Pestalotic acid compounds with antibacterial activity and applications thereof
A chemical compound, anti-bacterial technology, applied in the field of microbiology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Separation and preparation of pestalotic acid compound:
[0065] a) Medium and culture conditions
[0066] Modified M-1-D Medium: NaH 2 PO 4 ·H 2 O 20mg, FeCl 3 2.0mg, MgSO 4 360mg, KCl 60mg, Ca(NO 3 )2 2280mg, KNO 3 80mg, 30g sucrose, 5g ammonium tartrate, 0.5g yeast extract, MnSO 4 5.0mg, ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O2.5mg, H 3 BO 4 1.4mg, KI 0.7mg, distilled water 1000mL, agar 15-20g, pH natural.
[0067] Culture conditions: Strain cr014 was fermented with 30L of modified M-1-D medium and cultured at room temperature for 20 days.
[0068] b) Extraction and separation of fermentation products
[0069] The improved Fries medium that has been fermented for 20 days is cut into small pieces together with the bacterium colonies on it, and is soaked and extracted 3 times with ethyl acetate:methanol:acetic acid=80:15:5 (V / V / V) mixed solvent, and The three extracts were combined and concentrated, then extracted with ethyl acetate until the color did not change, and finall...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Pestalotic acid compound activity study:
[0077] a) Test compounds and reagents
[0078] Test compounds: compound 2, compound 3, compound 4, compound 5, compound 7, compound 8, compound 9;
[0079] Positive control: Cefotaxime;
[0080] Species tested: Ralstonia solanacearum, Salmonella typhi, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus.
[0081] b) Detection principle and method
[0082] The MICs of bacteria were determined by the modified microbial dilution method. Four strains of pathogenic bacteria were cultured on nutrient agar medium at 25°C for 18 to 24 hours, then the pathogenic bacterial cells were collected with a sterile inoculation loop, and cultured in a centrifuge tube filled with 10 mL of sterile normal saline. The concentration of the bacterial suspension was adjusted to 108 CFU / mL under standard conditions with an optical density of 0.10 at 630 nm. The bacterial suspension of this concentration was diluted 100 times before use, and the final concentra...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Pestalotic acid compound physical and chemical constants and spectral data:
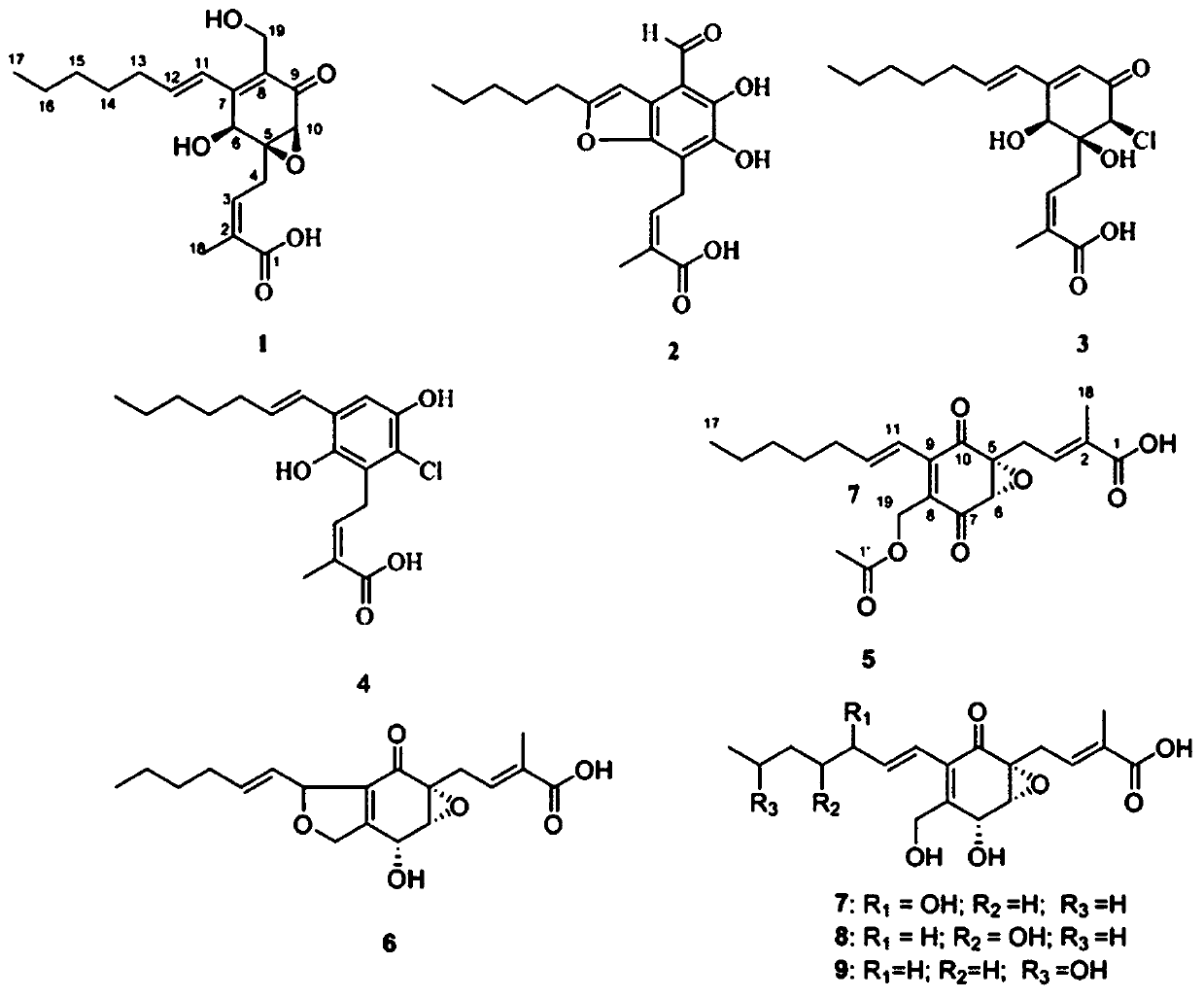
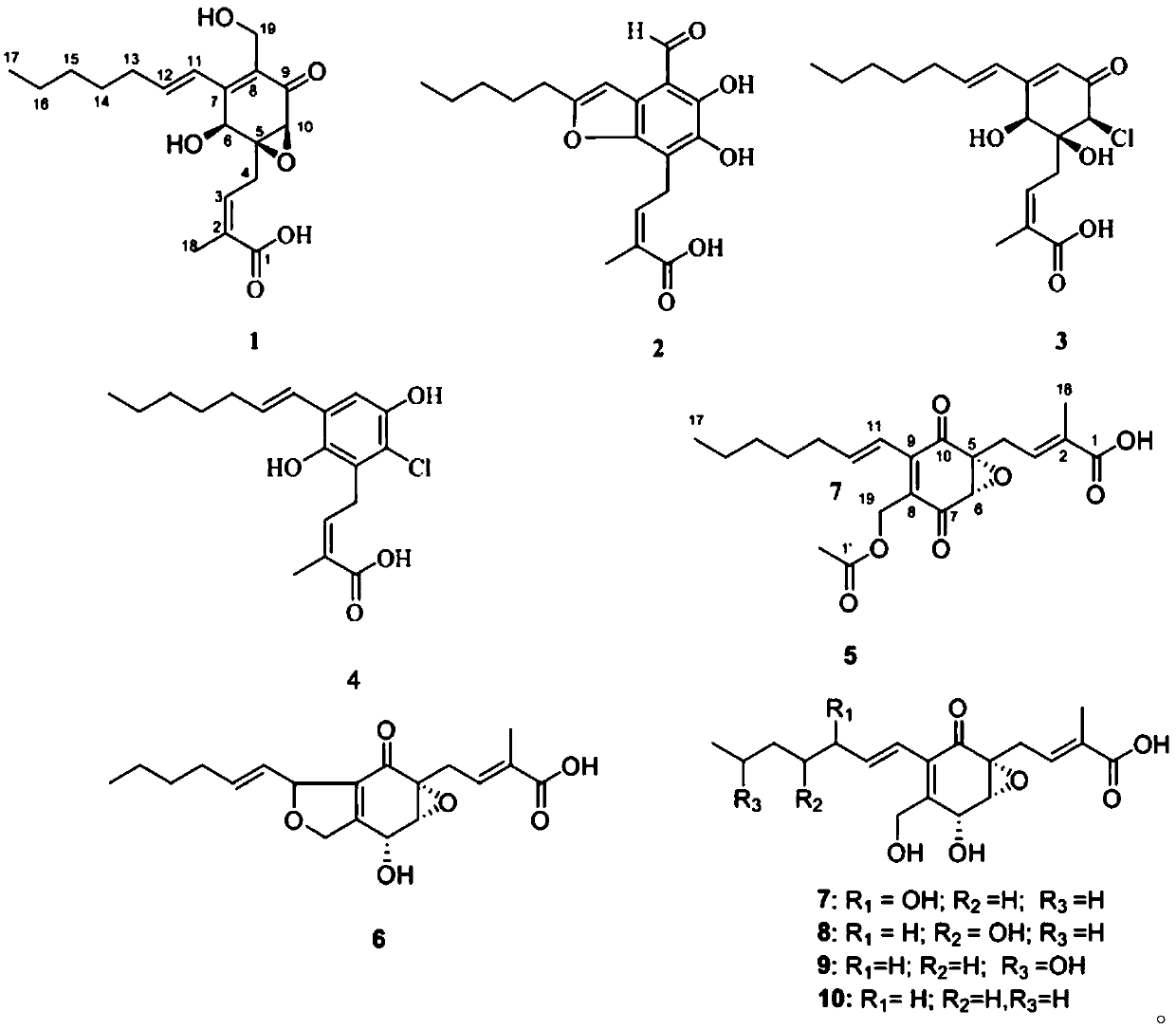
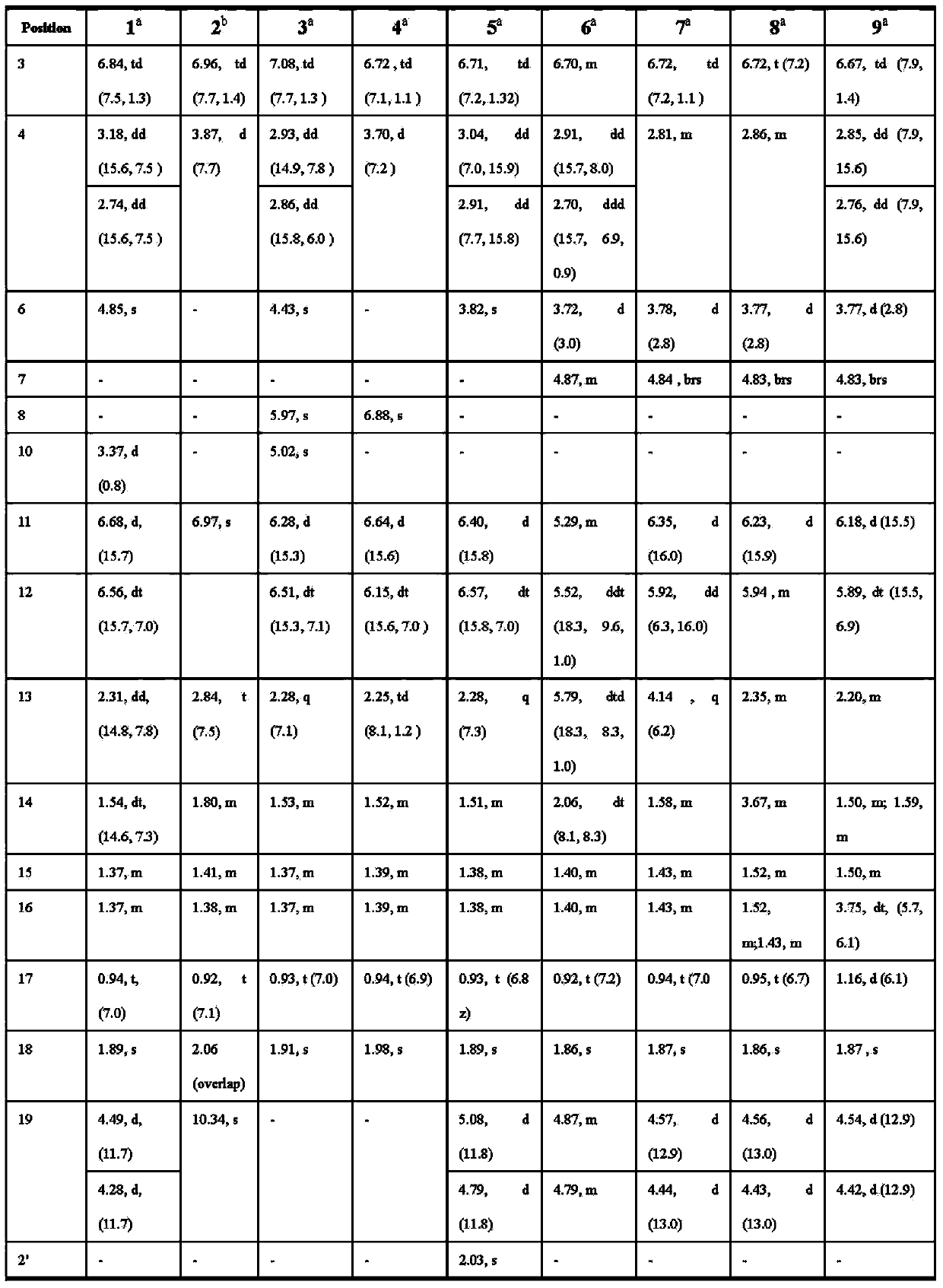
[0089] Pestalotic acidA(1): brown oil, UV(MeOH)λmax(logε):292(4.10),206(4.25); NMR data see Tables 1 and 2; ESI-MS:349[M–H] - ; HR-ESI-MS: 349.1658 (349[M–H] - ,calc.349.1651).
[0090] Pestalotic acidB(2): brown oil, UV (MeOH)λ max (logε):318(4.16),232(4.30),207(4.40);ESI-MS:345[M-H] - ; HR-ESI-MS: 345.1338 ([M-H] - ,calc.345.1338).
[0091] Pestalotic acid C (3): brown oil, UV(MeOH)λ max (logε)nm:285(4.31),204(4.20);ESI-MS:357[M+H] + ,359[M+2+H] + ,379[M+Na] + ,381[M+2+Na] + ; HR-ESI-MS: 379.1284 ([M+Na] + ,calc.379.1288).
[0092] Pestalotic acidD (4): brown oil, UV(MeOH)λ max (logε)nm:317(3.82),217(4.52);ESI-MS:337[M-H] - ,339[M+2-H] - ; HR-EI-MS: 338.1285 ([M] + ,calc.338.1285).
[0093] Pestalotic acidE (5): brown oil, UV(MeOH)λ max (logε):310(3.47),208(4.07);ESI-MS:413[M+H] + ; HR-ESI-MS: 413.2665 ([M+H] + ,calc.413.2668).
[0094] Pestalotic acid F(6): bro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com