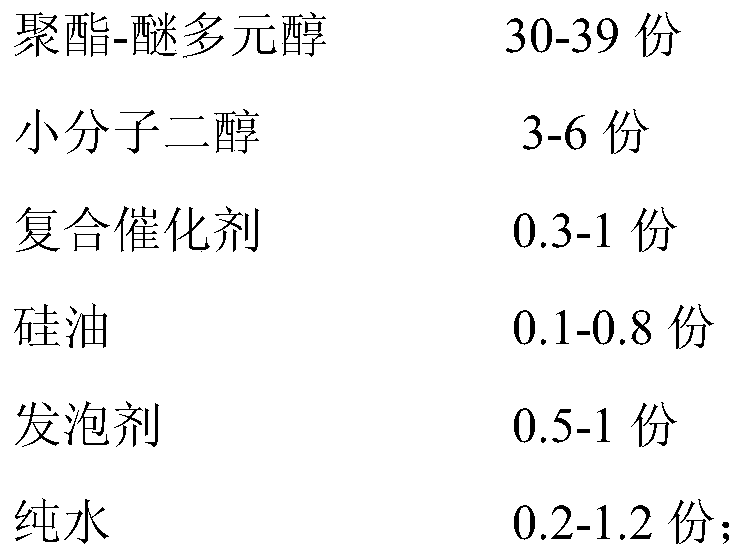
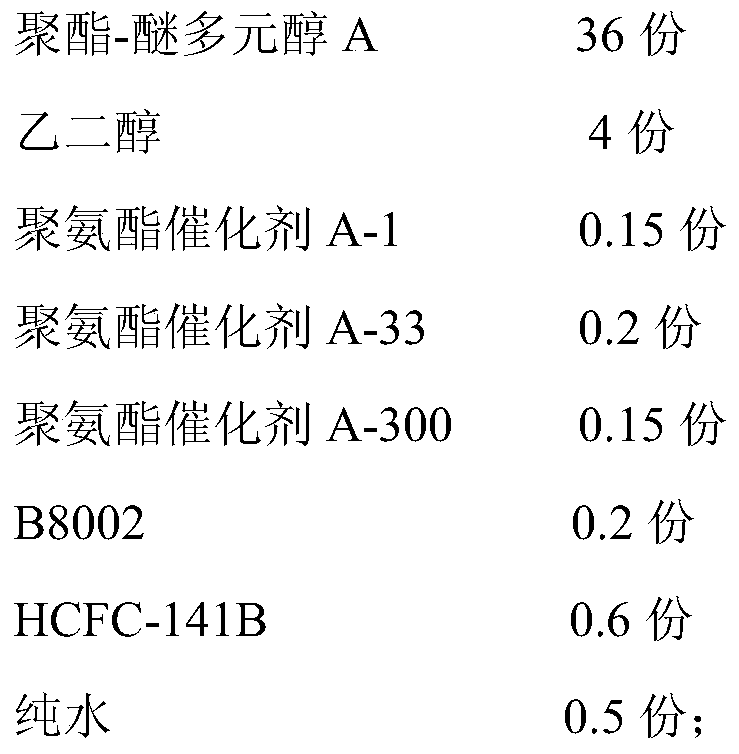
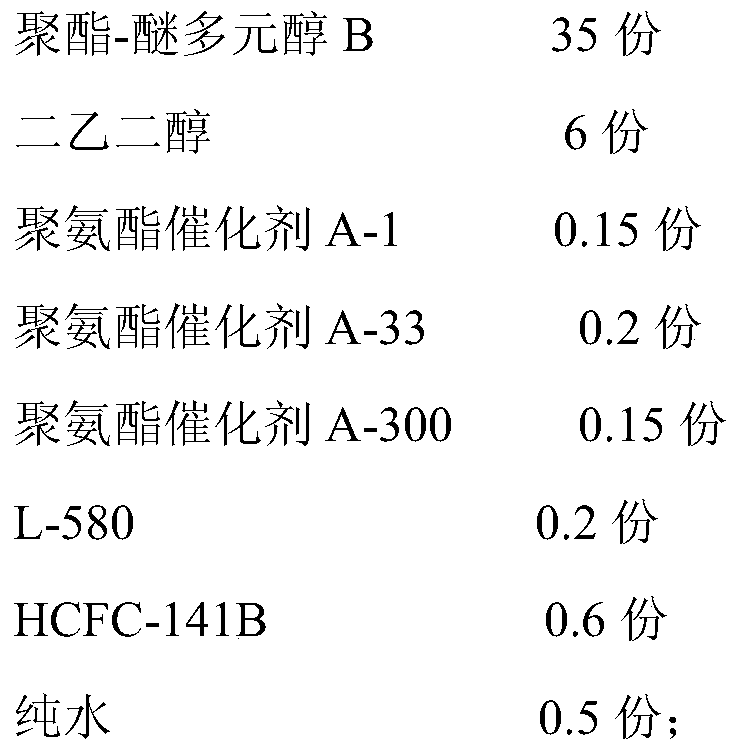
Polyester-ether polyol for microporous PU shoe soles, its preparation method and its prepared PU shoe sole stock solution and the preparation method of PU shoe sole stock solution
A technology for ether polyols and shoe soles, applied in the field of PU shoe sole stock solution and PU shoe sole stock solution, can solve the problems of inconvenient operation, poor temperature resistance, poor hydrolysis resistance, etc., and achieve wide tolerance, good dimensional stability, tear resistance The effect of high cracking strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] (1) At room temperature, add 175g polyethylene diethylene phthalate diol (Mn 350.6), 13g potassium hydroxide, 6.5g pure water into a 2.5L autoclave at room temperature, and replace with nitrogen 4 times. Evacuate to -0.095MPa, heat to 105℃, slowly add 942.5g of propylene oxide dropwise, carry out polymerization reaction at 105℃, continue the reaction for 2h after the addition is complete; then evacuate to -0.095Mpa, blow nitrogen to remove Unreacted residual monomer, timing 2h; then under 0.15Mpa pressure, continuously drip 197g ethylene oxide, carry out polymerization reaction at 110℃, continue to react for 2h after the addition is complete; then vacuum to remove unreacted Residual monomers were transferred to the post-treatment kettle after cooling to 90°C.
[0030] (2) Add a phosphoric acid aqueous solution composed of 27 g of phosphoric acid and 52 g of distilled water to the post-treatment tank, and stir and react at 85° C. for 1 hour. Then, 2.6g magnesium silicate a...
Embodiment 2
[0041] (1) Add 750g of polyphthalic acid-1,6-hexanediol ester diol (Mn is 2005), 24g of potassium hydroxide, and 24g of pure water into a 2.5L autoclave at room temperature, and replace with nitrogen 4 times. The temperature is raised to 105°C, the vacuum degree is -0.095Mpa, 470g of propylene oxide is slowly added dropwise, and the polymerization reaction is carried out at 105°C. After the feeding is completed, the reaction is continued for 2h; then the vacuum is pumped to -0.095Mpa, and nitrogen is blown to remove the The remaining monomer of the reaction is timed for 2 hours; then under a pressure of 0.15Mpa, 280g of ethylene oxide is continuously added dropwise, and the polymerization reaction is carried out at a temperature of 115℃. After the feeding is completed, the reaction is continued for 2h; then vacuum is applied to remove unreacted Residual monomers were transferred to the post-treatment kettle after cooling to 90°C.
[0042] (2) Add a phosphoric acid aqueous solutio...
Embodiment 3
[0053] (1) At room temperature, add 225g polyethylene diethylene phthalate diol (Mn 451), 22.4g potassium hydroxide, 22.4g pure water into a 2.5L autoclave at room temperature, and replace with nitrogen 4 times , Heat up to 105°C, evacuate to -0.095Mpa, slowly add 965g of propylene oxide dropwise, polymerize at 105°C, continue the reaction for 2h after the addition is complete; then evacuate to -0.095Mpa, bubbling nitrogen to remove Unreacted residual monomer, timing 2h; then under 0.20Mpa pressure, continuously add 210g ethylene oxide dropwise, carry out polymerization reaction at 105℃, continue the reaction for 2h after the addition is complete; then vacuumize to remove unreacted After cooling down to 90°C, the remaining monomers are transferred to the post-processing kettle.
[0054] (2) Add a phosphoric acid aqueous solution composed of 20.88 g of phosphoric acid and 39.2 g of distilled water to the post-treatment tank, and stir and react at 90° C. for 1 hour. Then, 1.96g ma...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hydroxyl value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com