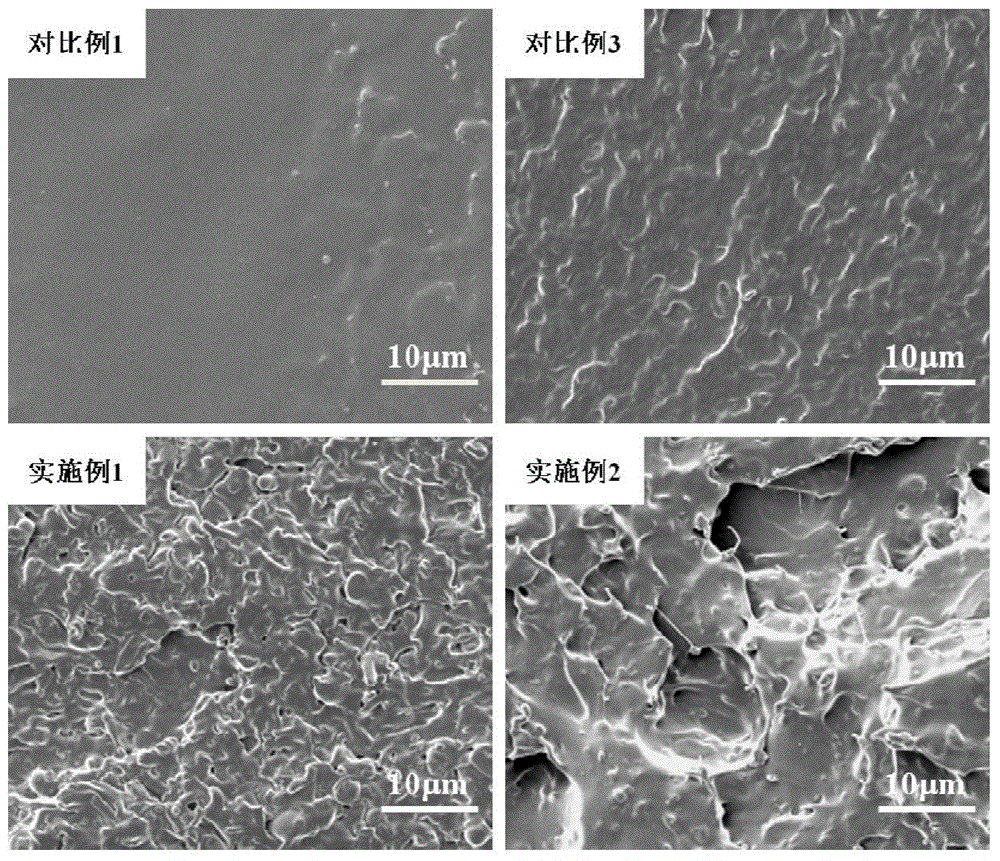
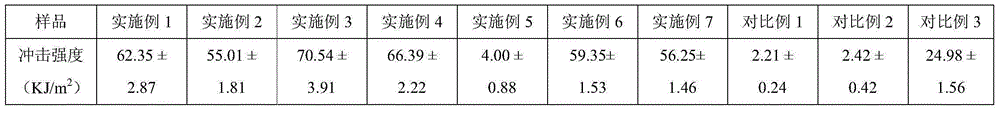
Reactive blending and toughening modified polylactic acid based composite material and preparation method thereof
A composite material, toughening modification technology, applied in the field of reactive blending toughening modified polylactic acid-based composite materials and their preparation, can solve the problem of limited toughness improvement effect, low interphase adhesion strength, loss of polylactic acid advantages and other problems, to achieve the effect of simple and easy preparation method, remarkable effect, novel and unique preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) getting the raw materials ready: 40g of polylactic acid, molecular weight is the PCL10g of 1000g / mol, glycerine 1g (being 10% of PCL), MDI6.6g (the total hydroxyl functional group contained in its contained isocyanic acid functional group and PCL, glycerol The ratio of the amount of substances is 1:1).
[0024] (2) Preparation method: According to the above formula, polylactic acid, PCL and glycerin were added to the torque rheometer, melted and pre-blended for 10 minutes at a temperature of 190 ° C and a rotor speed of 60 rpm, then MDI was added, and again Melt blending at a temperature of 190°C and a rotor speed of 60 rpm for 10 minutes until the torque balance indicated that the reaction was complete, and then the material was taken out and cooled to room temperature to obtain a reactive blended toughened modified polylactic acid-based composite material. The blending temperature and rotational speed were kept constant throughout the experiment. The polylactic a...
Embodiment 2
[0027] (1) getting the raw materials ready: 40g of polylactic acid, molecular weight is the PCL10g of 2000g / mol, glycerine 1g (being 10% of PCL), MDI5.38g (the total hydroxyl functional group contained in its contained isocyanic acid functional group and PCL, glycerin The ratio of the amount of substances is 1:1).
[0028] (2) Preparation method: According to the above formula, polylactic acid, PCL and glycerin were added to the torque rheometer, melted and pre-blended for 10 minutes at a temperature of 190 ° C and a rotor speed of 60 rpm, then MDI was added, and again Melt blending at a temperature of 190°C and a rotor speed of 60 rpm for 10 minutes until the torque balance indicated that the reaction was complete, and then the material was taken out and cooled to room temperature to obtain a reactive blended toughened modified polylactic acid-based composite material. The blending temperature and rotational speed were kept constant throughout the experiment. The polylactic ...
Embodiment 3
[0031] (1) raw materials: polylactic acid 40g, molecular weight is the PCL10g of 1000g / mol, glycerin 0.30g (being 3% of PCL), MDI3.73g (it contains isocyanic acid functional group and PCL, glycerin and contains total hydroxyl functional group The ratio of the amount of substance is 1:1).
[0032] (2) Preparation method: According to the above formula, polylactic acid, PCL and glycerin were added to the torque rheometer, melted and pre-blended for 10 minutes at a temperature of 190 ° C and a rotor speed of 60 rpm, then MDI was added, and again Melt blending at a temperature of 190°C and a rotor speed of 60 rpm for 10 minutes until the torque balance indicated that the reaction was complete, and then the material was taken out and cooled to room temperature to obtain a reactive blended toughened modified polylactic acid-based composite material. The blending temperature and rotational speed were kept constant throughout the experiment. The polylactic acid-based composite material...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| impact strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com