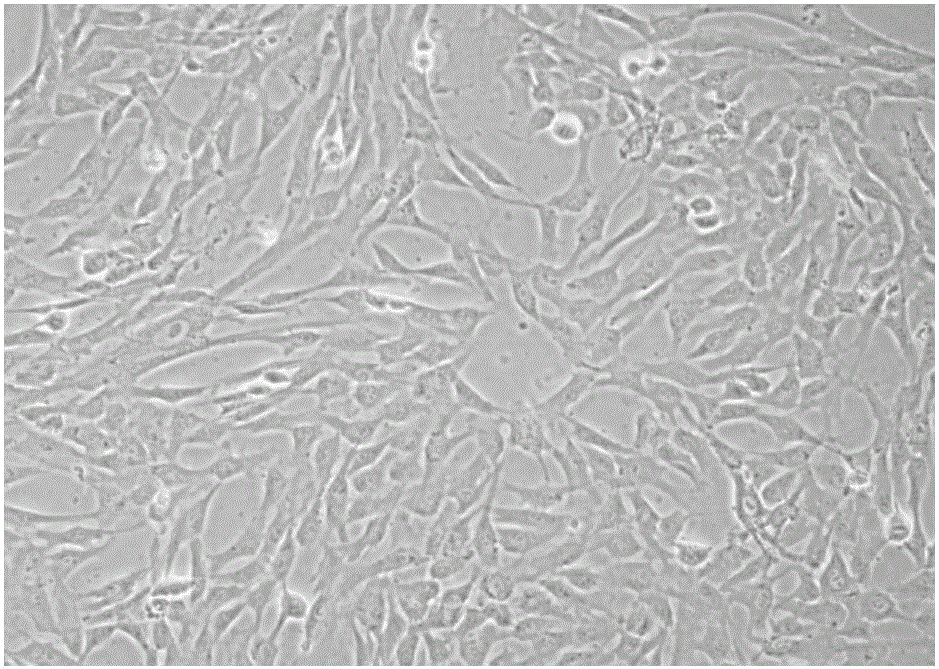
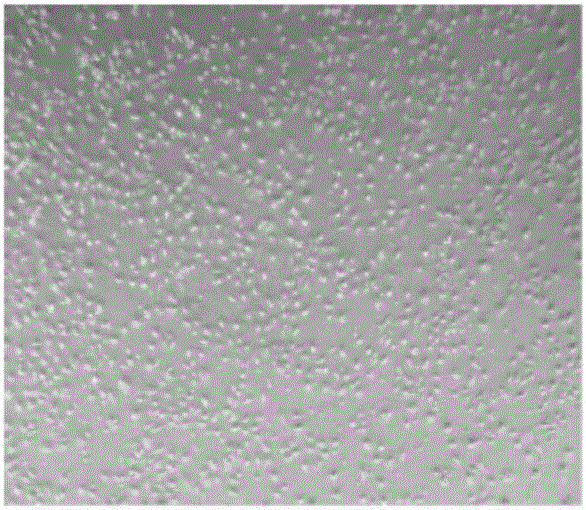
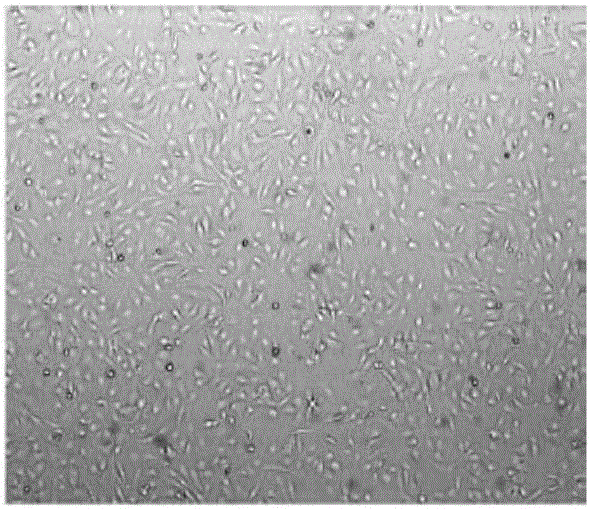
Bletilla striata polysaccharide hydrogel, culture medium and application thereof as well as method of inducing differentiation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to corneal epithelial cells
A technology of bletilla striata polysaccharides and mesenchymal stem cells, applied in the field of bletilla striata polysaccharide hydrogel to induce umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into corneal epithelial cells, can solve the problem of cell affinity, poor adhesion of hydrophilic cells, lack of cell recognition signal sites, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of vigorous cell growth, simple operation, and good porosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] The preparation of embodiment 1 bletilla striata polysaccharide
[0080] Bletilla striata decoction pieces were ground into powder, dispersed and dissolved in distilled water at 80°C for 4 hours, and then filtered to remove impurities.
[0081] The filtrate was soaked overnight in 3 volumes of 95% ethanol, and the precipitate was resuspended with distilled water.
[0082] Add 1 / 3 volume of a mixture of chloroform and butanol (volume ratio 5:1.) Mix evenly and centrifuge to extract protein components, and extract the liquid in the aqueous phase layer.
[0083] Dialyzed through a 30000D-50000D dialysis column (the dialysate is distilled water), made into freeze-dried powder, and obtained the crude product of Bletilla striata polysaccharide. The crude Bletilla striata polysaccharide was dissolved and further purified by cross-linked dextran G-100 to obtain the Bletilla striata polysaccharide.
Embodiment 2
[0084] The sulfation of embodiment 2 bletilla striata polysaccharide
[0085] The Bletilla striata polysaccharide prepared in Example 1 was modified by sulfation through the chlorosulfonic acid-pyridine method. The specific steps are:
[0086] Dissolve 0.2g of polysaccharide powder in 35ml of anhydrous N,N-dimethylformamide, stir at room temperature for 30min, add 17.5ml of sulfation reagent (volume ratio of chlorosulfonic acid to pyridine is 1:6), place in 60 ℃ water bath stirring reaction for 3h. Cool to room temperature after the reaction, add 100ml of ice water to the reaction solution, neutralize it with 1mol / L NaOH to pH 7.5, concentrate under reduced pressure to a certain concentration, dialyze with distilled water for 3 days, concentrate the dialysate and freeze-dry to obtain sulfated polysaccharide.
Embodiment 3
[0087] The preparation of embodiment 3 bletilla striata polysaccharide gel
[0088] The sulfated Bletilla striata polysaccharide prepared in Example 2 was dissolved in PBS to prepare a polysaccharide solution with a concentration of 200 μg / ml. Dissolve ε-polylysine in PBS with a mass fraction of 3% to prepare a cross-linking agent. Mix the polysaccharide solution and cross-linking agent at a volume ratio of 1:1, and let it stand at room temperature for 30 seconds to form a translucent film-like Bletilla striata polysaccharide hydrogel.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com