Calcium carbide process consumes 1100kg / t of standard
coal and 3400Kw of
electricity per hour.
Calcium carbide produced in a closed calcium carbide furnace at 2200°C contains
high heat, which can account for 21% of the overall
energy consumption. 231kg / t standard
coal. At the end of the “Thirteenth Five-Year Plan”, the production capacity of calcium carbide will be controlled at 50 million t / a, and the waste heat will reach 11.55 million t / a standard
coal. At present, there is no method and method for utilizing calcium carbide waste heat in actual projects. practical technology
[0003] The current patents for the utilization of calcium carbide waste heat are as follows:
Calcium carbide furnace-based
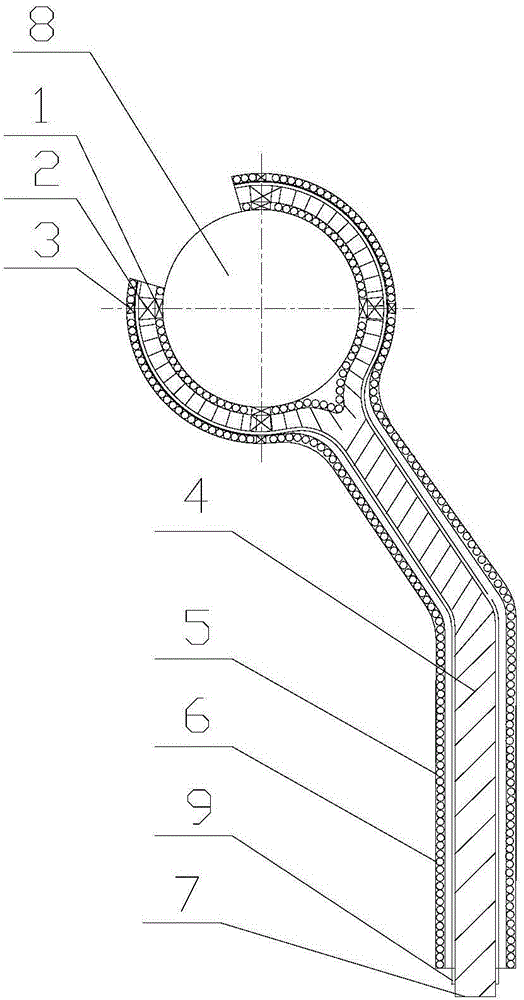
sensible heat power generation system and its realization method (application number 201410238546.0). This patent provides a ring-shaped heat exchange system around the calcium carbide furnace. The
heat exchanger is a heat conduction heat utilization method with low efficiency. For a
heat exchanger with a high temperature of 2200°C, existing materials cannot be used in
engineering applications; The
sensible heat collection system includes a calcium carbide liquid collection and storage device, a high-temperature-resistant heat insulation plate matching the top opening of the calcium carbide liquid collection and storage device, a superconducting heat exchange device connected to the calcium carbide liquid collection and storage device at one end, and an
evaporator at the other end, It is located at the top of the
evaporator and is used to discharge the steam-water mixture. The cavity of the calcium carbide liquid collection and storage device is composed of an inner wall and an outer wall that has a gap with the inner wall and forms a sealed structure. The inner and outer wall gaps of the calcium carbide liquid collection and storage device Arranged with seamless steel pipes, the interior of the seamless steel pipes is filled with a heat-conducting medium. This patent is also a
thermal energy utilization method of heat conduction; a calcium carbide furnace calcium carbide
sensible heat recovery equipment and
recovery method (application number 201410040367.6) mainly includes calcium carbide laundering, smoking Cover, hot air
tunnel kiln, transport out track, high temperature
cyclone dust collector, waste heat boiler,
bag filter, high
temperature induced draft fan and
automatic control system. This patent is also a heat utilization method of heat
convection, and the
convection heat transfer efficiency is low, and Dust removal and other equipment and problems have been added; a calcium carbide sensible heat collection device (application number 201420344707.X) includes a closed heat collection box. The two side walls and a ceiling at the top of the two side walls, the bottom surface, the side walls and the ceiling together form a storage space for storing calcium carbide pot cars. The wall and the ceiling include a
steel cylinder, a
phase change heat storage material filled in the
steel cylinder and an
insulation layer covering the outer surface of the top of the
steel cylinder. The outlet end of the
hot box is provided with an air outlet, and the air inlet is used to flow in
cold airIn the calcium carbide sensible heat collection device, the heat of the calcium carbide on the calcium carbide pot car is conducted to the phase-change
heat storage material through the steel cylinder, and the
cold air flowing in from the air inlet is heated during the process of flowing through the gap of the phase-change
heat storage material. It is a hot air flow, which flows out from the air outlet to be sent to the equipment that needs
heat energy for recycling. This patent can only recover waste heat at the bottom of the calcium carbide pot, and transfer heat through heat conduction and
convection. The efficiency is low. In addition, the center of the calcium carbide pot The heat and the edge are not uniform, so that the heat in the center of the calcium carbide pot cannot be used; a fused calcium carbide
power generation system (application number 201420550583.0), the energy conversion equipment includes a
hot blast stove (21), a waste heat boiler (22), and a circulating fan (23); A circulating air outlet (211) is provided on the end of the
hot blast stove close to the sealed chamber, and a circulating air inlet (212) is provided at the end far away from the sealed chamber; The air inlet is connected to the circulating fan; the waste heat boiler and the circulating fan are connected through the ventilation
pipe (25); related patents or applications also include a calcium carbide furnace calcium carbide sensible heat
recovery device (CN201410040368.0), a calcium carbide furnace calcium carbide
Sensible heat recovery device (CN201420053876.8), a calcium carbide sensible heat recovery device (CN201120489712.6), a calcium carbide sensible heat recovery system (CN201120209958.3), the above patents or applications are combined with the existing calcium carbide pot The traditional
convective heat transfer method cannot eliminate the technical problems existing in combination with existing calcium carbide pots, warehouses, and crushed material processes, and it is difficult to achieve
engineering and simple docking with existing devices
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More