Method for separating and recycling heavy metal in mercury, selenium and arsenic containing dirt acid sludge
A technology of polluted acid slag and heavy metals, applied in the direction of magnesium sulfate, selenium/tellurium, etc., can solve the problems of doubled volume, large porosity of solidified body, waste of resources, etc., achieve resource recovery, avoid gypsum hazardous waste, The effect of avoiding secondary pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
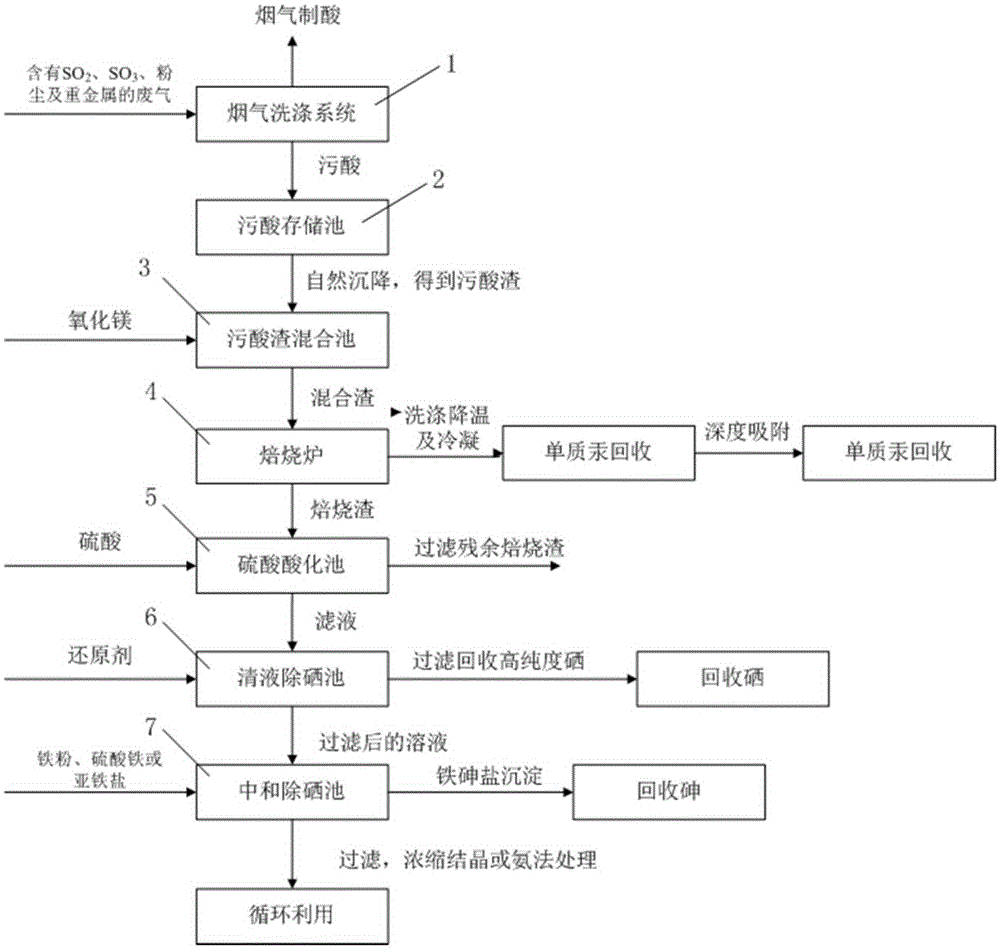
[0030] Taking the dirty acid residue produced in the actual washing section of a zinc smelter as the treatment object, after preliminary dehydration, the concentration of each main component is: water content 15%, mercury content 210mg / g, selenium content 134mg / g, arsenic ion 304mg / g. The specific processing steps are as follows:
[0031] 1. Weigh 500g of dehydrated acid residue into a beaker, add 250g of magnesium oxide powder, stir to mix it thoroughly, and then let it stand for 30 minutes;
[0032] 2. Move the mixed dirty acid slag into a quartz tube, stuff an appropriate amount of quartz wool at both ends to prevent leakage of the dirty acid slag, and then put the quartz tube into a tubular electric heating furnace for roasting. The temperature is set to 600 ℃ and the temperature is stable. When the temperature is set, start timing and pass air into the quartz tube, roast for 1 hour, the air volume is 15L / min, continue to pass in air for 2 hours, and continuously pass the hot...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Taking the sewage acid residue produced in the actual washing section of a lead smelter as the treatment object, after preliminary dehydration, the concentration of each main component is: water content 20%, mercury content 178mg / g, selenium content 114mg / g, arsenic ion 332mg / g. The specific processing steps are as follows:
[0039] 1. Weigh 300g of the dehydrated acid residue into a beaker, add 150g of magnesium oxide powder, stir to mix it thoroughly, and then let it stand for 30 minutes;
[0040] 2. Move the mixed dirty acid slag into a quartz tube, stuff an appropriate amount of quartz wool at both ends to prevent leakage of the dirty acid slag, and then put the quartz tube into a tubular electric heating furnace for roasting. The temperature is set to 600 ℃ and the temperature is stable. When the temperature is set, start timing and pass air into the quartz tube, roast for 40 minutes, the air volume is 15L / min, continue to pass in air for 90 minutes, and the hot flue ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Taking the sewage acid residue produced in the actual washing section of a lead smelter as the treatment object, after preliminary dehydration, the concentration of each main component is: moisture content 5%, mercury content 2mg / g, selenium content 200mg / g, arsenic ion 400mg / g. The specific processing steps are as follows:
[0047] 1. Weigh 300g of dehydrated acid residue into a beaker, add 30g of magnesium oxide powder, stir to mix it thoroughly, and then let it stand for 30 minutes;
[0048] 2. Move the mixed dirty acid slag into a quartz tube, stuff an appropriate amount of quartz wool at both ends to prevent the dirty acid slag from leaking, and then put the quartz tube into a blast furnace for roasting. The temperature is set at 400℃ and the temperature is stable. When the temperature is set, start timing and pass air into the quartz tube, roast for 5 hours, the air volume is 15L / min, continue to pass air for 90 minutes, and the hot flue gas discharged from the quart...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com