Treating and utilizing technology of waste liquid from Solvay process
A technology for waste liquid treatment and ammonia alkali is applied in the field of calcium stearate production, which can solve the problems of limitation, large solubility, and reduce the viscosity of reaction materials, so as to reduce the cost of calcium raw materials, solve the discharge problem, and achieve the effect of high comprehensive economic benefits.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
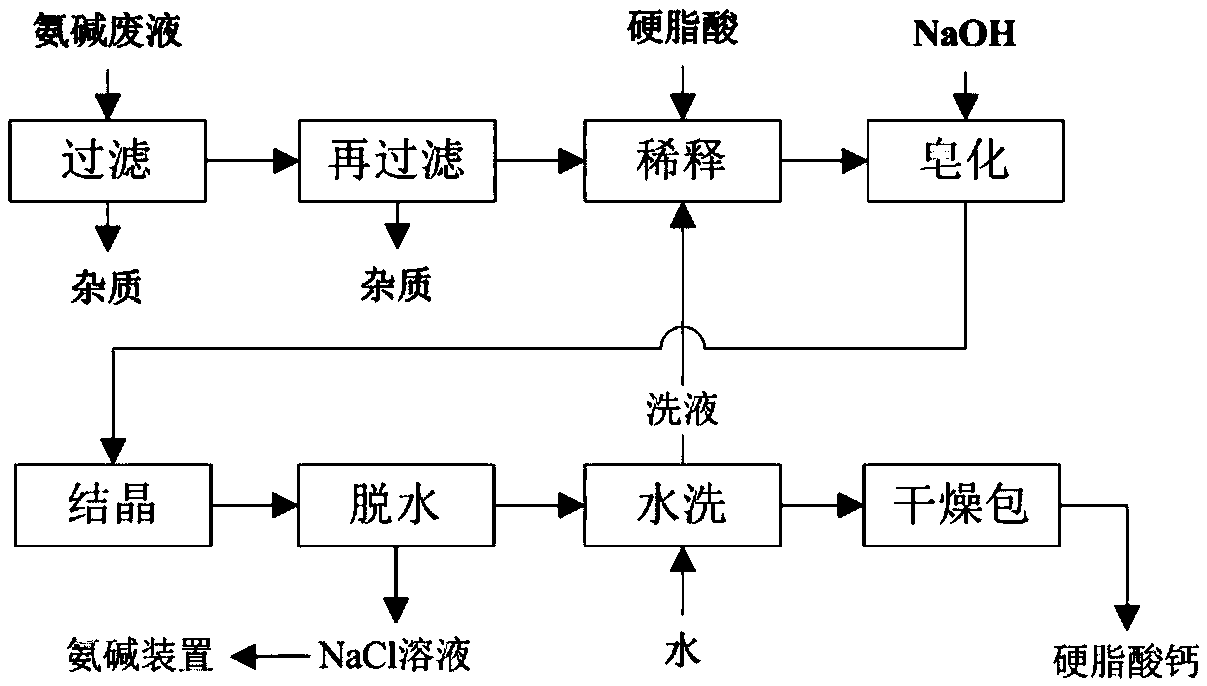
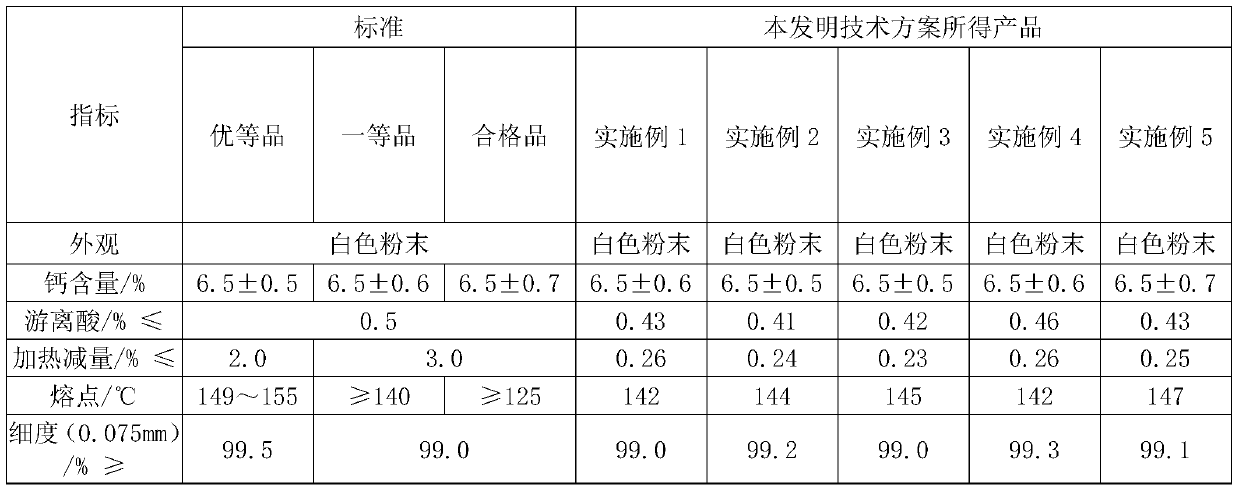
[0047] The ammonia alkali waste liquid mainly containing 9.5% calcium chloride and 4.7% sodium chloride is initially filtered with a precision of 80 mesh, and then filtered with a precision of 200 mesh to obtain a clarified filtrate; adding cleaning liquid to the obtained filtrate to dilute, and then heating And when keeping the temperature at 60°C, add stearic acid according to the mass ratio of the filtrate to stearic acid at 1.7, and stir to dissolve the stearic acid thoroughly; The mass ratio of sodium solution and stearic acid is 0.9; Constantly stirring takes place saponification and salt-forming reaction to generate calcium stearate, and sodium hydroxide is converted into sodium chloride and exists in the solution; when the free acid content is 0.47%, it is cooled to room temperature to make The generated calcium stearate is crystallized and dehydrated; the calcium stearate dehydration solution mainly contains sodium chloride, which is sent to the ammonia-alkali plant as...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The ammonia alkali waste liquid mainly containing 9.5% calcium chloride and 4.7% sodium chloride is initially filtered with a precision of 80 mesh, and then filtered with a precision of 210 mesh to obtain a clarified filtrate; adding cleaning liquid to the obtained filtrate to dilute, and then heating And when keeping the temperature at 74°C, add stearic acid according to the mass ratio of the filtrate to stearic acid at 1.9, and stir to completely dissolve the stearic acid; The mass ratio of sodium solution and stearic acid is 0.8; Constantly stirring takes place saponification and salt-forming reaction to generate calcium stearate, and sodium hydroxide is converted into sodium chloride and exists in the solution; when the free acid content is 0.44%, it is cooled to room temperature to make The generated calcium stearate is crystallized and dehydrated; the calcium stearate dehydration solution mainly contains sodium chloride, which is sent to the ammonia-alkali plant as...
Embodiment 3
[0051] By mainly containing 9.5% calcium chloride and 4.7% sodium chloride ammonia alkali waste liquid, preliminarily filter with 90 mesh precision, filter again with 180 mesh precision, obtain clarification filtrate; Add cleaning solution to the obtained filtrate and dilute, then When heating and keeping the temperature at 92°C, add stearic acid according to the mass ratio of the filtrate to stearic acid at 2.1, and stir to dissolve the stearic acid completely; add 18% sodium hydroxide solution to it, the hydrogenated The mass ratio of sodium oxide solution to stearic acid is 1.2; Constantly stirring takes place saponification and salt-forming reaction to generate calcium stearate, and sodium hydroxide is converted into sodium chloride and exists in the solution; when the free acid content is 0.41%, it is cooled to room temperature, Make the generated calcium stearate crystallize and dehydrate; the calcium stearate dehydration solution mainly contains sodium chloride, and is s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com