Detection method and application of antibiotic residues in milk
A detection method, antibiotic technology, applied in food safety detection, food safety field, to achieve the effects of strong selectivity, reduced operational risk, and less dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1. Detection of multiple antibiotic residues in pasteurized milk
[0024] ⑴Sample preparation
[0025] Accurately weigh 1.00g (±0.01g) of milk sample into a centrifuge tube, add 0.5ml of zinc acetate solution with a concentration of 1mol / L, vortex and mix, then add 1ml of 1mol / L phosphate buffer solution to control the pH of the solution The value is 4.5. After centrifugal filtration, pass through a 0.45 μm filter membrane into a sampling bottle for determination by an online solid phase extraction-high resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometer.
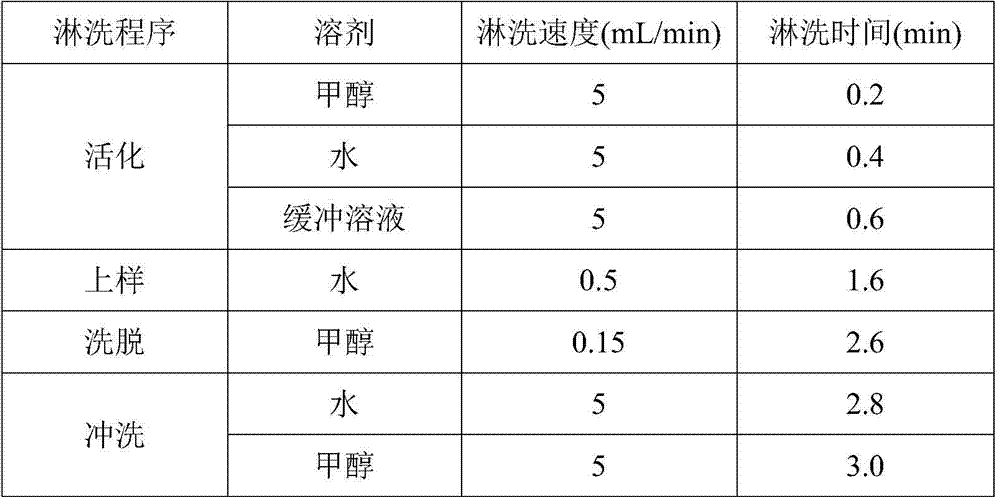
[0026] (2) The gradient elution conditions of the online solid phase extraction column are shown in Table 1, and the required solid phase extraction column is a C18 or HLB column.
[0027] Table 1 Gradient conditions of online solid phase extraction
[0028]
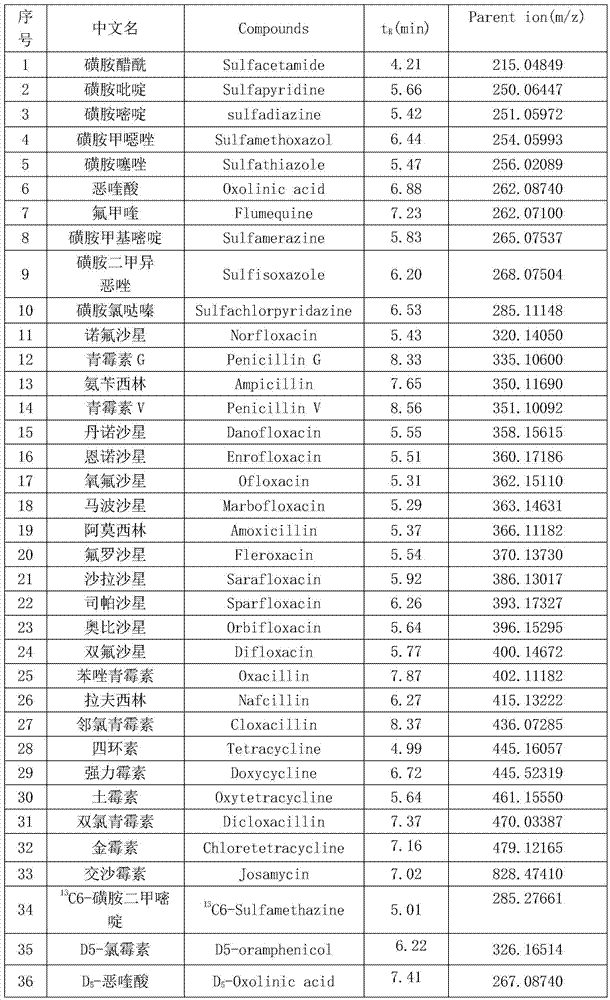
[0029] (3) The chromatographic separation conditions of the high-performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometer are shown in T...
Embodiment 2
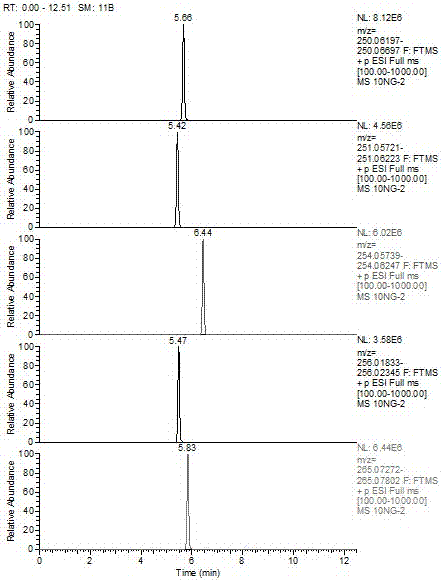
[0037] On the basis of Example 1, further in this example, standard working solutions with mass concentrations of 10, 50, 75, 100.0, and 200.0 ng / mL were prepared, and the ratio of the peak area of the standard solution to the area of the internal standard was used as the ordinate , the solution concentration (ng / ml) is the abscissa, and the standard working curve is drawn. All compounds had a good linear relationship in the range of 10-200ng / mL, and the correlation coefficient (r) was greater than 0.99. Samples were quantified using a standard working curve. The response value of the drug in the sample solution should be within the linear range of the instrument.
[0038]To determine whether there is a certain antibiotic in the sample, the following conditions must be met: the retention time of the chromatographic peak that appears in the sample does not differ from the retention time of the standard by more than ± 2.5%; the deviation of the accurate mass number between ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3. Detection of multiple antibiotic residues in organic milk
[0042] Using pasteurized milk as a negative control, the antibiotic residues in pasteurized milk and organic milk were detected respectively.
[0043] Treat pasteurized milk and organic milk separately as follows.
[0044] Accurately weigh 1.00g (±0.01g) of milk sample into a centrifuge tube, add 0.5mL zinc acetate solution with a concentration of 1mol / L, vortex and mix well, then add 1mL of 1mol / L phosphate buffer solution to control the pH of the solution The value is 4.5. After centrifugal filtration, pass through a 0.45 μm filter membrane into a sampling bottle for determination by an online solid phase extraction-high resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometer. The online solid phase extraction and analysis chromatographic conditions are shown in Table 2 and Table 3. The recoveries for pasteurized milk and organic milk for negative samples analyzed are shown in Table 4.
[0045] Table...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| correlation coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com