Treatment method for waste copper-bearing magnesite brick
A processing method and technology for waste magnesia bricks, applied in the field of non-ferrous metal metallurgy, can solve the problems of long process flow, waste of resources, environmental pollution and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
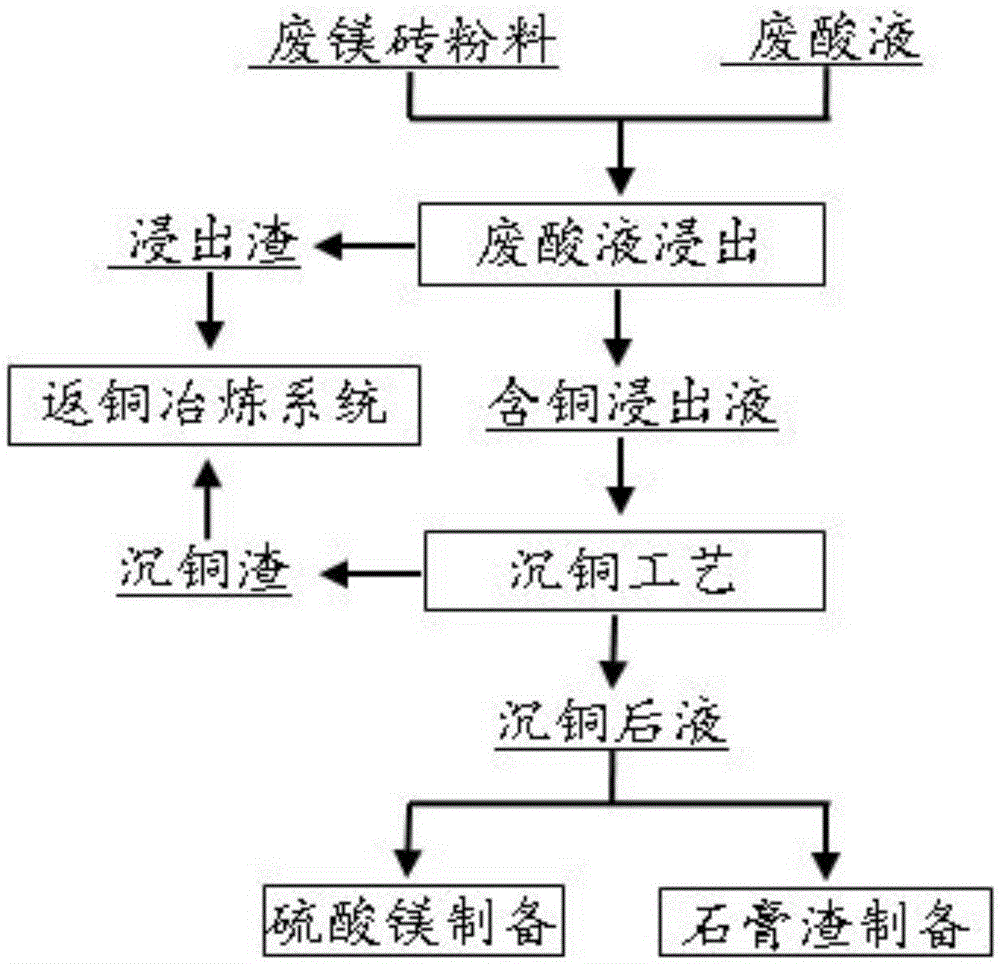
[0024] Take 2kg copper-containing waste magnesia bricks as raw material, conduct a leaching test for 2.5 hours in a waste sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 1.2mol / L, a liquid-solid ratio of 5:1, and a temperature of 75°C. After the reaction is completed, filter and collect the leaching residue. The content of copper in the medium is 17.09%, and the content of magnesium is 1.51%. Add Mg(OH) to the copper-containing leaching solution 2 Adjust the pH of the solution to 5.0 to precipitate Cu(OH) 2 , wherein the copper content in the liquid after copper precipitation is less than 10mg / L, and the copper precipitation slag is collected by filtration; the leaching residue and copper precipitation slag are washed with clean water until neutral, dried and returned to the copper smelting system for treatment, and the copper, gold, Valuable metal elements such as silver; add Mg(OH) to the solution after copper precipitation 2 Control the pH in the solution to 8.0, purify and...
example 2
[0026] Take 2kg copper-containing waste magnesia bricks as raw material, conduct a leaching test for 2.0 hours in waste sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 2.5mol / L, a liquid-solid ratio of 10:1, and a temperature of 50°C. After the reaction is completed, filter and collect the leaching residue. The content of copper in the medium is 17.93%, and the content of magnesium is 1.28%. Add Na to the copper-containing leaching solution 2 S adjust the pH of the solution to 4.0 to precipitate Cu 2 S, wherein the copper content in the liquid after copper precipitation is less than 10mg / L, and the copper precipitation slag is collected by filtration; the leaching slag and copper precipitation slag are washed with clean water until neutral, dried and returned to the copper smelting system for treatment, and the copper and gold in it are recovered , silver and other valuable metal elements; Ca(OH) is added to the liquid after copper precipitation 2 The pH in the solution is con...
example 3
[0028] Take 2 kg of copper-containing waste magnesia bricks as raw materials, in the waste sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 4.0mol / L, the liquid-solid ratio is 15:1, the reaction temperature is normal temperature, and the leaching test is carried out for 2.0 hours. After the reaction is completed, filter and collect the leaching residue. The content of copper in the medium is 18.37%, and the content of magnesium is 0.71%. Adjust the pH of the solution to 5.5 with the copper-containing leaching solution, and then add iron powder to precipitate metal Cu. Copper slag; mix leaching slag and copper precipitation slag, wash with water until neutral, dry and return to the copper smelting system for treatment, and recover valuable metal elements such as copper, gold, silver, etc.; add CaCO to the liquid after copper precipitation 3 Control the pH in the solution to 6.0 to remove impurities, then add Ca(OH) 2 The pH in the solution is controlled to 10.0, and the magnesium...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com