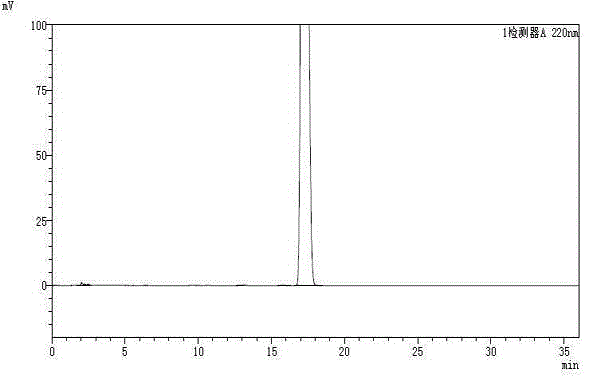
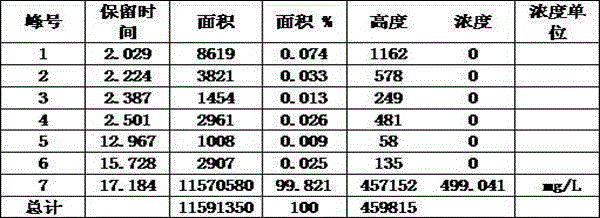
Method for separating and purifying high-purity artemisinic acid
A technology for separation and purification of artemisinic acid, applied in the field of separation and purification of high-purity artemisinic acid, which can solve the problems of large amount of organic solvent usage, complicated operation, and low separation efficiency, and achieve easy control of production conditions, simple process steps, and high purity high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] 6 L of fermentation broth was suction filtered to obtain 1 kg of wet mycelia. The mycelium was dried at 50° C. for 12 hours to obtain 430 g of dry mycelium. Add 1.6 L of butyl acetate to the dried mycelium, and stir for 5 hours. Suction filtration to collect the butyl acetate layer. 1.6 L of a pH 8 aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate was added. After stirring for 30 minutes, the layers were separated, and the butyl acetate layer was collected. The butyl acetate layer was concentrated at 70°C until the concentration of artemisinic acid was 150g / L, and the volume was about 400ml. Add 400ml of water to the butyl acetate layer, heat the feed solution to 75°C, add 30% sodium hydroxide solution dropwise with stirring, and adjust the pH to 11.5. After cooling to room temperature, the layers were separated and the aqueous layer was collected. The aqueous layer was heated to 70°C. Add 10% sulfuric acid under stirring to adjust the pH to 5.5. Slowly lower the temperatur...
Embodiment 2
[0047] 34L of the fermentation broth was suction filtered to obtain 3.6kg of wet mycelium. The mycelium was dried at 50° C. for 12 hours to obtain 2.1 kg of dry mycelium. Add 8.4 L of methyl isobutyl ketone to the dry mycelium, and stir for 5 hours. Suction filtration to collect the methyl isobutyl ketone layer. 8.4 L of a pH 9 aqueous solution of sodium carbonate was added. After stirring for 30 minutes, the layers were separated, and the methyl isobutyl ketone layer was collected. The methyl isobutyl ketone layer was concentrated at 70°C until the concentration of artemisinic acid was about 150g / L, and the volume was about 2.3L. Add 2.3 L of water to the methyl isobutyl ketone layer, heat the feed solution to 75°C, add 20% potassium hydroxide solution dropwise with stirring, and adjust the pH to 13. After cooling to room temperature, the layers were separated and the aqueous layer was collected. The aqueous layer was heated to 70°C. 10% hydrochloric acid was added unde...
Embodiment 3
[0049] 36L of the fermentation broth was suction-filtered to obtain 3.6kg of mycelia. The mycelium was dried overnight at 50° C. to obtain dry mycelium. Add 8.4 L of methyl isobutyl ketone to the dry mycelium, and stir for 5 hours. Suction filtration to collect the methyl isobutyl ketone layer. 8.4 L of a pH 8 aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate was added. After stirring for 30 minutes, the layers were separated, and the methyl isobutyl ketone layer was collected. The methyl isobutyl ketone layer was concentrated at 75°C until the concentration of artemisinic acid was about 150g / L, and the volume was about 2L. Add 2L of pure water to the methyl isobutyl ketone layer, heat the feed solution to 75°C, add 30% sodium hydroxide solution dropwise with stirring, and adjust the pH to 11.5. After cooling to room temperature, the layers were separated and the aqueous layer was collected. The aqueous layer was heated to 70°C. Add 10% sulfuric acid under stirring to adjust the pH...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com