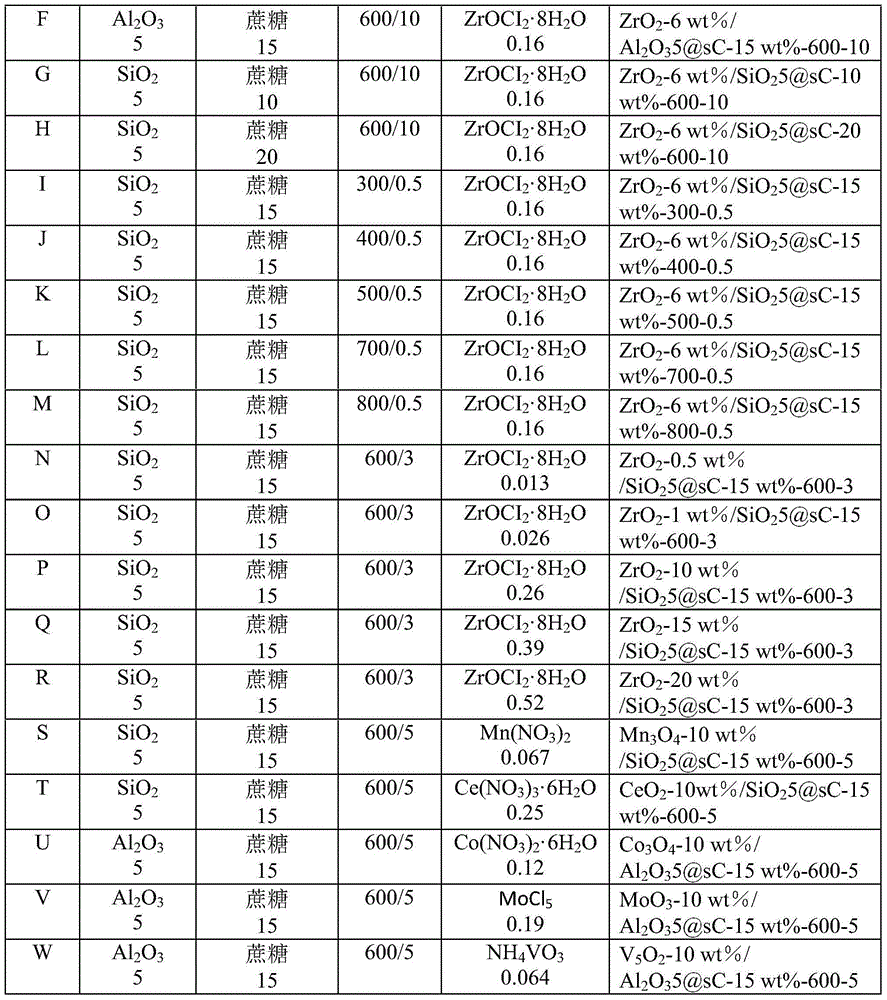
[0019] The preparation method and steps of catalyst B-W are the same as those of catalyst A, the difference is the type and size of carrier pellets, the type and concentration of carbon deposition precursor, calcination temperature and time; the type and quantity of metal precursor, calcination temperature, etc., the obtained catalyst named MO x -a wt% / SbgC-c wt%-d-e or MO x -a wt% / SbsC-cwt%-d-e. where MO x Represents the type of metal oxide; a represents the loading capacity of metal oxide; S represents the type of carrier; b represents the mesh number of the carrier; c represents the concentration of carbon deposition precursor; d represents the calcination temperature; e represents the calcination temperature; g represents the carbon deposition precursor is glucose; s means that the carbon deposition precursor is sucrose. See Table 1 for details.
[0020] Table 1 Catalyst B-W preparation conditions
[0021]
[0022]
Embodiment 3
[0024] The obtained catalysts A-J are used for methanol reduction of dilute nitric acid to prepare methyl nitrite. The reaction is carried out on a fixed-bed reaction device. Catalysts A-J are added to a glass tube reactor, and the upper part of the catalyst is filled with silica pellets (preheated raw materials ), the lower part is filled with stainless steel wire (supporting the catalyst layer). Under a hydrogen atmosphere, the catalyst was reduced at 400°C for 5 hours; under a nitrogen atmosphere, the reaction device was heated to a certain temperature, and 2wt% dilute nitric acid and 18wt% methanol aqueous solution were added with a metering pump. The reaction temperature is 70°C and the WHSV is 2.5h -1 , the pressure is normal pressure. The content of nitric acid in the effluent was analyzed by ionic liquid chromatography, and the conversion rate of nitric acid was calculated; the content of methyl nitrite in the gas was analyzed by gas chromatography, and the selectivit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com