Synthetic zinc phlogopite via hydrothermal preparation
A phlogopite, hydrate technology, applied in the direction of zinc compounds, silicon compounds, non-metallic elements, etc., can solve the problems of smoothness, transparency, length of preparation time, unsatisfactory aspect ratio temperature and pressure, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
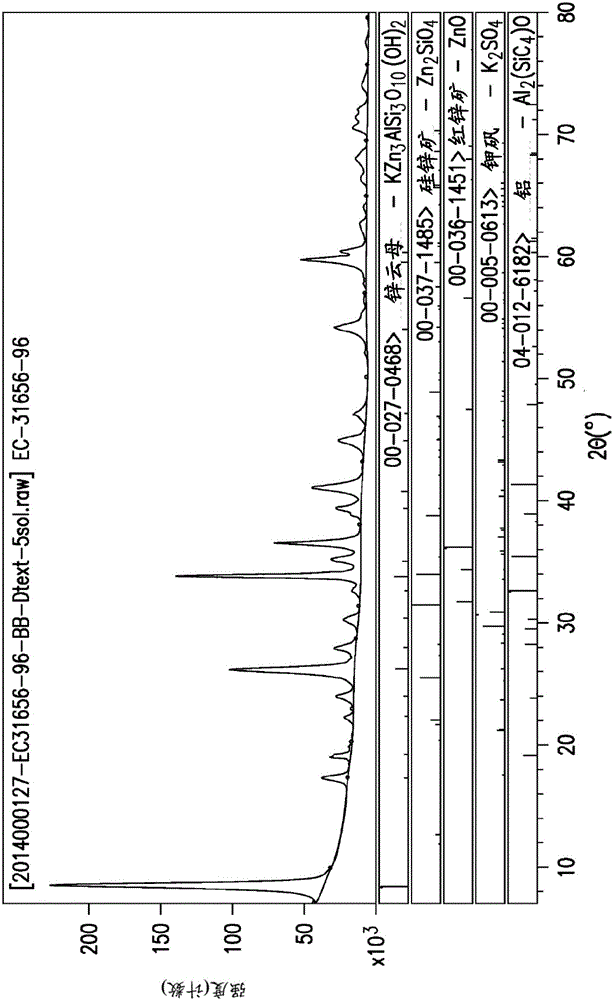
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0142] The preparation method of the synthetic mica flakes includes the step of adding a habit-changing agent to the hydrothermal reaction mixture, wherein the habit-changing agent is a weak acid, its salt or hydrate, or sugar.
[0143] Preferably, the hydrothermal reaction mixture is used to prepare the synthetic zinc phlogopite platelets of formula (1) and typically comprises:
[0144] Source of I, source of monovalent cations, where the source is K + 、Na + , NH 4 + or Li + , preferably K + ; Silicon source;
[0145] source of aluminum;
[0146] Zn source;
[0147] Habit-modifying agents, wherein the habit-modifying agent is a weak organic or inorganic acid, a salt or hydrate thereof, or a sugar; optionally a source of fluoride and / or a source of hydroxide, preferably a source of hydroxide;
[0148] and
[0149] Optionally preformed phlogopite seed crystal seeds,
[0150] and treating the reaction mixture under alkaline conditions at a temperature of from about 125...
Embodiment 1
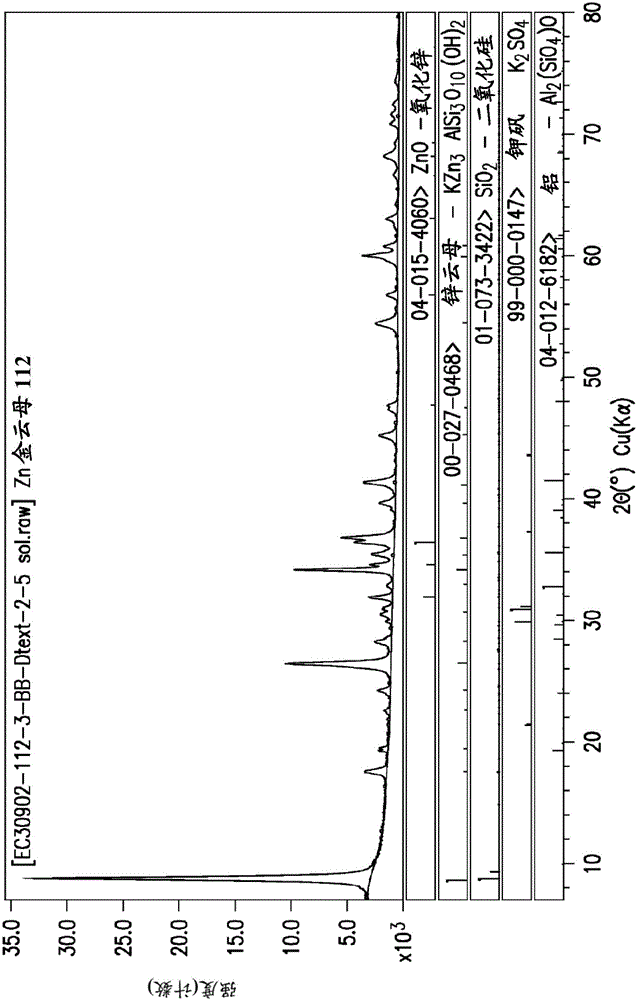
[0376] The starting reagents were potassium aluminate, zinc sulfate heptahydrate, potassium hydroxide and colloidal silica. The 6M KOH solution was added to the zinc sulfate heptahydrate and the mixture was stirred for about 5 minutes. Add 6M KOH to the potassium aluminate and vortex the contents to mix. Combine the two mixtures and add water and trisodium citrate dihydrate. The reaction mixture was transferred to a Parr reactor and colloidal silica was added to form a gel. The Parr reactor was sealed and placed in an oven at 200°C for 24 hours. When cooled to room temperature, the reaction was filtered and washed with D.I. water to give a white powder.
[0377] FIG. 1 shows the powder X-ray diffraction pattern of zinc phlogopite formed in the examples.
[0378] Figure 4 shows an optical micrograph at 100x magnification of the zinc phlogopite formed in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
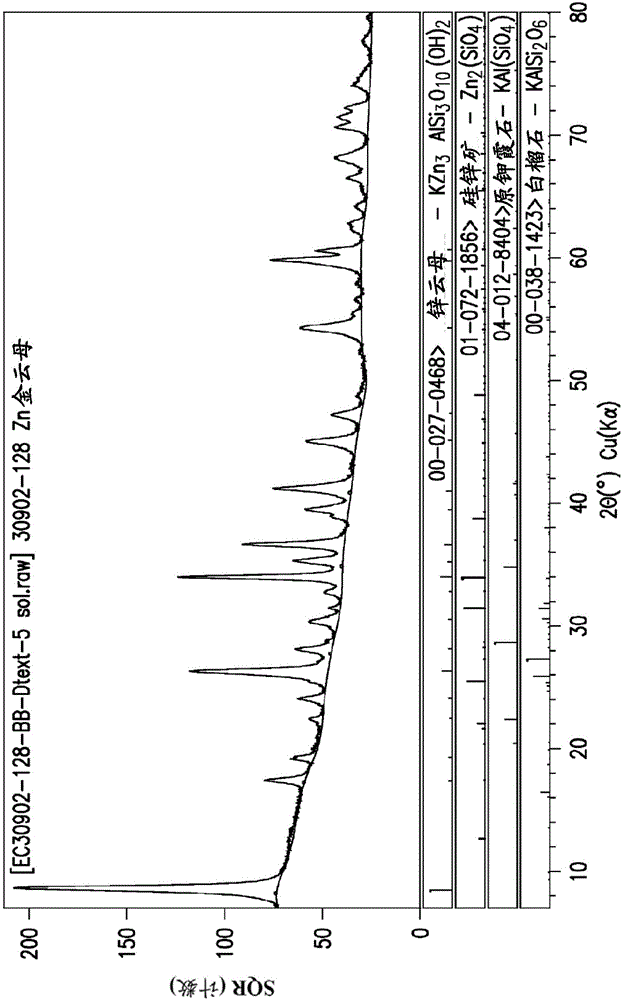
[0380] The starting reagents were potassium aluminate, zinc sulfate heptahydrate, potassium hydroxide and colloidal silica. The 6M KOH solution was added to the zinc sulfate heptahydrate and the mixture was stirred for about 5 minutes. Add 6M KOH to the potassium aluminate and vortex the contents to mix. Combine the two mixtures and add water and trisodium citrate dihydrate. The reaction mixture was transferred to a stirred Parr reactor and colloidal silica was added, forming a gel. The Parr reactor was sealed and the stirring rate was set to 100 rpm. The reactor was heated to 200°C and maintained at this temperature for 24 hours. When cooled to room temperature, the reaction was filtered and washed with D.I. water to give a white powder.
[0381] FIG. 2 shows an X-ray diffraction pattern of the zinc phlogopite that was confirmed to be formed in Example 3. FIG.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com