Dipeptide based polymer materials and application of dipeptide based polymer materials in saccharide separation and glycopeptide enrichment
A technology of polymer materials and peptide compounds, applied in the field of material chemistry, can solve the problems of sugar chain biological information loss, low glycosylation coverage, and damage to sugar chain structure, achieving high repeatability, high selectivity, and improved The effect of identification number
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] This embodiment provides dipeptide compounds, which are screened by the following methods:
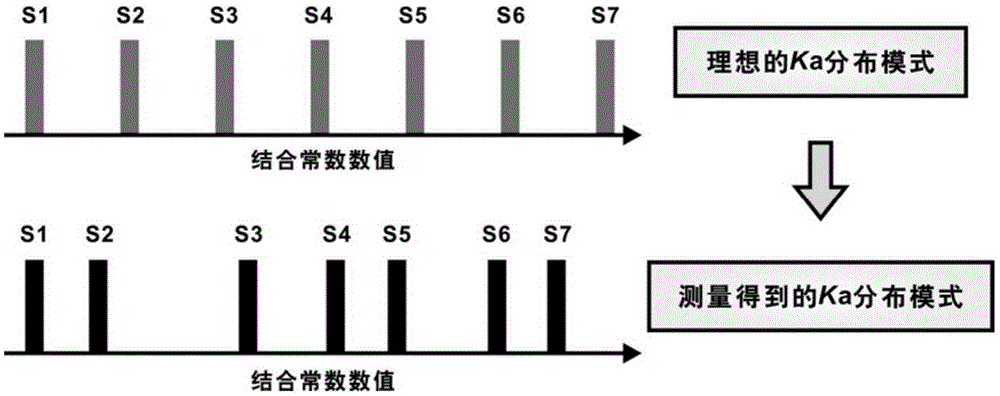
[0051] The first step: determine the binding ability between 54 dipeptide sequences with different combinations and 7 representative monosaccharides, and obtain 54 sets of measured values of binding constants Ka', the number of measured values of binding constants in each set is 7, Subtract the minimum value of the binding constant measurement value among the 7 binding constant measurement values of each group, and then use the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value as the difference between the 7 numerical values obtained after subtracting the minimum value respectively. Normalize to obtain S1' to S7' respectively, arrange S1' to S7' from small to large, and obtain the distribution of measured values of binding constants, please refer to figure 1 .
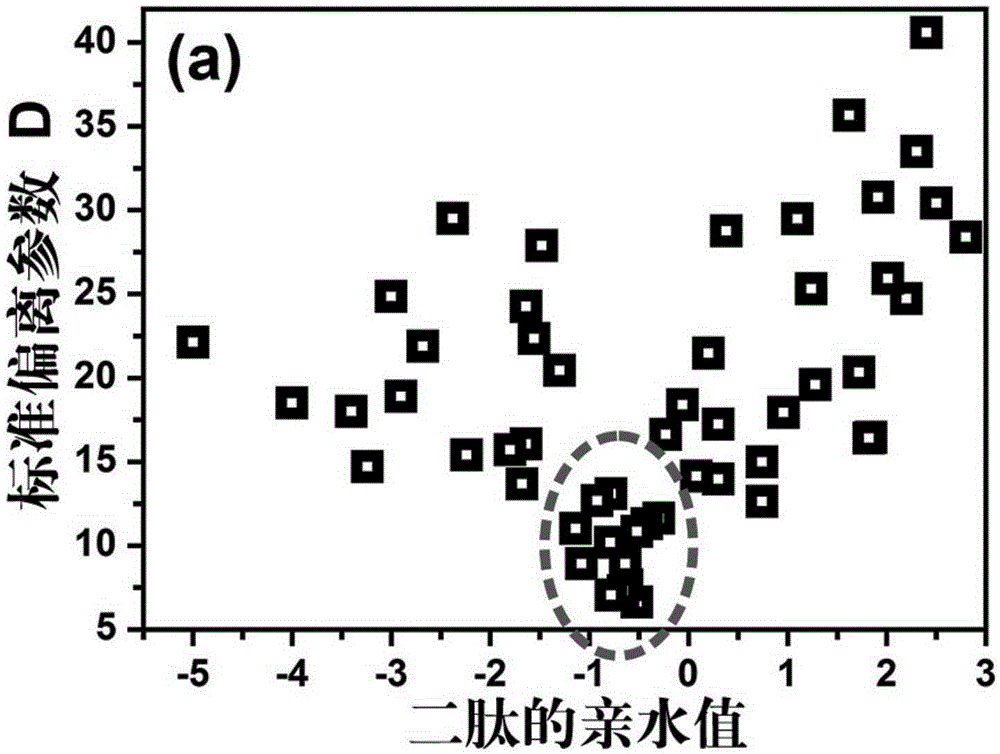
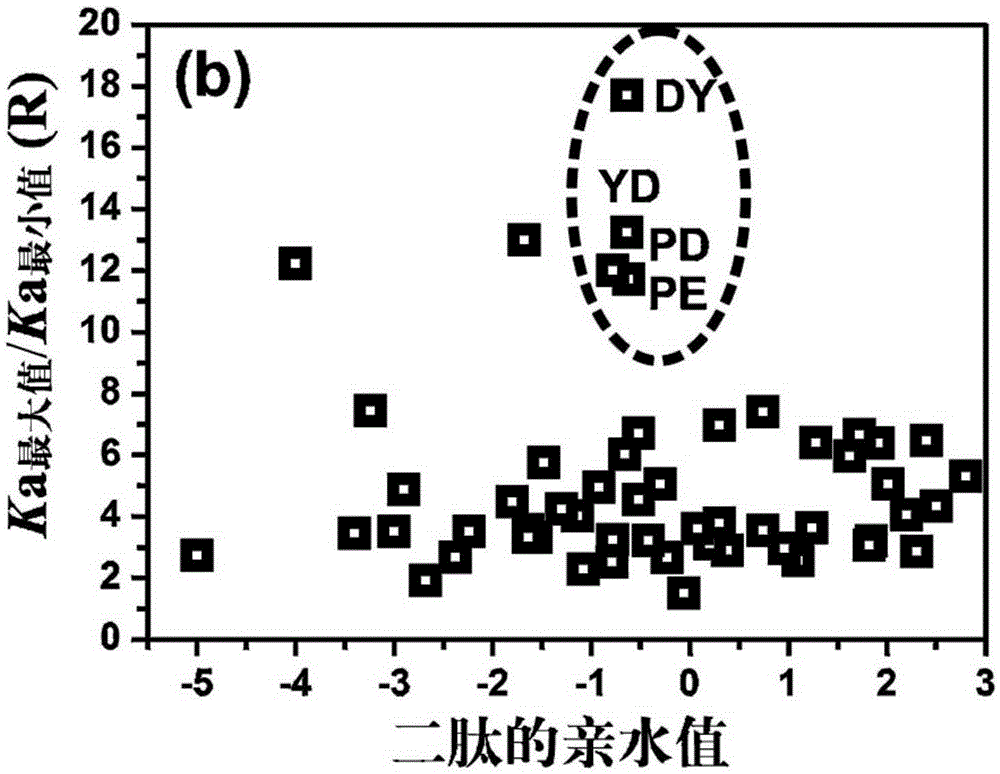
[0052] In this example, N is selected as 54, which is mainly selected according to the hydrophilic...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Preparation of acrylamidated dipeptide functional monomer (taking Pro-Asp, Pro-Glu, Tyr-Asp as examples):
[0082] Under ice bath conditions, 1.15g (5mmol) Pro-Asp and 1.01g (5mmol) triethylamine were dissolved in 30mL of anhydrous chloroform / DMF (volume ratio: 1:1) mixed solution, and under stirring conditions, 0.453 g (5 mmol) of acryloyl chloride was added dropwise to the above solution, and after the dropwise addition, the reaction was continued for 6 hours at room temperature. After the reaction was completed, the reaction liquid was extracted four times with 30 mL of pure water, the aqueous phase solutions were combined, most of the water was distilled off under reduced pressure, and then lyophilized. The crude product was separated and purified by liquid chromatography, and a C18 reverse-phase semi-preparative column was used for separation in reverse-phase mode. Finally, 0.92 g of white powder was obtained with a yield of 65%. The structure of the product was ...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Grafting method of dipeptide polymer on planar substrate:
[0091] Taking the polymerized Pro-Asp as an example, add 1.0g of acrylamidated Pro-Asp to a 25mL flask, and add 3mL of H at the same time 2 O, 3mLCH 3 OH and 3mL DMF were used as solvents; nitrogen gas was introduced under stirring, and after the monomers were fully dissolved, 0.032g of catalyst CuBr and 0.16mL of PMDETA or bipyridine ligand were added under the protection of nitrogen, and then the reaction system was evacuated—nitrogen gas was filled to remove the reaction The residual oxygen in the system; the brominated Si, SiO 2、 Au, Ag, Pt, CuO, Al 2 o 3 、TiO 2 , ZrO 2 or Fe 3 o 4 The surface is immersed in the prepared reaction solution; the temperature of the flask is controlled at 60°C and left to react for 4-6 hours; after the reaction is completed, use DMF, H 2 O washed the polymer grafted surface sequentially to obtain the surface modified by Pro-Asp dipeptide polymer material, the thickness ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com